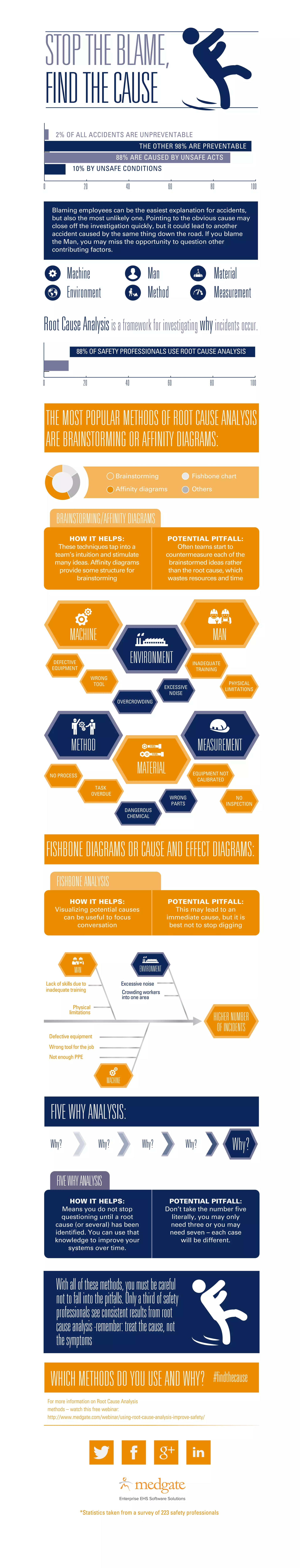
The document emphasizes that 98% of accidents are preventable, primarily due to unsafe acts and conditions, and cautions against blaming employees as it may hinder thorough investigations into root causes. It discusses various root cause analysis methods, such as brainstorming and fishbone diagrams, while highlighting common pitfalls and the importance of focusing on underlying causes rather than symptoms. Additionally, it stresses that consistent success with these methods is limited, urging safety professionals to treat the cause behind incidents.