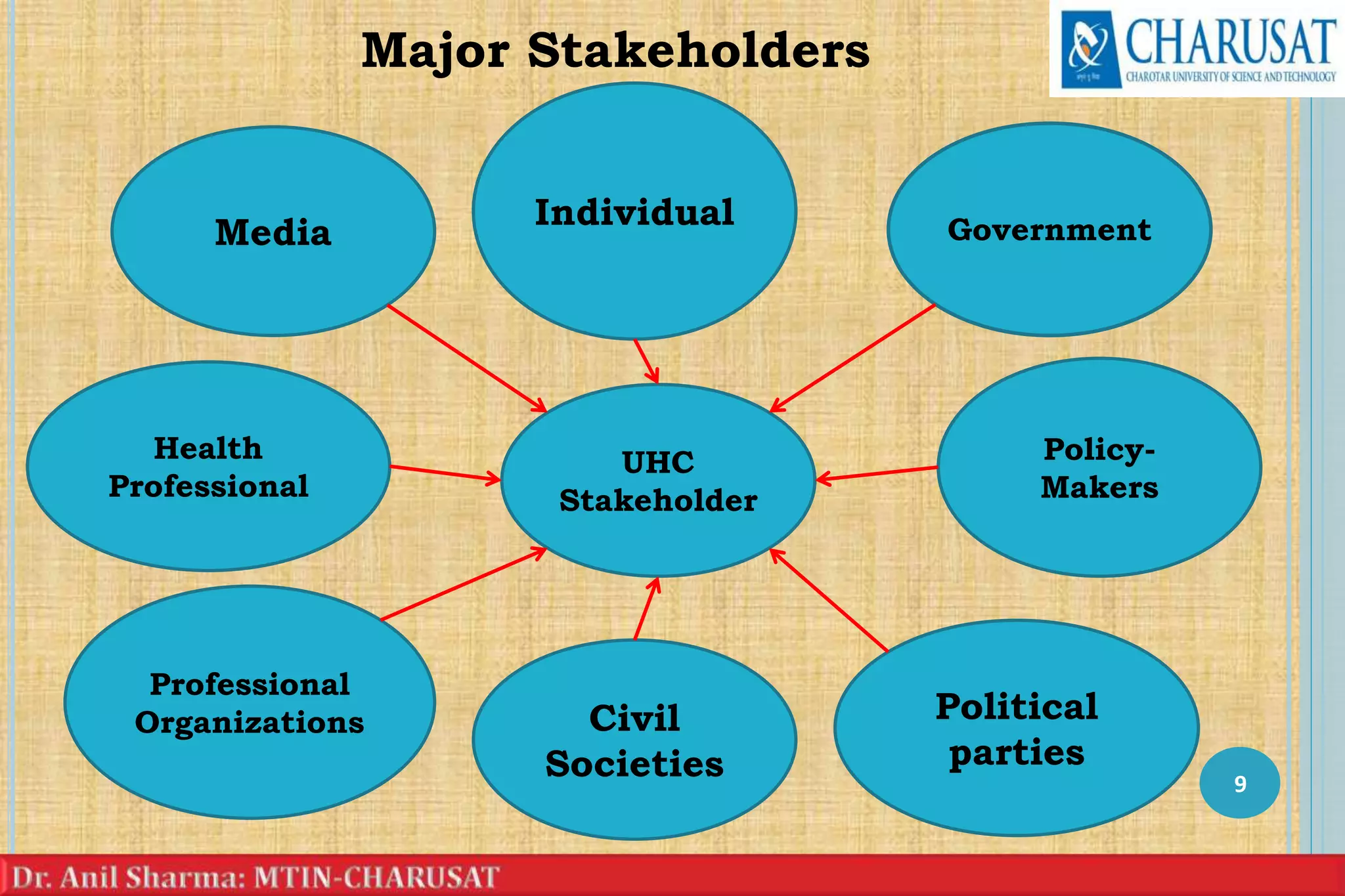
1) Government, individuals, policy-makers, civil societies, media, political parties, and professional organizations are the major stakeholders in universal health coverage (UHC).
2) The government implements policies to improve health and economic growth, individuals advocate for their healthcare needs, and policy-makers develop solutions through stakeholder engagement.
3) Civil societies represent community concerns, media raises awareness, and political parties advocate for social solidarity and economic growth to achieve UHC. Professional organizations ensure available facilities meet patient needs.