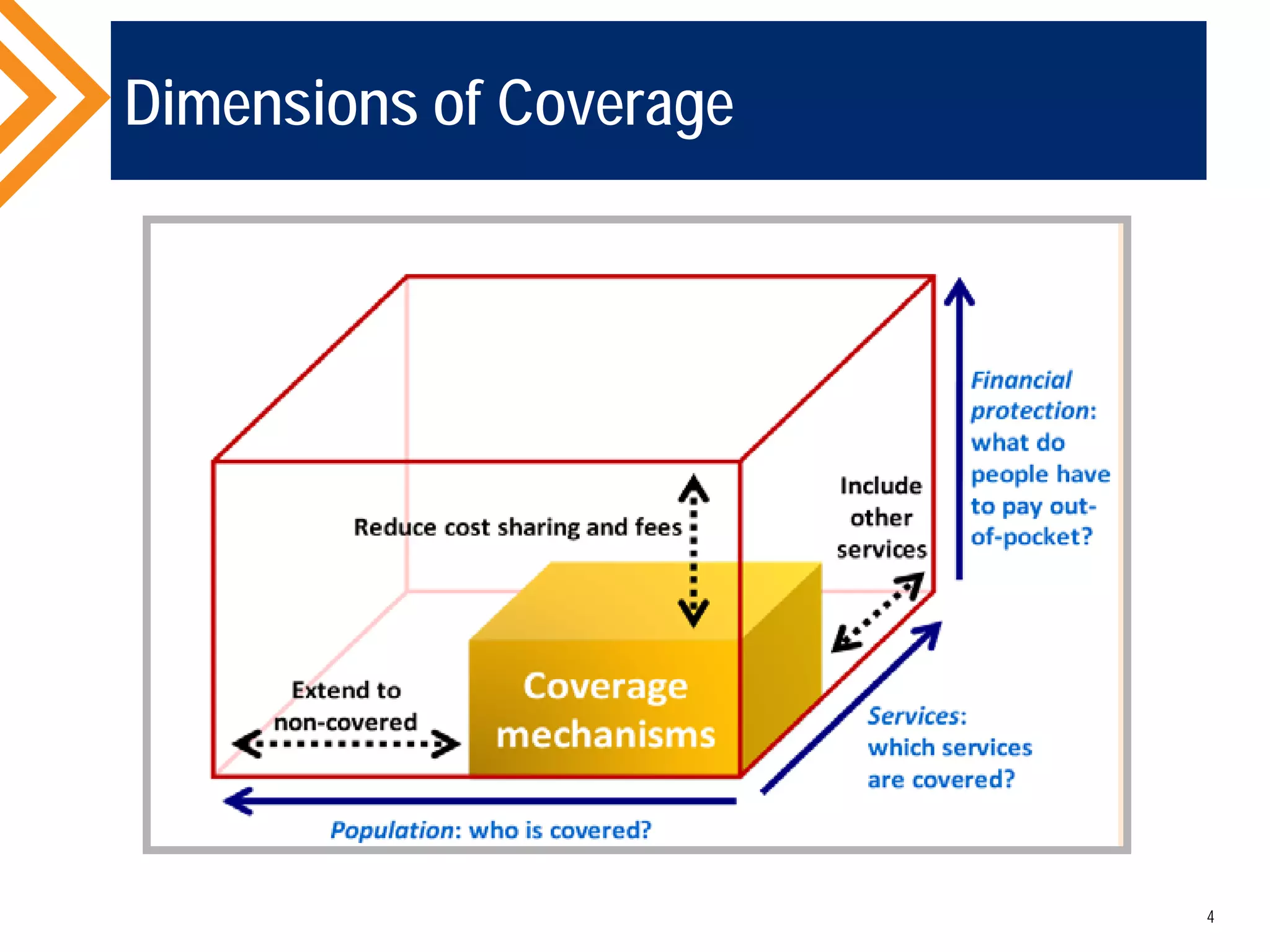
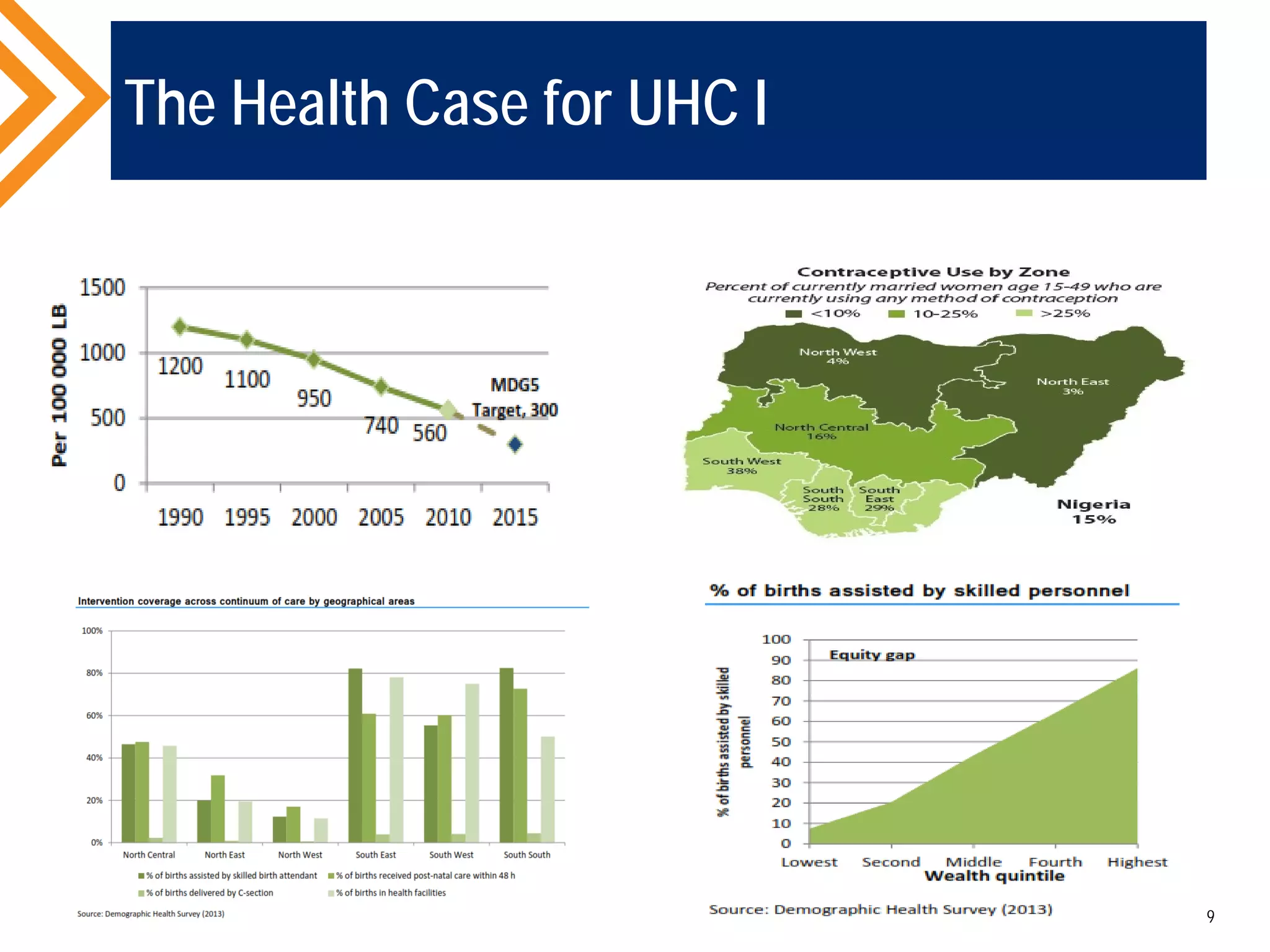
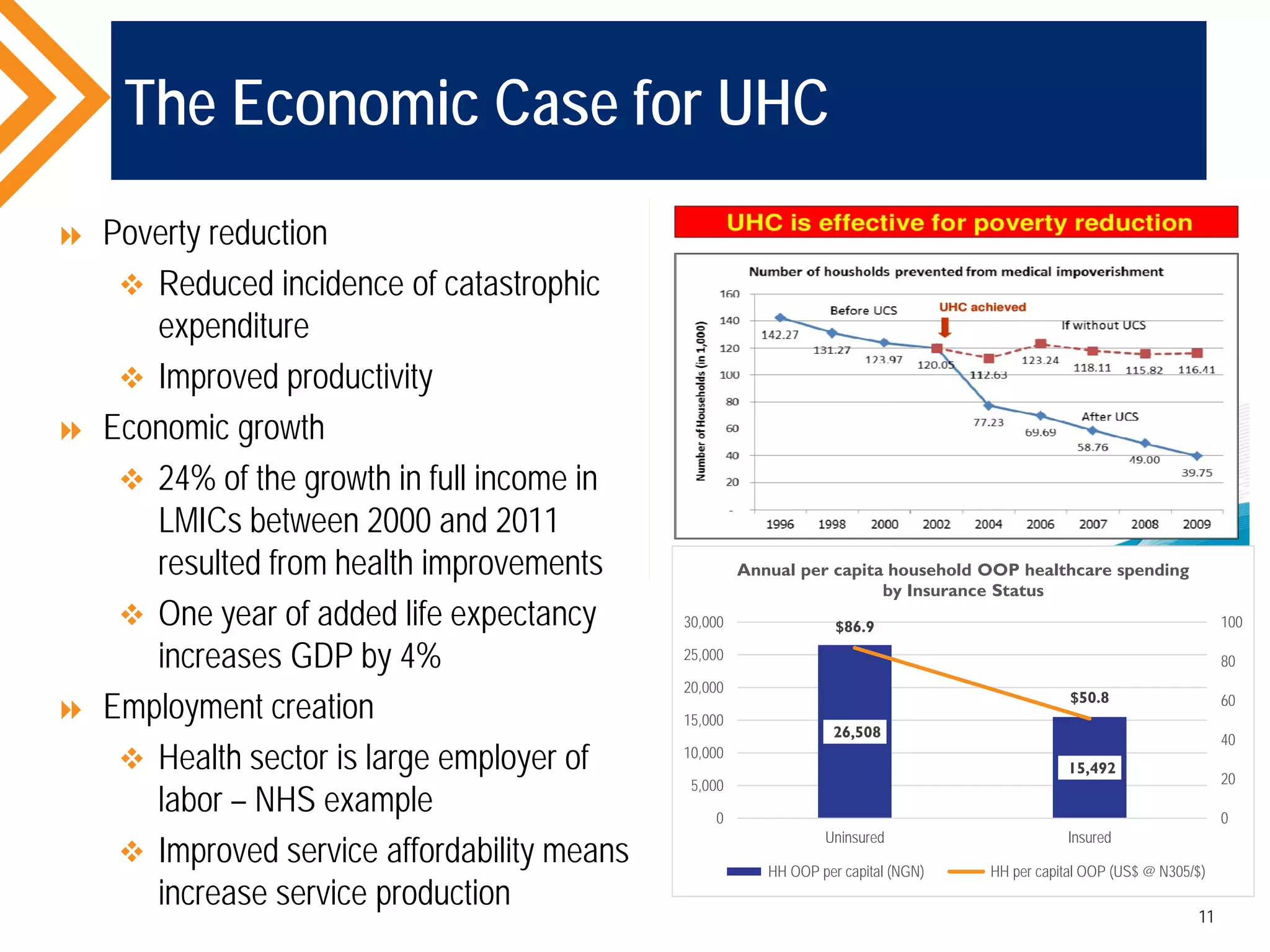
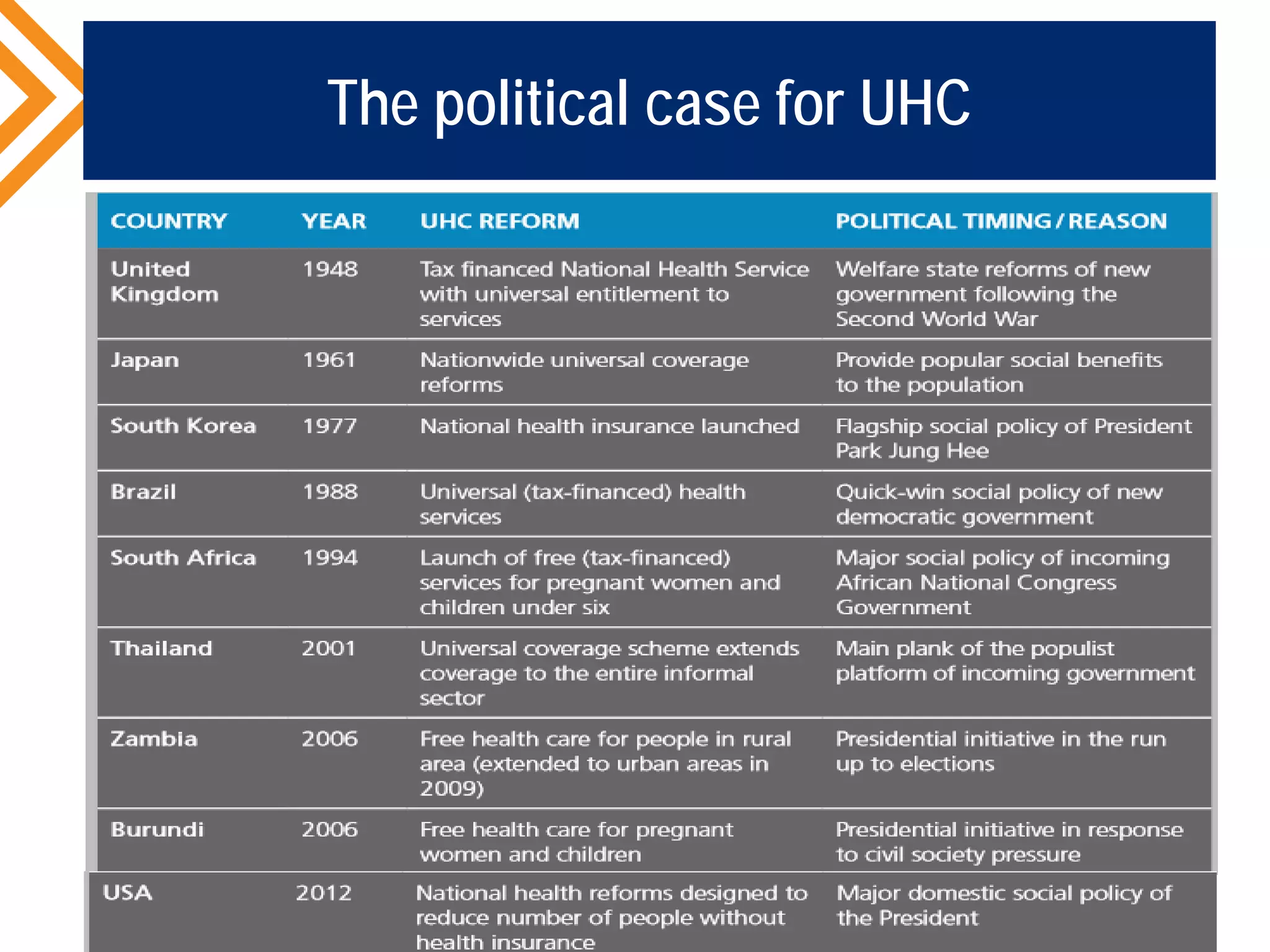
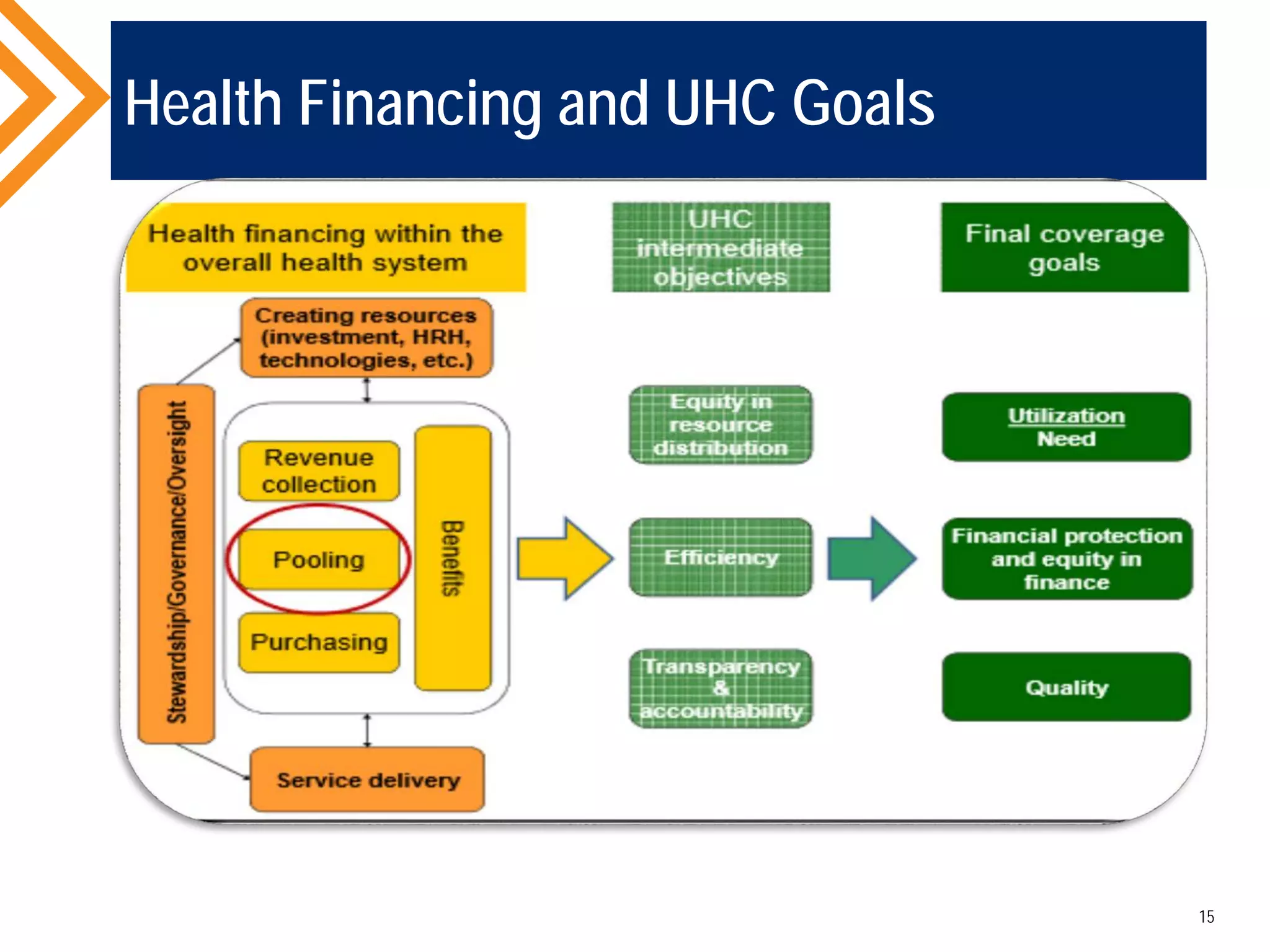
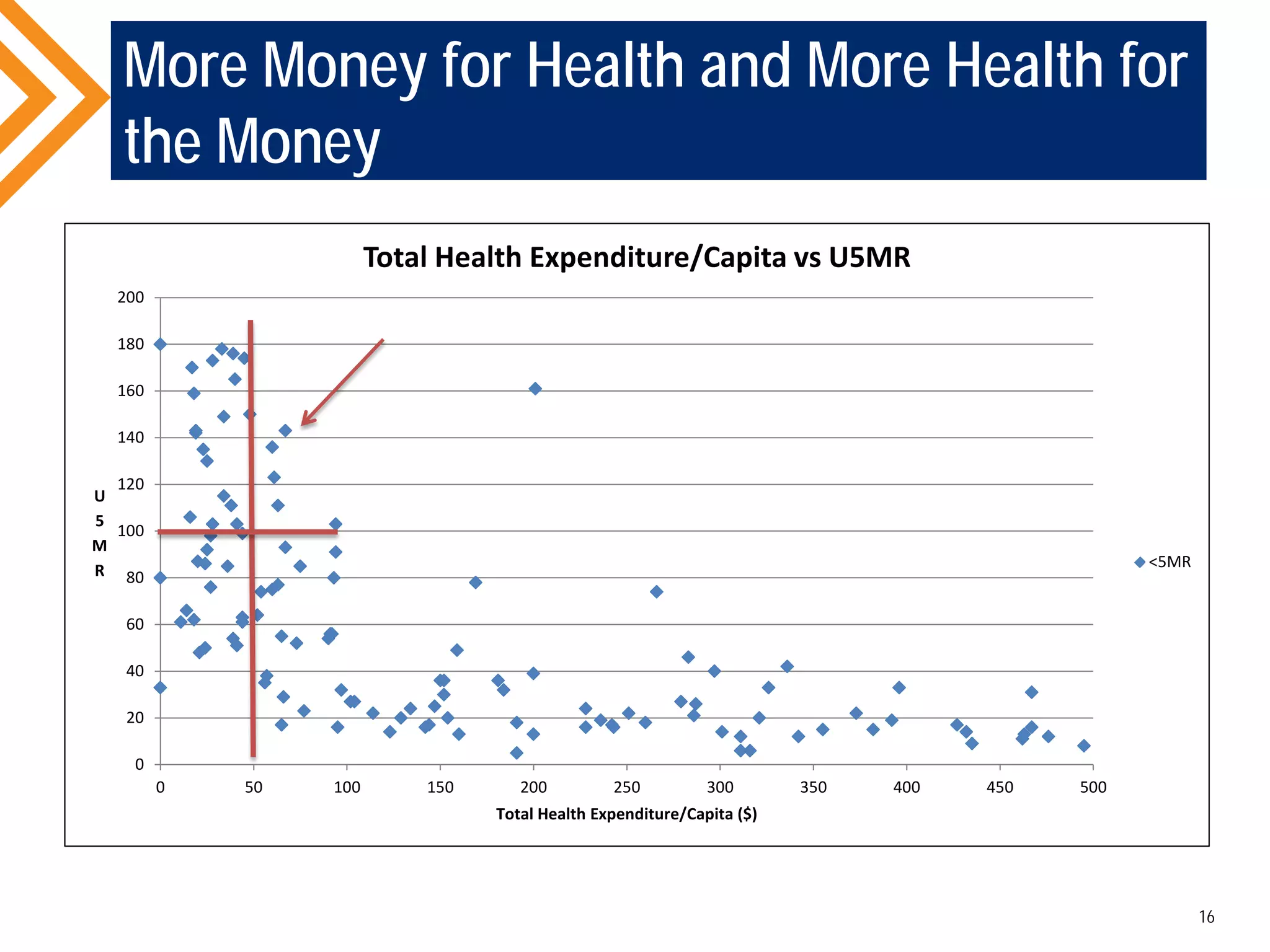
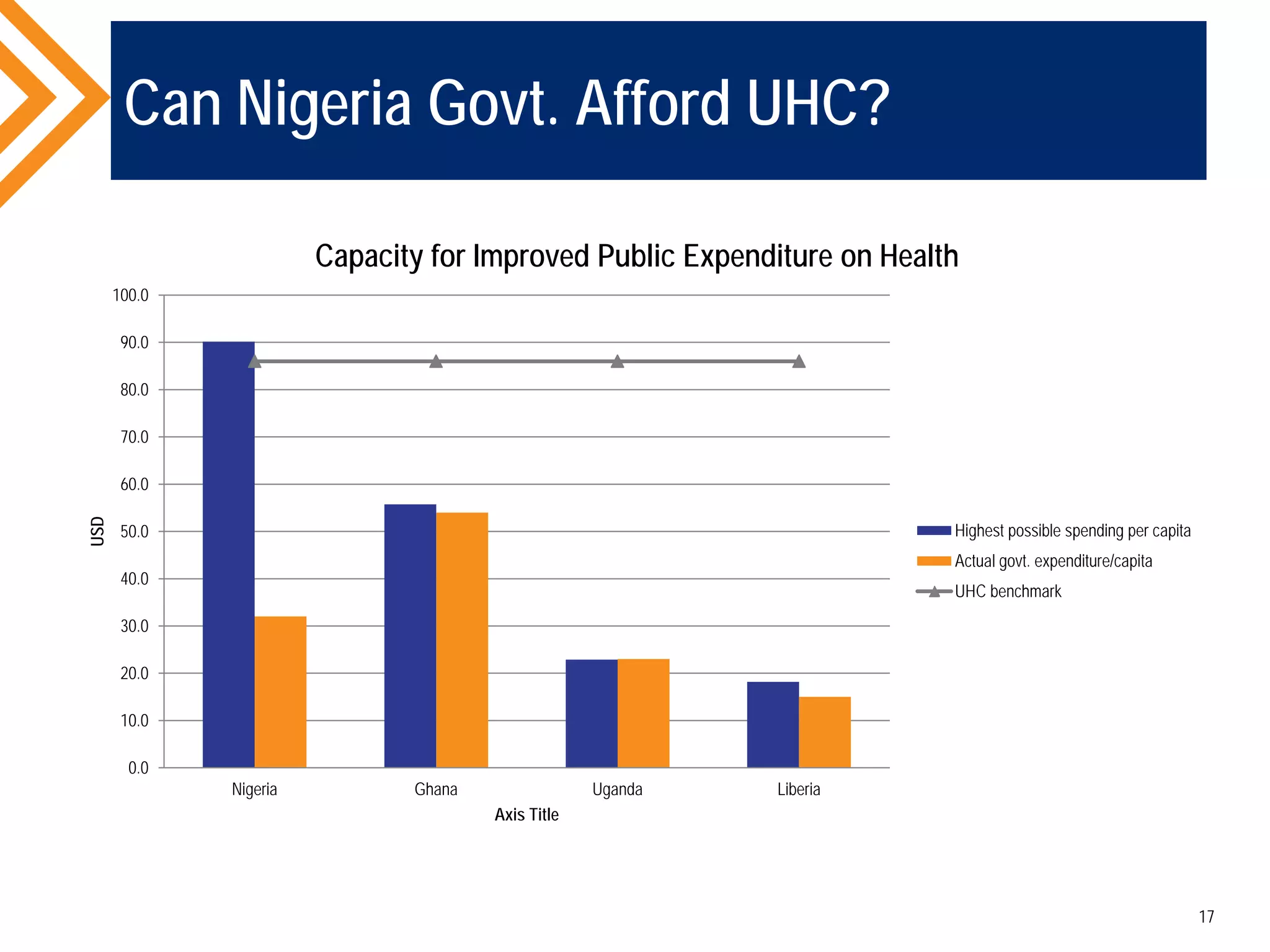
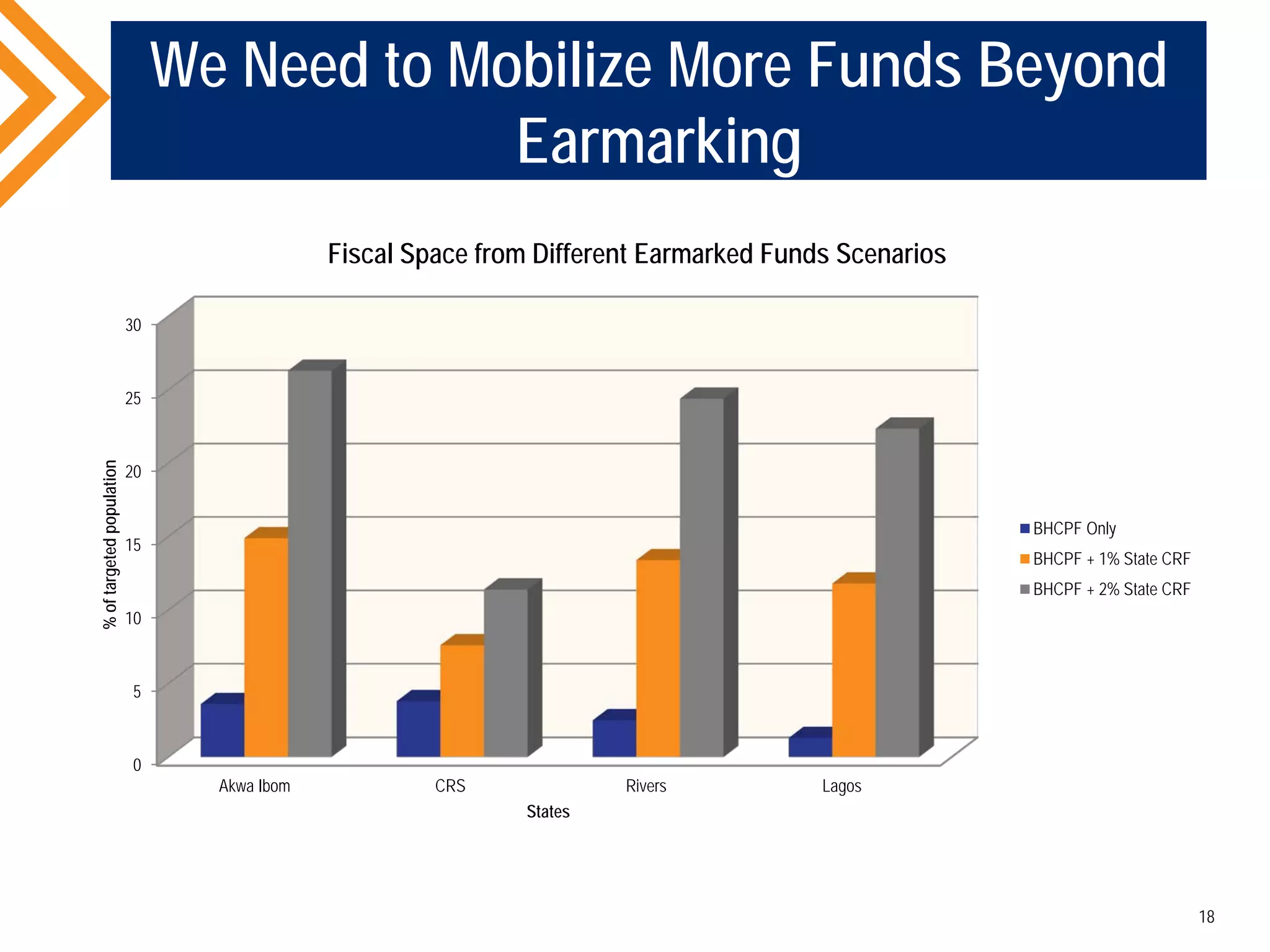
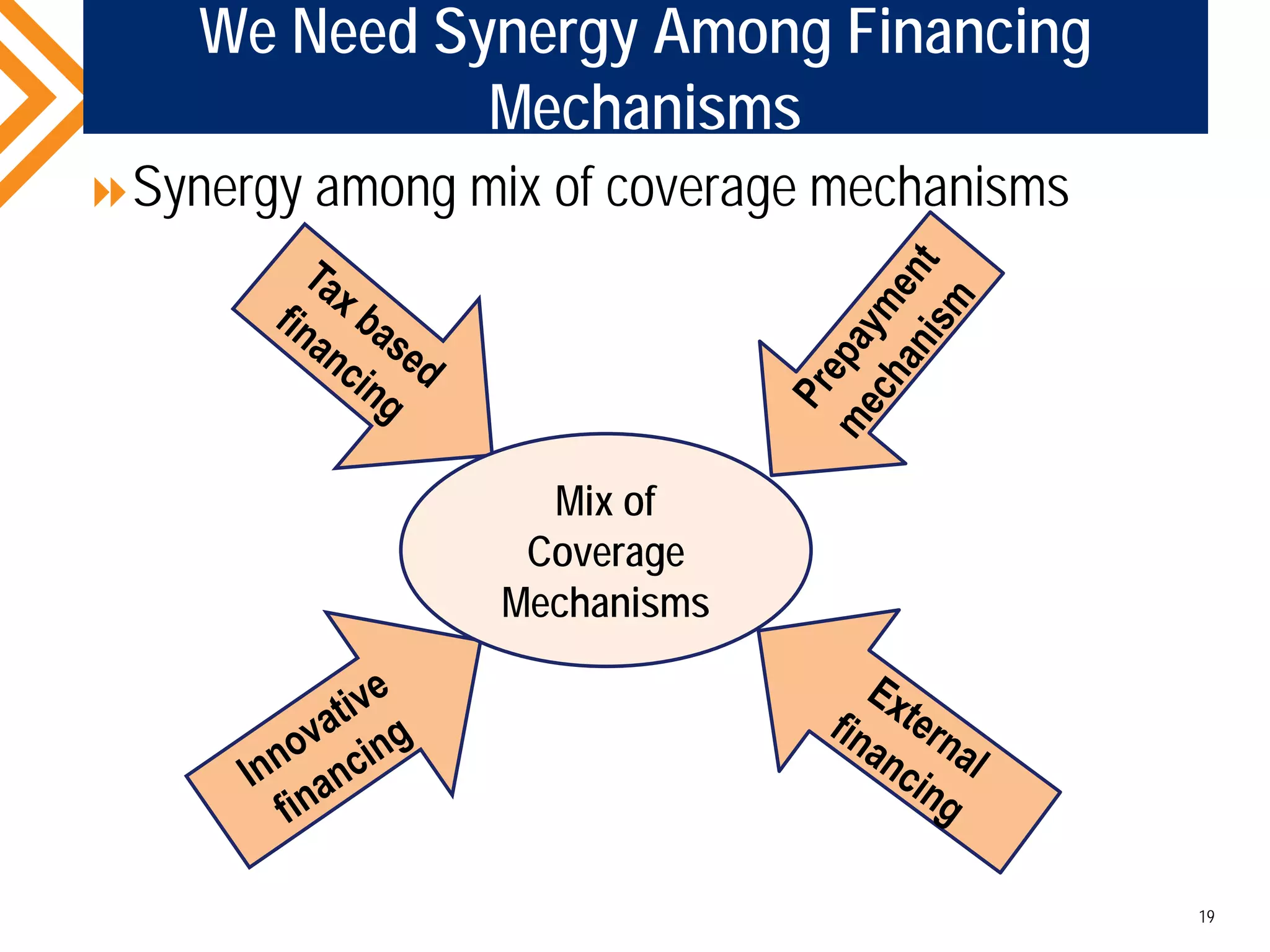
The document outlines the concept of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and its significance, emphasizing access to high-quality health services for all individuals without financial hardship. It discusses historical trends, the connection between healthcare financing and UHC, and advocates for a multi-dimensional case supporting UHC from health, economic, social, and political perspectives. The document also identifies key steps and ingredients necessary for moving towards achieving UHC.