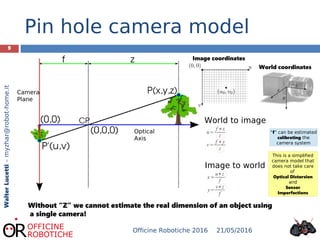
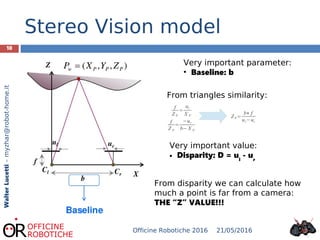
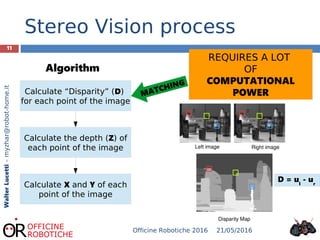
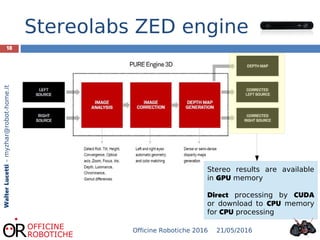
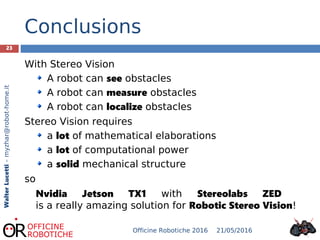
The document discusses the development of robotic stereo vision systems using the NVIDIA Jetson TX1 and the Stereolabs ZED camera. It outlines the principles of stereo vision, including the requirements for replication of human binocular vision, the essential components of the system, and provides insights into the coding examples necessary for camera operation. The findings conclude that stereo vision enables robots to detect, measure, and localize obstacles, emphasizing the importance of powerful computational resources in achieving effective robotic vision.




![Stereo “Binocular” Vision
5
[from Wikipedia: Binocular vision]
Vision made with TWO “EYES”
It gives a “creature” a spare eye in case one is damaged
It gives a wider field of view
It can give stereopsis in which binocular disparity (or
parallax) provided by the two eyes' different positions on
the head gives precise depth perception
It allows a creature to see more of, or all of, an object
behind an obstacle
It gives binocular summation in which the ability to detect
faint objects is enhanced
WalterLucetti–myzhar@robot-home.it
21/05/2016Officine Robotiche 2016](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robotsthatseelikehumans-160524075352/85/Robots-that-see-like-humans-5-320.jpg)