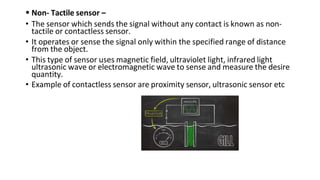
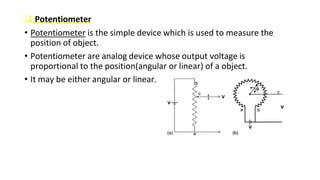
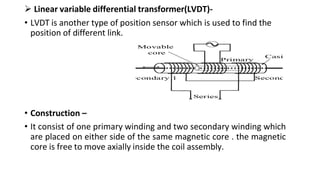
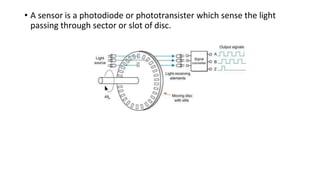
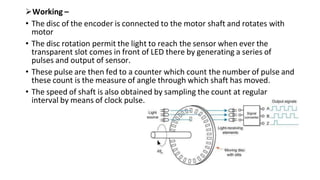
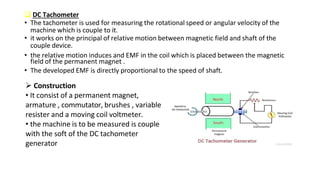
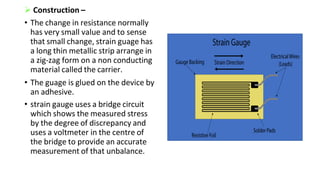
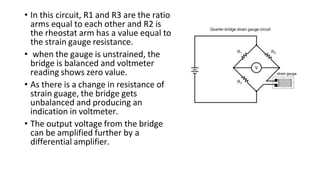
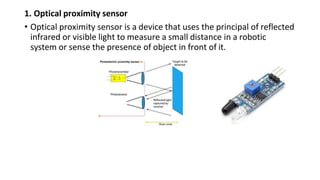
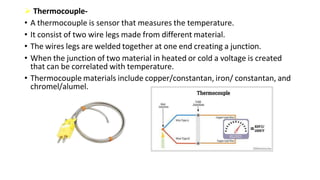
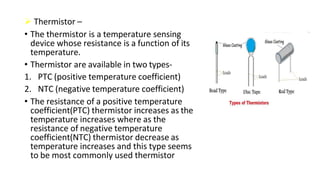
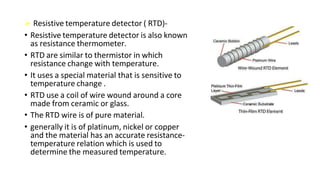
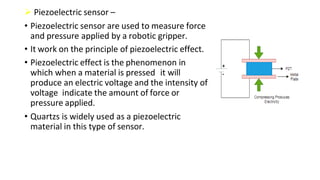
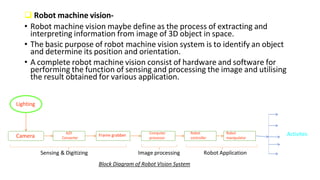
Robot machine vision systems allow robots to visually perceive their environment. The key components include cameras, lighting, analog-to-digital converters, frame grabbers, and computer processors. Images captured by the cameras are converted to digital data and processed by the computer to identify objects, determine their positions and orientations, and allow the robot to interact with or manipulate the objects appropriately. Machine vision enables robots to perform tasks like assembly, inspection, and packaging with visual feedback for precision and accuracy.