Recommended
PDF
SSII2019TS: 実践カメラキャリブレーション ~カメラを用いた実世界計測の基礎と応用~
PDF
PPTX
PDF
semantic segmentation サーベイ
PPTX
[解説スライド] NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
PDF
深層学習によるHuman Pose Estimationの基礎
PPTX
PPTX
StyleGAN解説 CVPR2019読み会@DeNA
PPTX
Swin Transformer (ICCV'21 Best Paper) を完璧に理解する資料
PDF
SSII2019TS: 実践カメラキャリブレーション ~カメラを用いた実世界計測の基礎と応用~
PDF
SSII2022 [SS1] ニューラル3D表現の最新動向〜 ニューラルネットでなんでも表せる?? 〜
PDF
PDF
SSII2021 [TS1] Visual SLAM ~カメラ幾何の基礎から最近の技術動向まで~
PDF
Cartographer を用いた 3D SLAM
PDF
[DL輪読会]NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
PDF
PPTX
SuperGlue;�Learning Feature Matching with Graph Neural Networks (CVPR'20)
PPTX
[DL輪読会]YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection
PPTX
強化学習の基礎と深層強化学習(東京大学 松尾研究室 深層強化学習サマースクール講義資料)
PDF
3次元レジストレーション(PCLデモとコード付き)
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
最近強化学習の良記事がたくさん出てきたので勉強しながらまとめた
PPTX
PDF
PDF
PDF
PPTX
Direct Sparse Odometryの解説
PDF
Visual SLAM: Why Bundle Adjust?の解説(第4回3D勉強会@関東)
More Related Content
PDF
SSII2019TS: 実践カメラキャリブレーション ~カメラを用いた実世界計測の基礎と応用~
PDF
PPTX
PDF
semantic segmentation サーベイ
PPTX
[解説スライド] NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
PDF
深層学習によるHuman Pose Estimationの基礎
PPTX
PPTX
StyleGAN解説 CVPR2019読み会@DeNA
What's hot
PPTX
Swin Transformer (ICCV'21 Best Paper) を完璧に理解する資料
PDF
SSII2019TS: 実践カメラキャリブレーション ~カメラを用いた実世界計測の基礎と応用~
PDF
SSII2022 [SS1] ニューラル3D表現の最新動向〜 ニューラルネットでなんでも表せる?? 〜
PDF
PDF
SSII2021 [TS1] Visual SLAM ~カメラ幾何の基礎から最近の技術動向まで~
PDF
Cartographer を用いた 3D SLAM
PDF
[DL輪読会]NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
PDF
PPTX
SuperGlue;�Learning Feature Matching with Graph Neural Networks (CVPR'20)
PPTX
[DL輪読会]YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection
PPTX
強化学習の基礎と深層強化学習(東京大学 松尾研究室 深層強化学習サマースクール講義資料)
PDF
3次元レジストレーション(PCLデモとコード付き)
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
最近強化学習の良記事がたくさん出てきたので勉強しながらまとめた
PPTX
PDF
PDF
PDF
Similar to BA-Net: Dense Bundle Adjustment Network (3D勉強会@関東)
PPTX
Direct Sparse Odometryの解説
PDF
Visual SLAM: Why Bundle Adjust?の解説(第4回3D勉強会@関東)
PPTX
PDF
PDF
ICCV2019読み会「Learning Meshes for Dense Visual SLAM」
PPTX
[DL輪読会]Depth Prediction Without the Sensors: Leveraging Structure for Unsuper...
PPTX
CVPR2018 pix2pixHD論文紹介 (CV勉強会@関東)
PPTX
Depth from Videos in the Wild: Unsupervised Monocular Depth Learning from Unk...
PDF
Taking a Deeper Look at the Inverse Compositional Algorithm
PDF
FastDepth: Fast Monocular Depth Estimation on Embedded Systems
PPT
PDF
【DLゼミ】XFeat: Accelerated Features for Lightweight Image Matching
PDF
Tutorial-DeepLearning-PCSJ-IMPS2016
PDF
【2015.07】(1/2)cvpaper.challenge@CVPR2015
PDF
Learning Deep Architectures for AI (第 3 回 Deep Learning 勉強会資料; 松尾)
PDF
PDF
Learning Spatial Common Sense with Geometry-Aware Recurrent Networks
PDF
PDF
PDF
BA-Net: Dense Bundle Adjustment Network (3D勉強会@関東) 1. 2. about.me
@denkiwakame
● 〜2015 京都大学 松山研究室(B4〜M2)
● 〜2017 某企業研
● 2017〜 都内ベンチャー
Interests
● Generalized Camera Calibration [M.Nishimura+,ICCV15]
● MRF optimization (low-level vision)
● Model Compression
● GPGPU (CUDA),SIMD
● Quantum Computing
2
[M.Nishimura+, ICCV15] A Linear Generalized Camera Calibration from Three Intersecting
Reference Planes
3. 4. 5. 6. CodeSLAM [M.Bloesch+,CVPR18]
● VAE によって depth の圧縮表現(code)を得る
6
● Pose (R,t) - depth optimization が解ける
○ gauss-newton 法で最適化(ヤコビアンが計算できる)
〜128dim
parametrized depth
pose
photometric error
geometric error
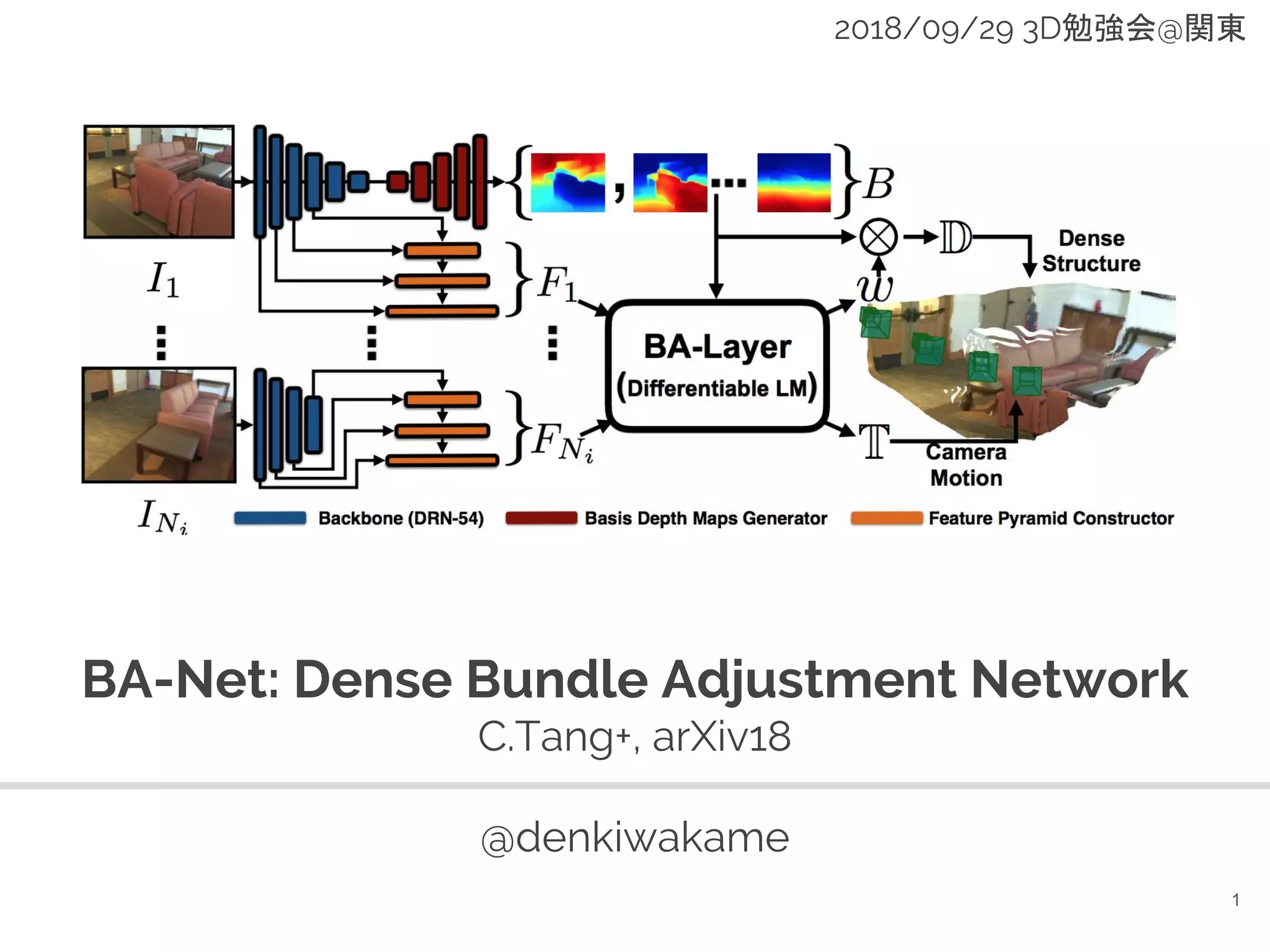
7. 8. BA-Net : Dense Bundle Adjustment Network
● 特徴抽出,depth の圧縮表現学習,バンドル調整を全てNN
で行う
8
SfM の一連の要素を end-to-end でモデリング
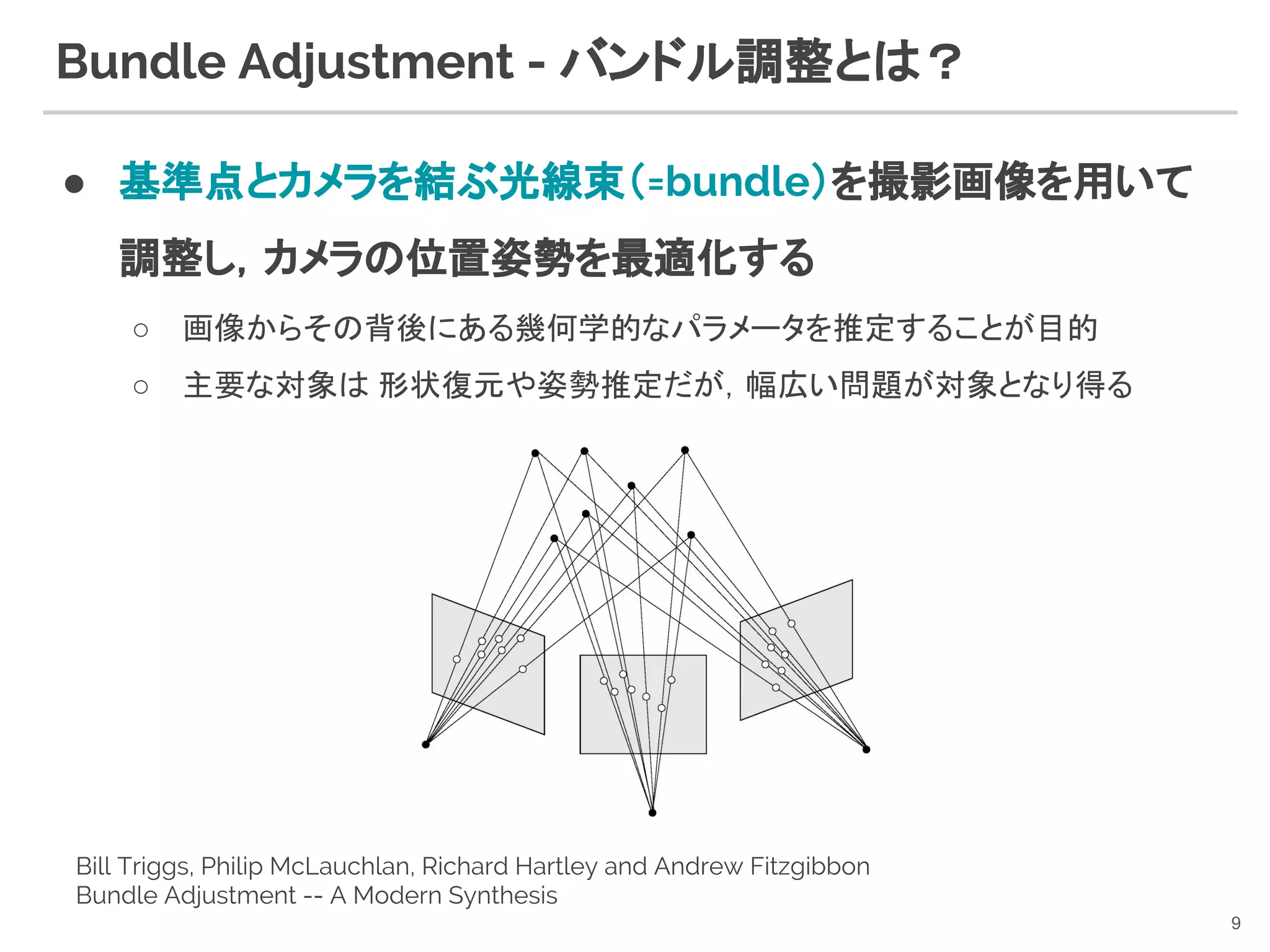
9. Bundle Adjustment - バンドル調整とは?
● 基準点とカメラを結ぶ光線束(=bundle)を撮影画像を用いて
調整し,カメラの位置姿勢を最適化する
○ 画像からその背後にある幾何学的なパラメータを推定することが目的
○ 主要な対象は 形状復元や姿勢推定だが,幅広い問題が対象となり得る
9
Bill Triggs, Philip McLauchlan, Richard Hartley and Andrew Fitzgibbon
Bundle Adjustment -- A Modern Synthesis
10. Bundle Adjustment - historical overview
● [T.Bill+,VA99] Bundle Adjustment - a modern
synthesis
10
Triggs, Bill, et al. "Bundle adjustment—a modern synthesis." International workshop on vision
algorithms. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1999. (鉄板)
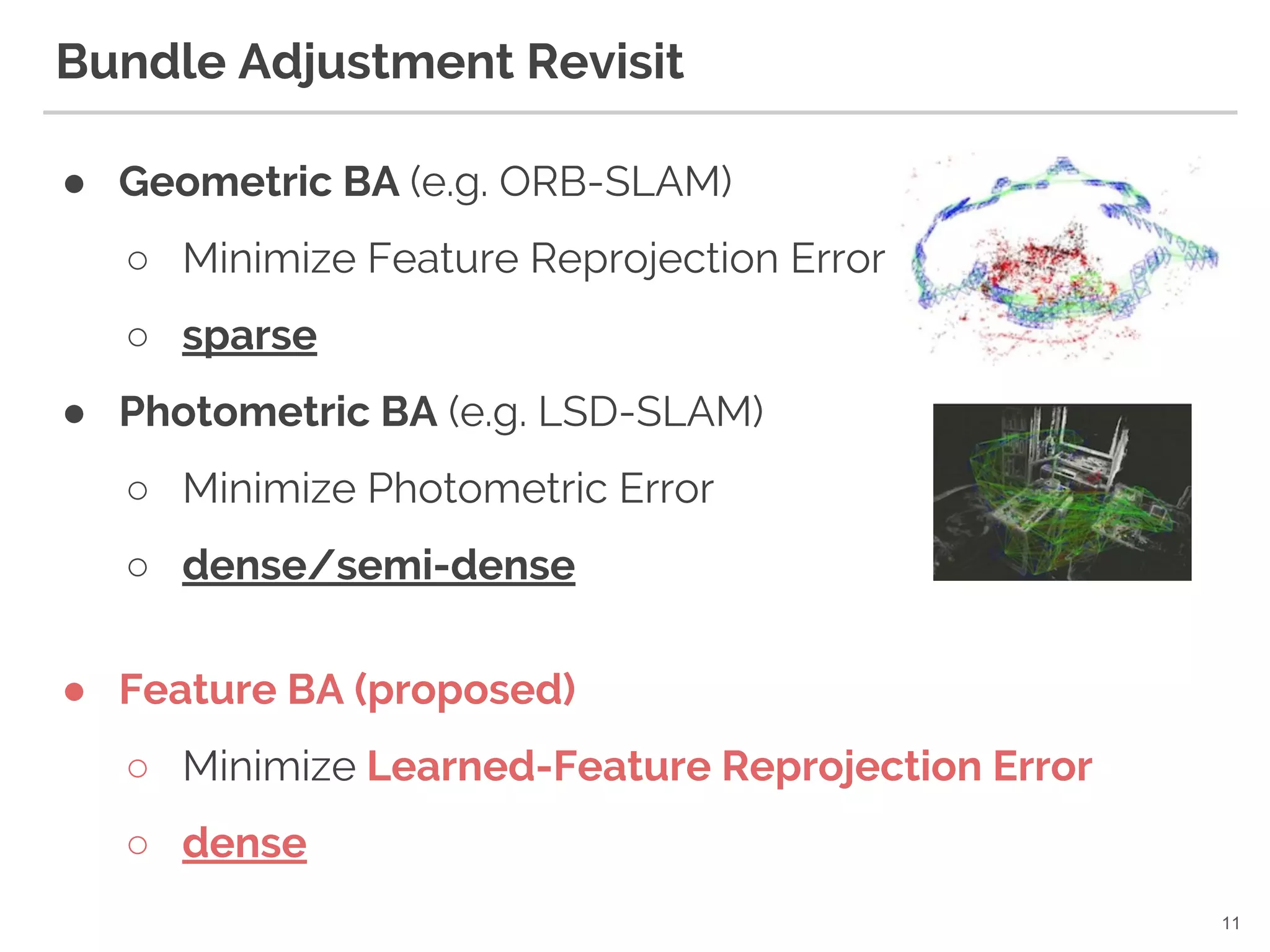
11. Bundle Adjustment Revisit
● Geometric BA (e.g. ORB-SLAM)
○ Minimize Feature Reprojection Error
○ sparse
● Photometric BA (e.g. LSD-SLAM)
○ Minimize Photometric Error
○ dense/semi-dense
11
● Feature BA (proposed)
○ Minimize Learned-Feature Reprojection Error
○ dense
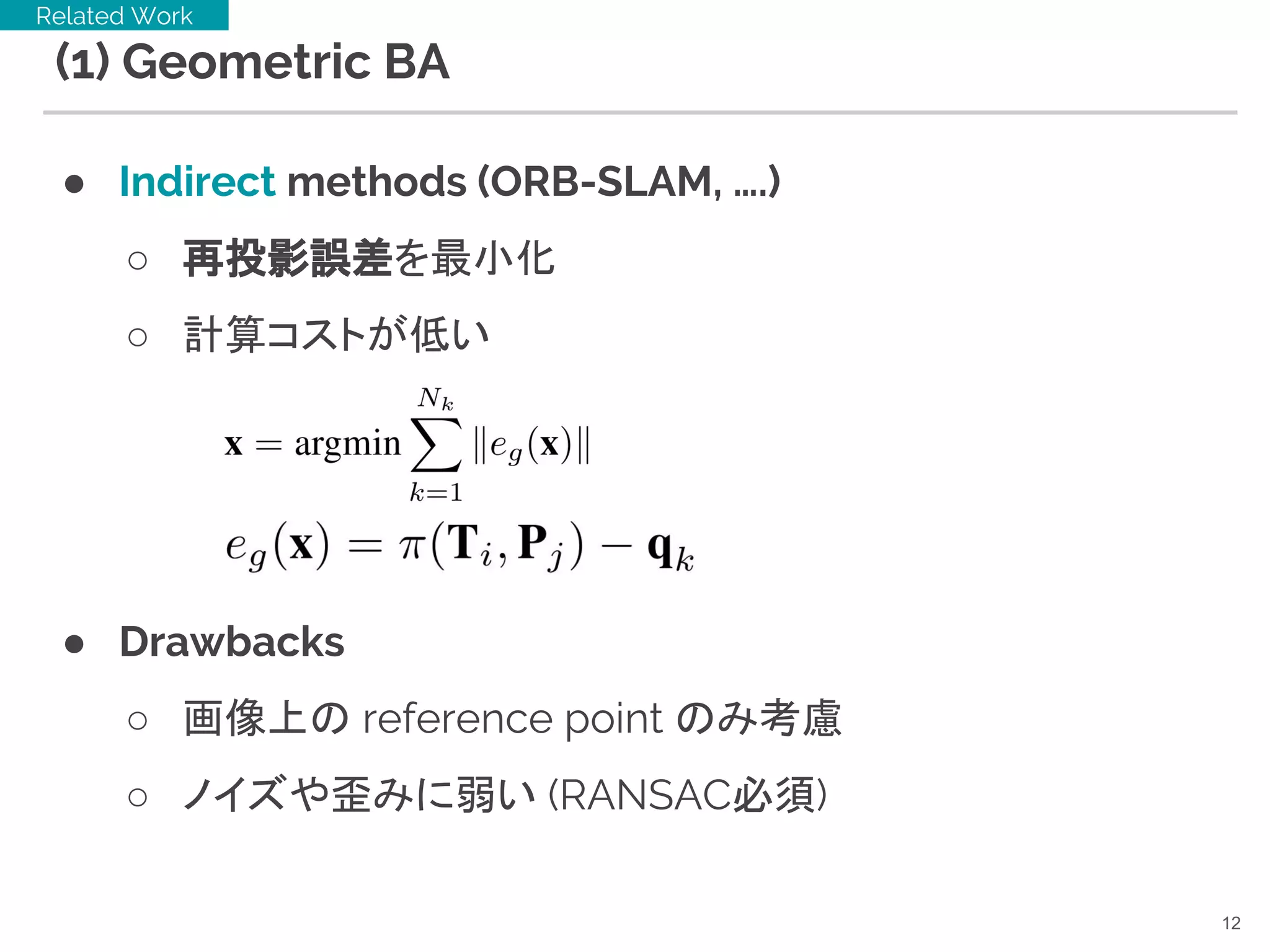
12. (1) Geometric BA
● Indirect methods (ORB-SLAM, ….)
○ 再投影誤差を最小化
○ 計算コストが低い
● Drawbacks
○ 画像上の reference point のみ考慮
○ ノイズや歪みに弱い (RANSAC必須)
12
Related Work
13. (2) Photometric BA
● Direct methods (LSD-SLAM, ...)
○ (再投影された) 画素の輝度値の差を最小化
○ テクスチャが疎らな環境でも有効
● Drawbacks
○ 初期値に依存(非凸性が強い)
○ 照明環境の変化に弱い(photometric calib 必須)
○ 動物体など,outlier に弱い
13
Related Work
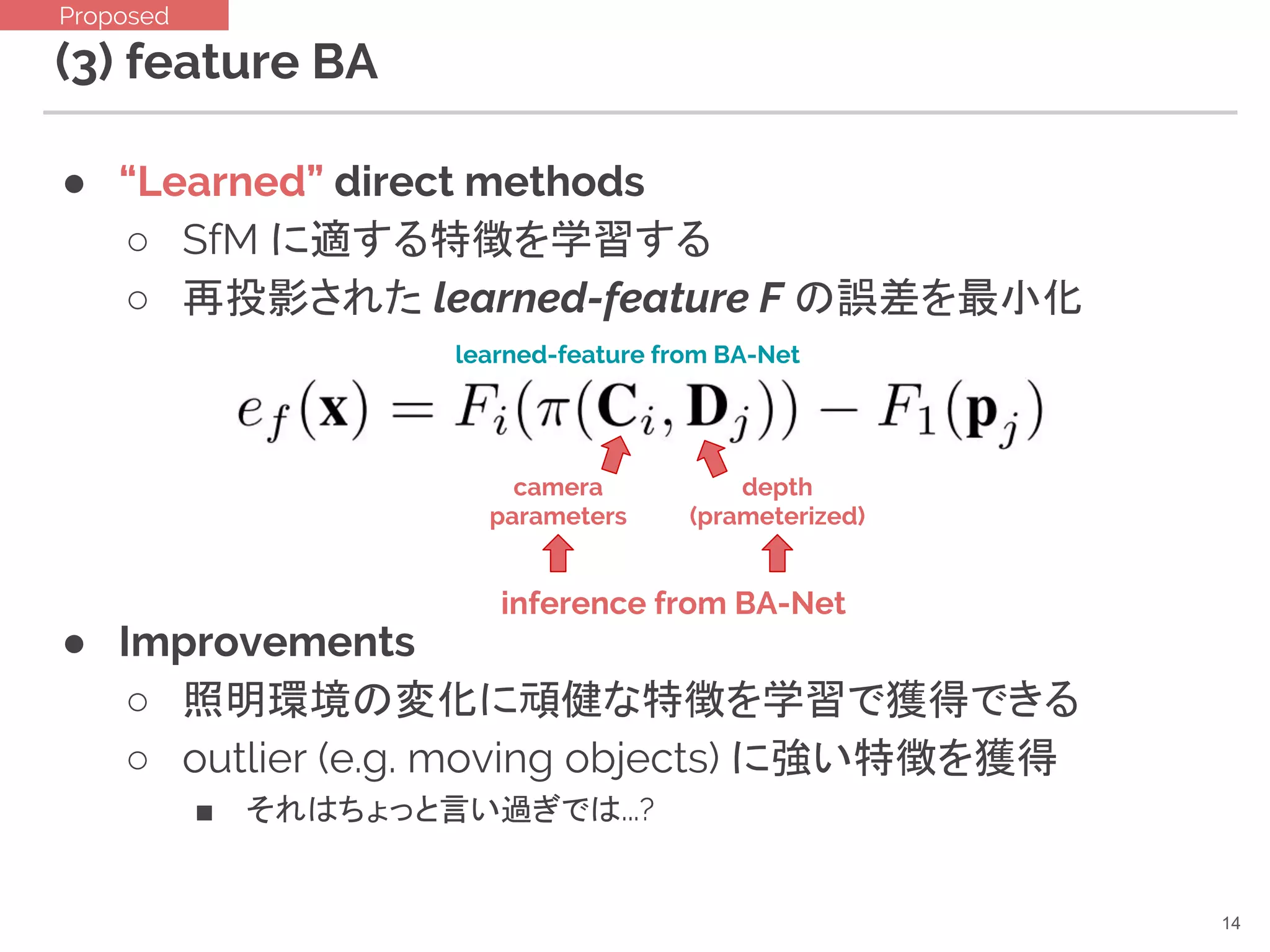
14. (3) feature BA
● “Learned” direct methods
○ SfM に適する特徴を学習する
○ 再投影された learned-feature F の誤差を最小化
● Improvements
○ 照明環境の変化に頑健な特徴を学習で獲得できる
○ outlier (e.g. moving objects) に強い特徴を獲得
■ それはちょっと言い過ぎでは...?
14
Proposed
camera
parameters
depth
(prameterized)
inference from BA-Net
learned-feature from BA-Net
15. ● Feature learning for SfM (2-view setting)
○ BA-Net の minor contribution
Network overview - feature & depth learning
15
depth parametrization
sub-network
feature pyramid
network
base-network
[F.Yu+,CVPR17]
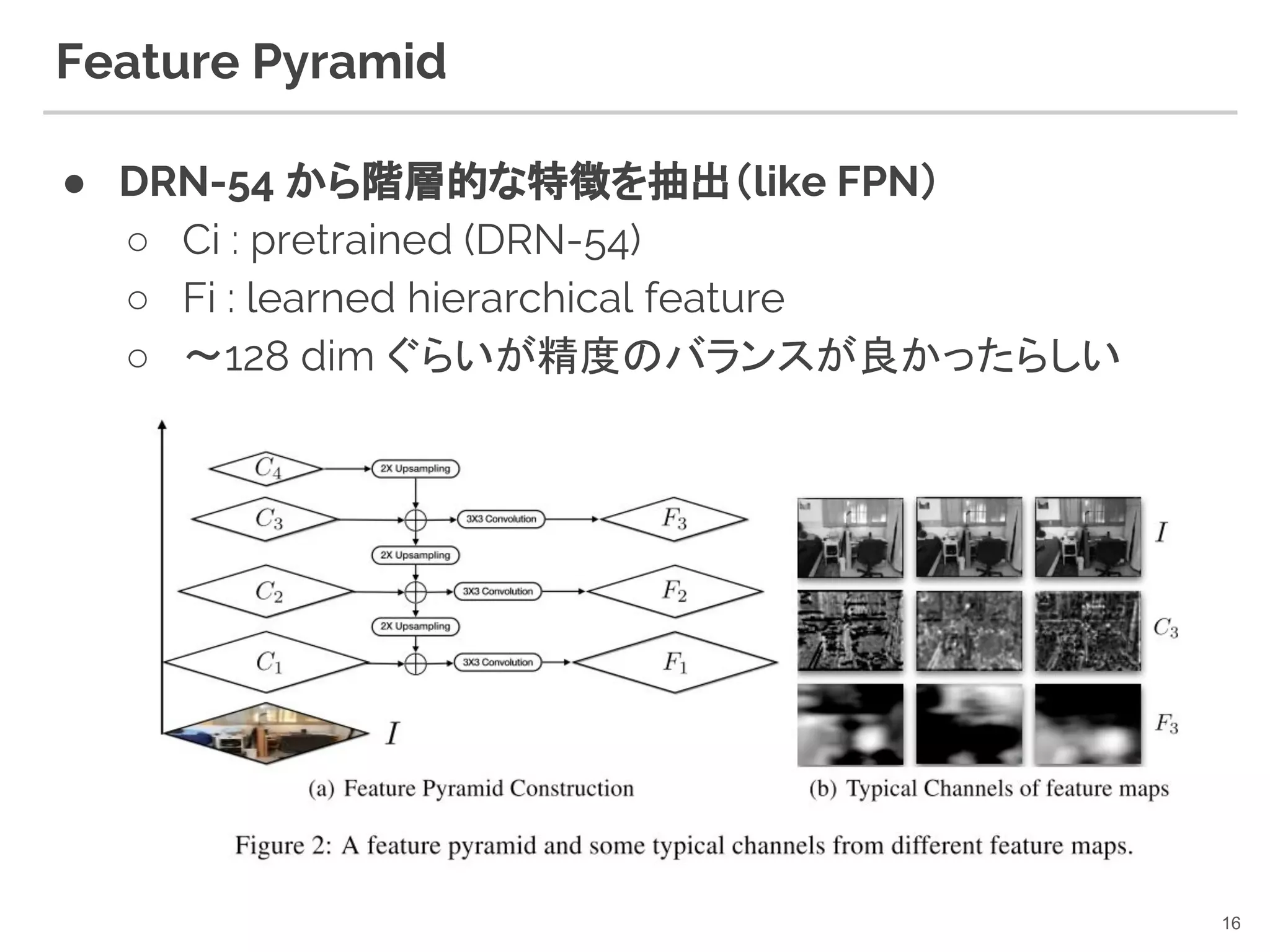
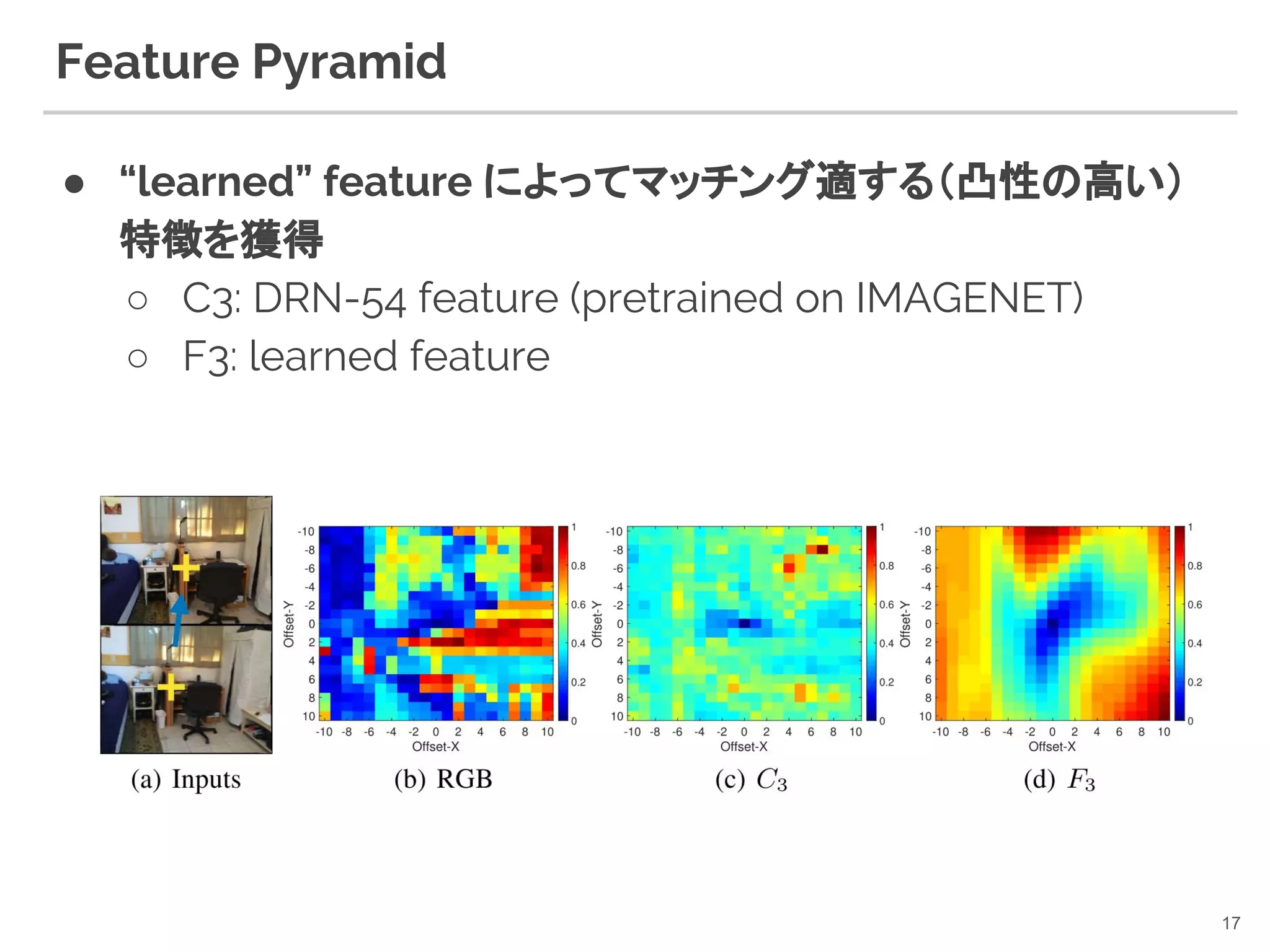
16. Feature Pyramid
● DRN-54 から階層的な特徴を抽出(like FPN)
○ Ci : pretrained (DRN-54)
○ Fi : learned hierarchical feature
○ 〜128 dim ぐらいが精度のバランスが良かったらしい
16
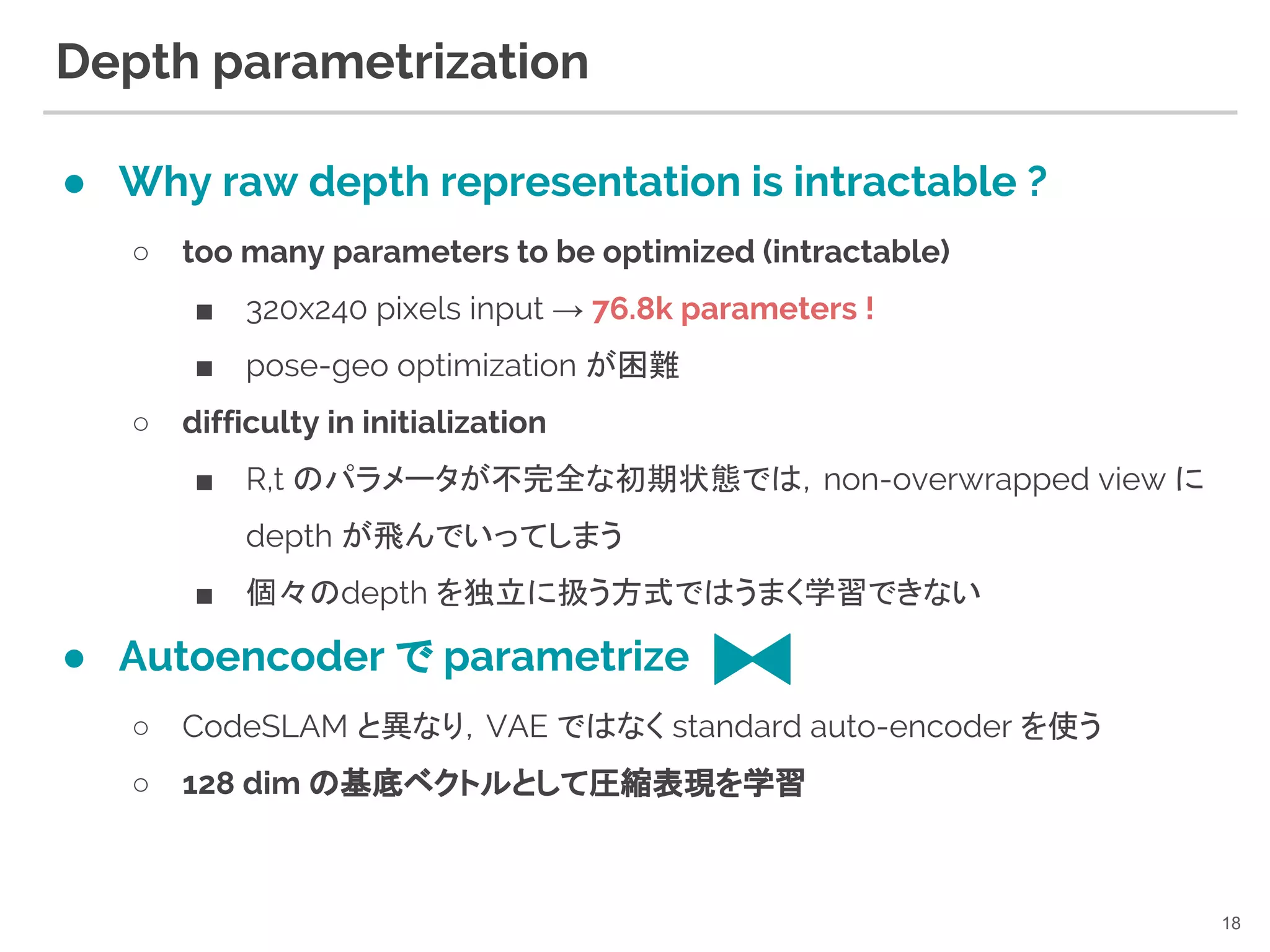
17. 18. Depth parametrization
● Why raw depth representation is intractable ?
○ too many parameters to be optimized (intractable)
■ 320x240 pixels input → 76.8k parameters !
■ pose-geo optimization が困難
○ difficulty in initialization
■ R,t のパラメータが不完全な初期状態では,non-overwrapped view に
depth が飛んでいってしまう
■ 個々のdepth を独立に扱う方式ではうまく学習できない
● Autoencoder で parametrize
○ CodeSLAM と異なり,VAE ではなく standard auto-encoder を使う
○ 128 dim の基底ベクトルとして圧縮表現を学習
18
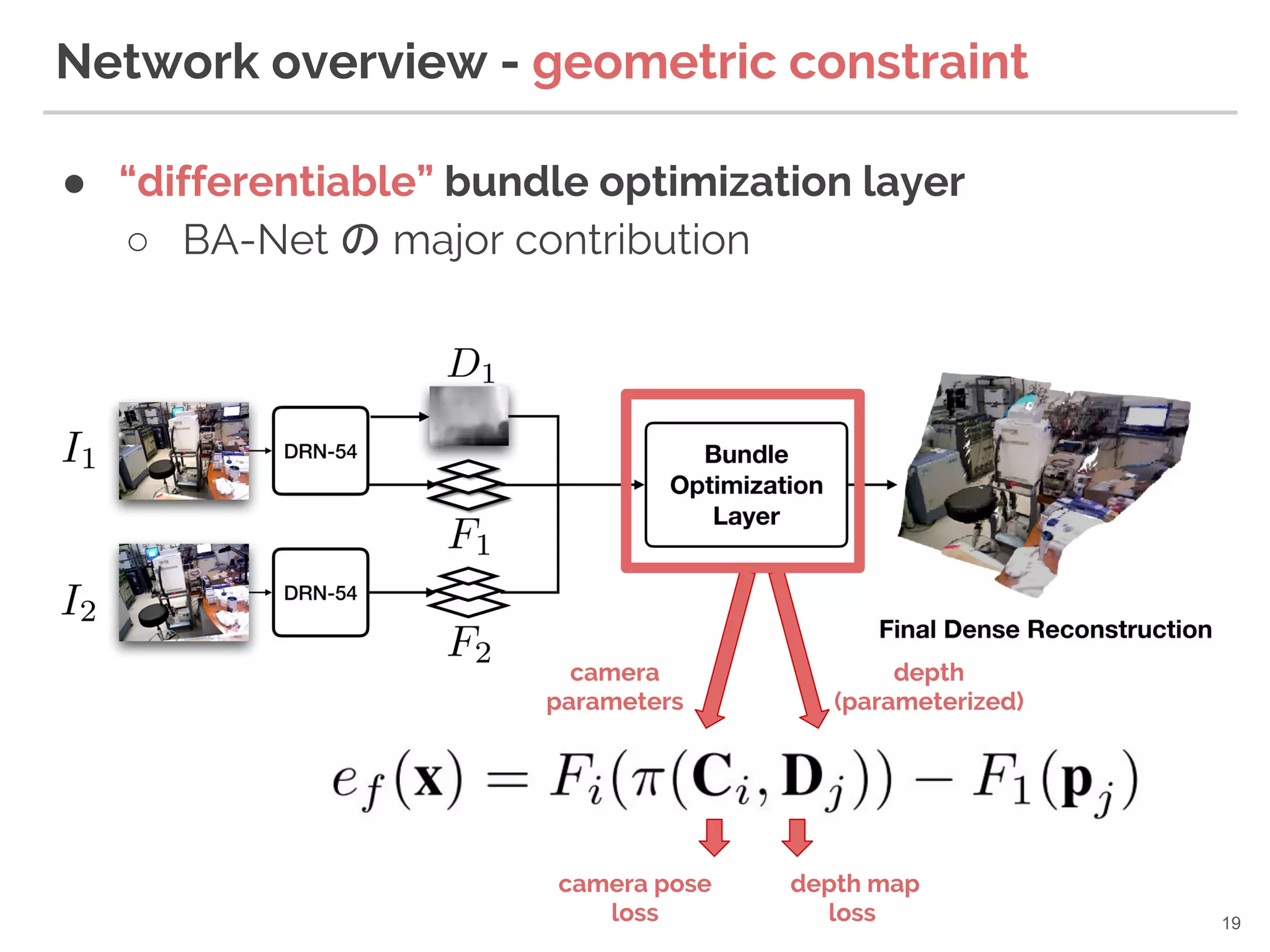
19. ● “differentiable” bundle optimization layer
○ BA-Net の major contribution
Network overview - geometric constraint
19
camera
parameters
depth
(parameterized)
camera pose
loss
depth map
loss
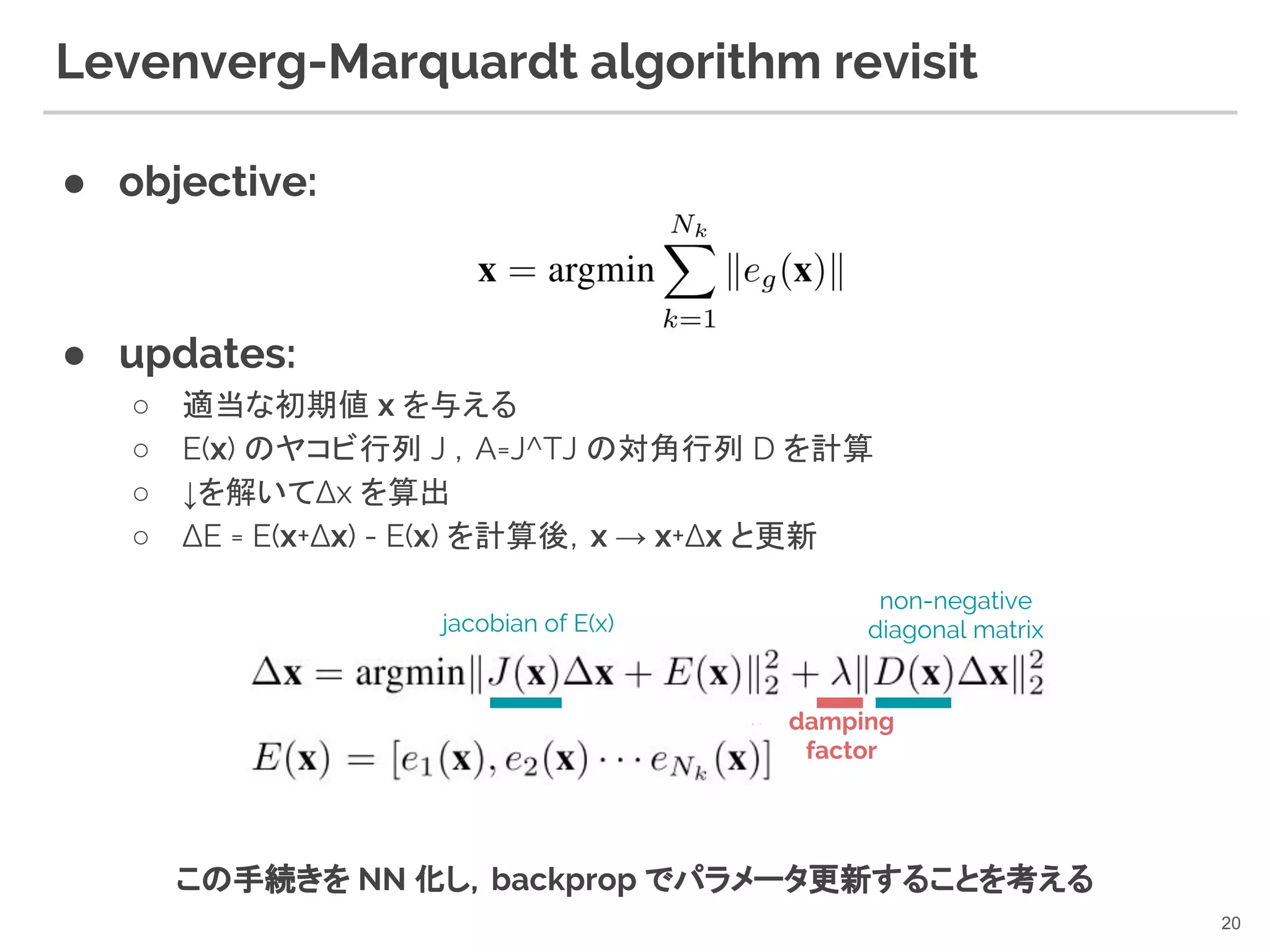
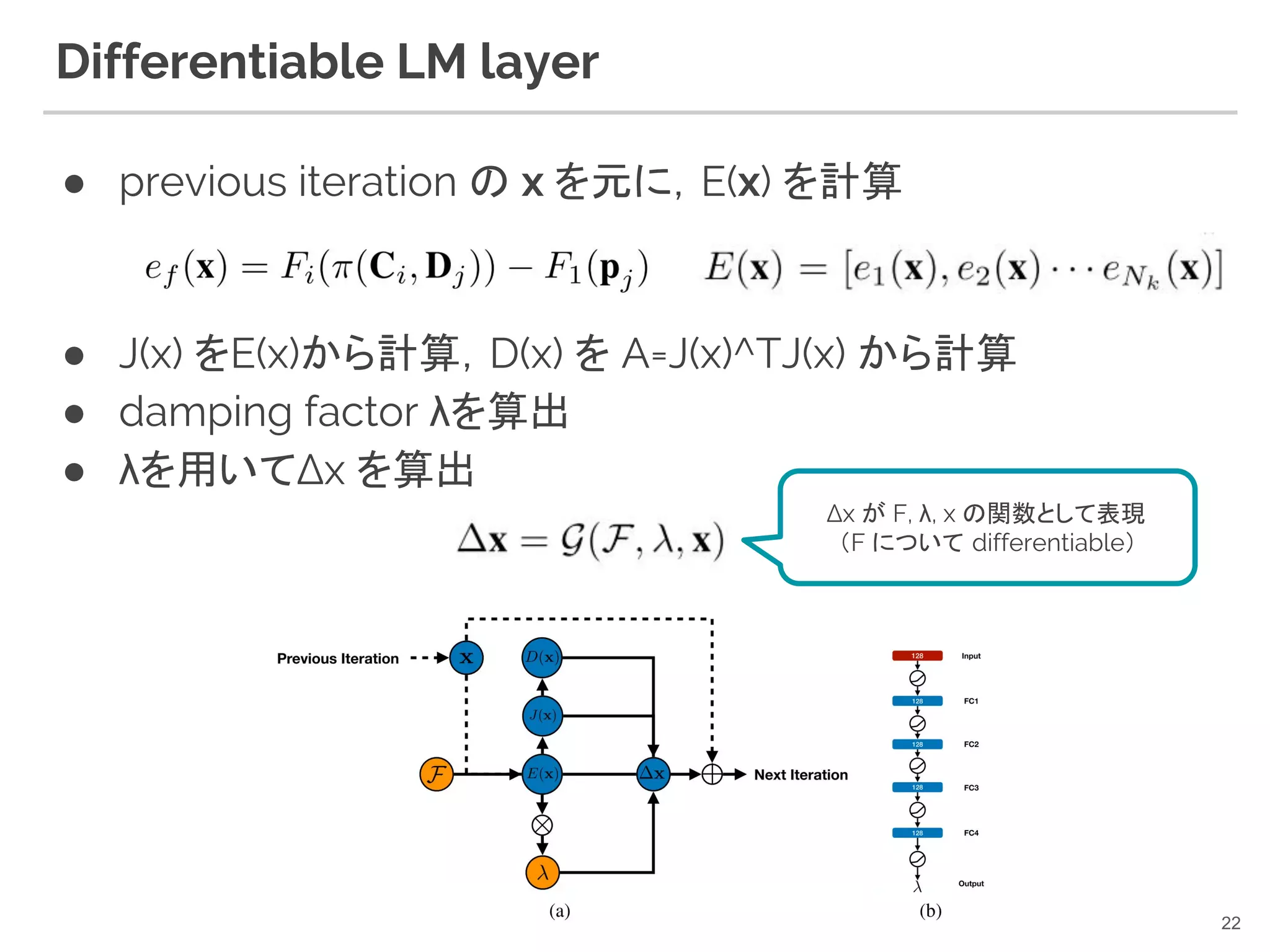
20. Levenverg-Marquardt algorithm revisit
● objective:
● updates:
○ 適当な初期値 x を与える
○ E(x) のヤコビ行列 J ,A=J^TJ の対角行列 D を計算
○ ↓を解いてΔx を算出
○ ΔE = E(x+Δx) - E(x) を計算後,x → x+Δx と更新
20
damping
factor
non-negative
diagonal matrixjacobian of E(x)
この手続きを NN 化し,backprop でパラメータ更新することを考える
21. ● Difficulties:
○ LM法の反復解法は収束閾値に達すると打ち切り
■ 条件分岐を含む非連続関数になってしまう(微分不能)
○ 各反復試行において,目的関数に応じ λ を操作
■ E(x) が減少するまでλを大きくし続ける(減少した際にλを小さくする)
■ 条件分岐(ry
● Simple yet effective approach
○ 固定回数の反復を実装する (※)
○ lambda を network で推論
Differentiable LM layer
21
※ [J.Domke+, AISTATS12] Generic Methods for Optimization-Based Modeling
22. Differentiable LM layer
● previous iteration の x を元に,E(x) を計算
● J(x) をE(x)から計算,D(x) を A=J(x)^TJ(x) から計算
● damping factor λを算出
● λを用いてΔx を算出
22
Δx が F, λ, x の関数として表現
(F について differentiable)
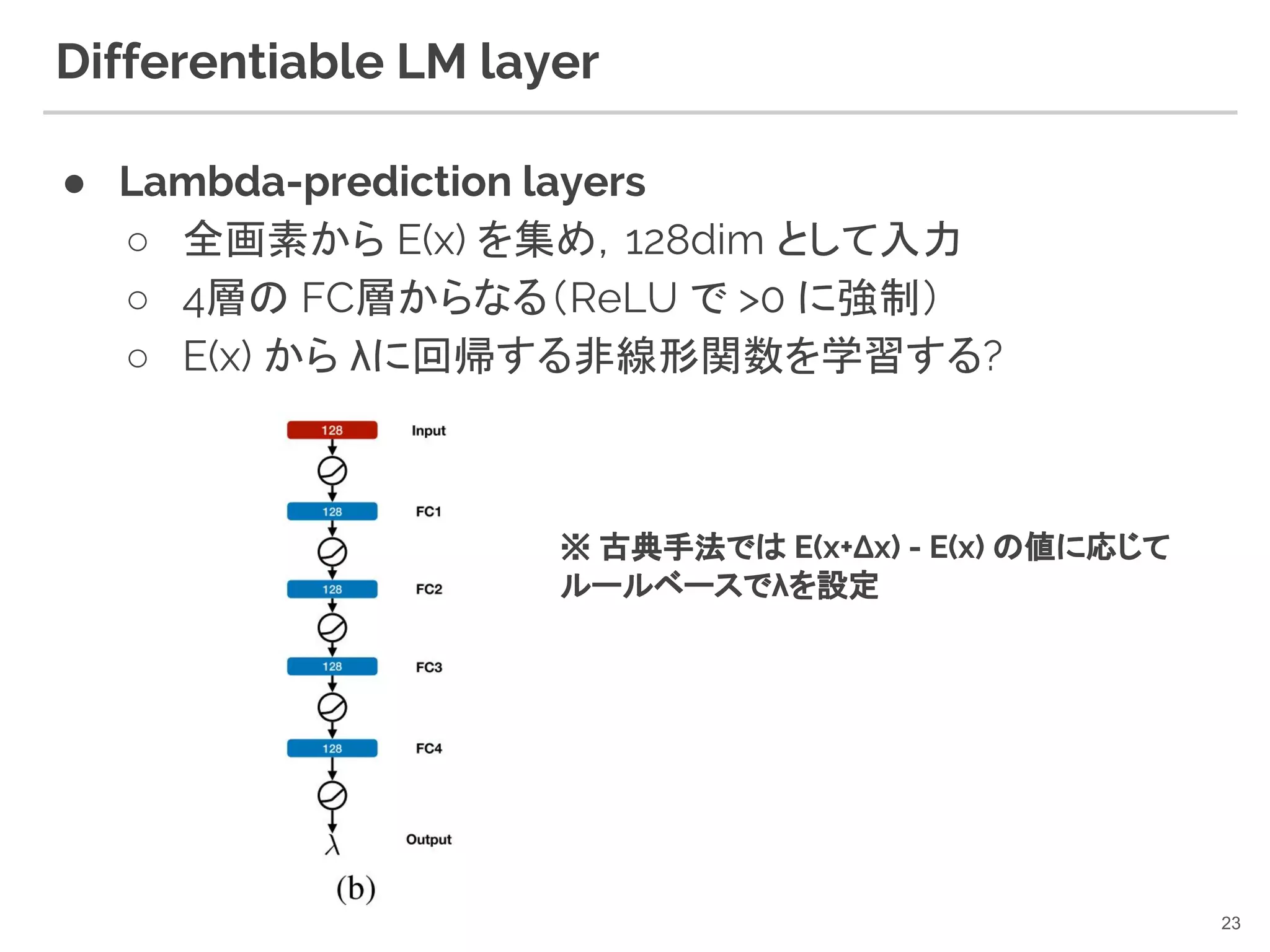
23. Differentiable LM layer
● Lambda-prediction layers
○ 全画素から E(x) を集め,128dim として入力
○ 4層の FC層からなる(ReLU で >0 に強制)
○ E(x) から λに回帰する非線形関数を学習する?
23
※ 古典手法では E(x+Δx) - E(x) の値に応じて
ルールベースでλを設定
24. Differentiable LM layer
● Coarse-to-fine optimization
○ LSD-SLAM [J.ENgel+,ECCV14] や DSO
[J.Engel+,TPAMI17] と同様,Coarse-to-fine BA を適用
○ feature pyramid の各 layer で 5-iteration
○ 計 15-iteration を 1回の forward-pass で反復
24
25. 関連:CRF as RNN
● Semantic Segmentation において, 後段に平均場近似
(mean-field approximation)の手続きをRNNで実装
○ CRFの最適化は post-processing として当初分離されていた
○ RNN で 平均場近似を実装することにより,CRF の学習と最適化が1つのネッ
トワークで行えるようになった
25[S.Zheng+, ICCV15] Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Networks
26. Training Objective
● Camera Pose Loss
○ 普通の rotation (quaternion), translation loss
● Depth Map Loss
○ berHu Loss [L.Zwald+,arXiv12] が単純なL2ノルムよりも良い
26
27. Dataset
● ScanNet
○ large-scale indoor dataset with 1513 sequences in
706 different scenes
■ training: 1413 sequences (547991 images)
■ testing: 100 sequences (2000 images)
● KITTI
○ generated camera poses from LibVISO2
27
28. Quantitative Evaluation (on ScanNet)
● outperformed DeMoN[B.Ummenhofer+,CVPR17]
○ ours*, DeMoN* : trained on SUN3D dataset
○ 別データ(SUN3D)で trained したモデルでも DeMoN を上回る
● outperformed also geometric/photometric BA
○ geometric BA が苦手な indoor scenes (テクスチャが貧しい) に有効な特徴
を学習できた
○ photometric BA よりも凸性の高い特徴が有効だった
28
29. 30. Qualitative Evaluation (on KITTI)
● unsupervised [Wang+,CVPR18], supervised
[Godard+,CVPR17] 両方を outperformed
30
[Wang+,CVPR18] Learning depth from monocular videos using direct methods.
[C. Godard+,CVPR17] Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency.
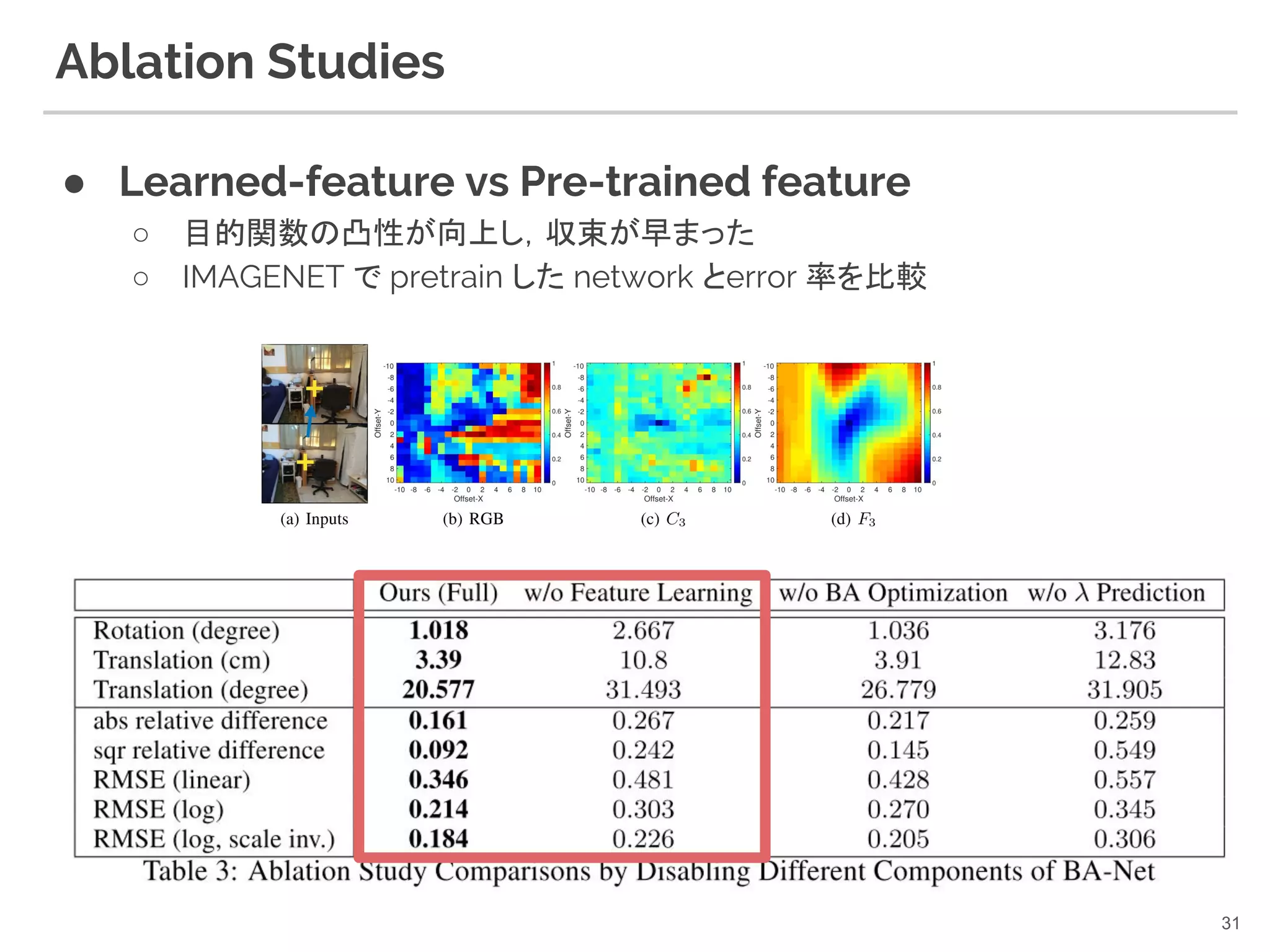
31. 32. Ablation Studies
● BA-layer vs pose estimation
○ fixed depth map に対し pose estimation をした結果と比較
○ BA-layer (jointly optimize depth and camera pose) が優位
● to make the comparison fair:
○ どちらも learned-feature F を用いる
32
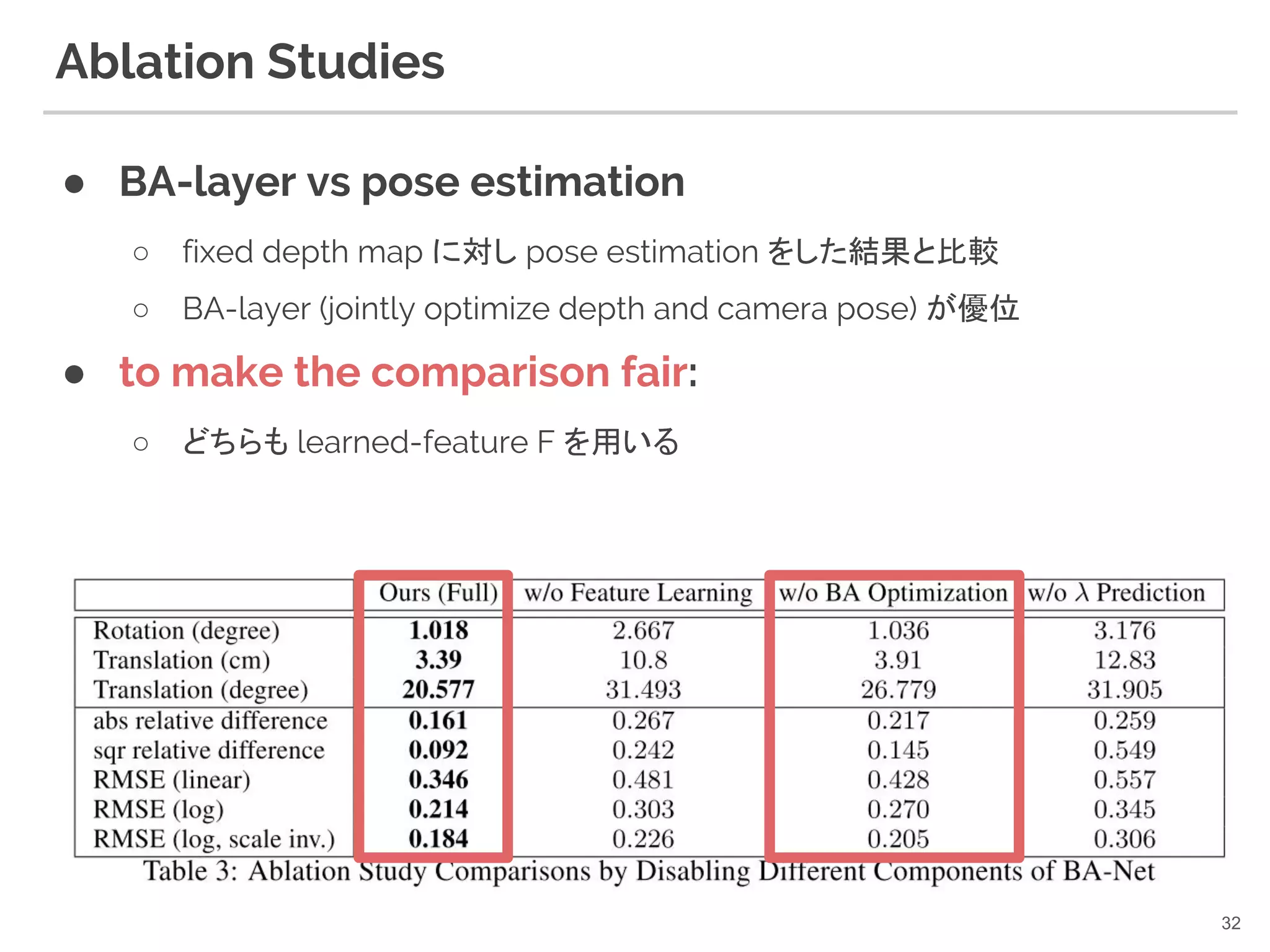
33. Ablation Studies
● Differentiable LM vs Damped gauss newton
○ λ=prefixed な damped gauss newton 法との比較
■ CodeSLAM[CVPR18] で利用
○ λが固定な方法に比べて,λを推論しつつ update する BA-Net の結果が大き
く上回る
● Again, for fair comparison,
○ 両方で learned-feature F を利用
33
34. Conclusion
● Contributions:
○ SfM に適した特徴 を 自動獲得する feature BA を提案
○ LM法を differentiable に変形した BA-layer を提案
○ learned-feature representation + depth parametrization + BA
optimization をend-to-end で行うことが可能になった
● Future work
○ multi-view extension
■ 本論文では two-view の検証のみ
■ 1 camera 1 network (intrinsic parameter に相当する特性を内包)
■ 原理上は easily extensible
34
35. Learning to solve NLLS [R.Clark+,ECCV18] との比較
● LS-Net: Learning to Solve Nonlinear Least Squares for Monocular Stereo
○ CodeSLAM [R.Clark+,CVPR18] グループの成果
○ gauss-newton の optimizer 自体を学習する(meta-learning)
● BA-Net: Dense Bundle Adjustment Network
○ LM法をNNで実装
35
Appendix
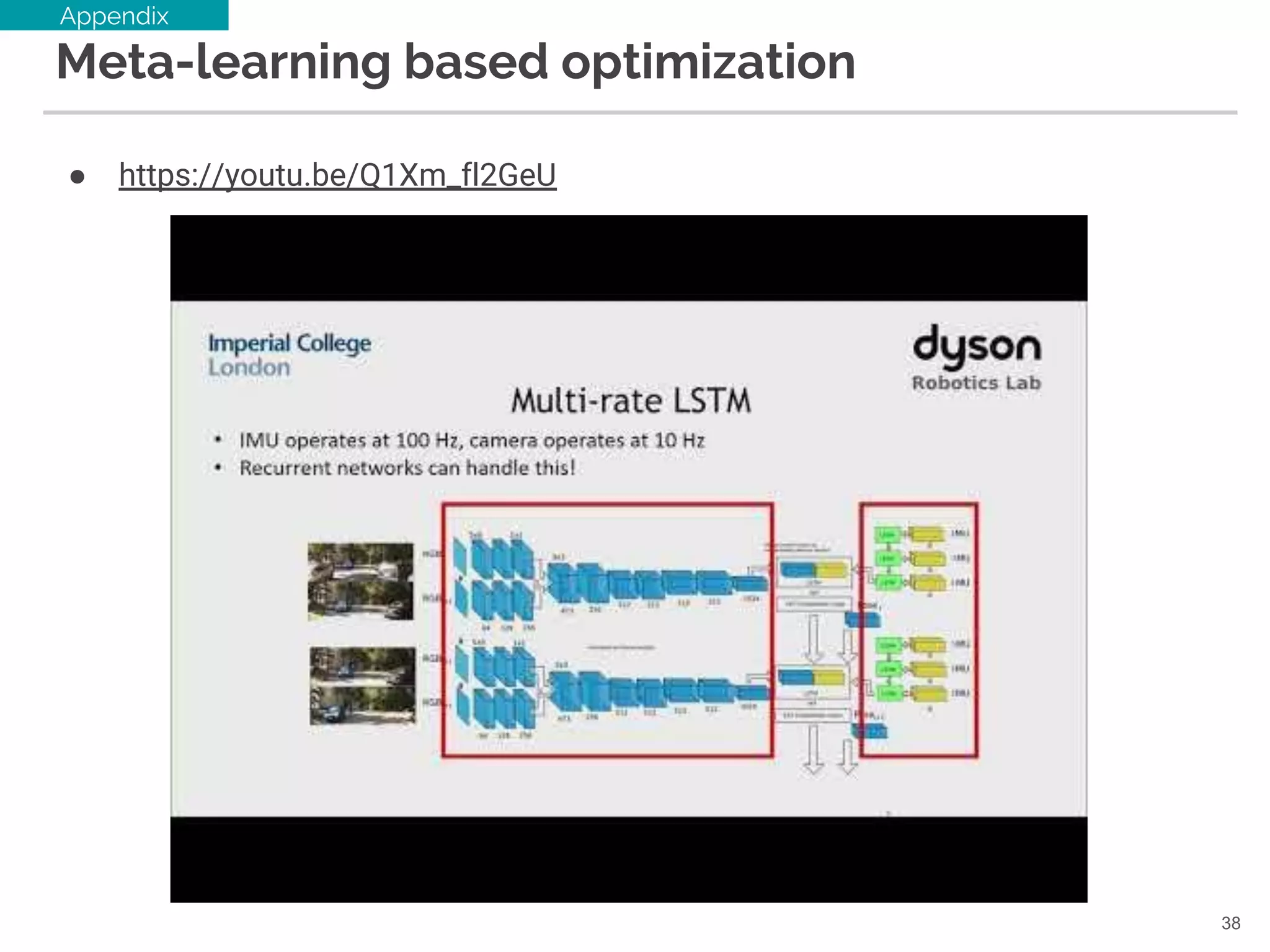
36. Meta-learning
● Learning to learn gradient descent by gradient descent [NIPS16]
○ https://github.com/deepmind/learning-to-learn
○ Optimizer を用いて(SGDとか)Optimizer 自体を学習する
36
Appendix
データに応じて,最適な g を学習できる!(はず)
なんだこの絵は...
37. Learning to solve NLLS [R.Clark+,ECCV18] との比較
● LS-Net: Learning to Solve Nonlinear Least Squares for Monocular Stereo
● BA-Net: Dense Bundle Adjustment Network
37
Appendix
Jacobian,残差を入力とする optimizer 自体をRNN-LSTM で学習
λのみNNで表現し,LM法は計算グラフとして実装
38. 39.
![about.me
@denkiwakame
● 〜2015 京都大学 松山研究室(B4〜M2)
● 〜2017 某企業研
● 2017〜 都内ベンチャー
Interests
● Generalized Camera Calibration [M.Nishimura+,ICCV15]
● MRF optimization (low-level vision)
● Model Compression
● GPGPU (CUDA),SIMD
● Quantum Computing
2
[M.Nishimura+, ICCV15] A Linear Generalized Camera Calibration from Three Intersecting
Reference Planes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-2-2048.jpg)


![CodeSLAM [M.Bloesch+,CVPR18]
● VAE によって depth の圧縮表現(code)を得る
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-5-2048.jpg)
![CodeSLAM [M.Bloesch+,CVPR18]
● VAE によって depth の圧縮表現(code)を得る
6
● Pose (R,t) - depth optimization が解ける
○ gauss-newton 法で最適化(ヤコビアンが計算できる)
〜128dim
parametrized depth
pose
photometric error
geometric error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-6-2048.jpg)
![depth parametrization
CodeSLAM [M.Bloesch+,CVPR18]
● pose / depth estimation は BAと独立
○ joint optimization の結果が VAE に feedback されることはない
7
Bundle Adjustment / GN
(pose-geo optimization)
camera pose estimation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-7-2048.jpg)
![Bundle Adjustment - historical overview
● [T.Bill+,VA99] Bundle Adjustment - a modern
synthesis
10
Triggs, Bill, et al. "Bundle adjustment—a modern synthesis." International workshop on vision
algorithms. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1999. (鉄板)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-10-2048.jpg)

![● Feature learning for SfM (2-view setting)
○ BA-Net の minor contribution
Network overview - feature & depth learning
15
depth parametrization
sub-network
feature pyramid
network
base-network
[F.Yu+,CVPR17]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-15-2048.jpg)
![● Difficulties:
○ LM法の反復解法は収束閾値に達すると打ち切り
■ 条件分岐を含む非連続関数になってしまう(微分不能)
○ 各反復試行において,目的関数に応じ λ を操作
■ E(x) が減少するまでλを大きくし続ける(減少した際にλを小さくする)
■ 条件分岐(ry
● Simple yet effective approach
○ 固定回数の反復を実装する (※)
○ lambda を network で推論
Differentiable LM layer
21
※ [J.Domke+, AISTATS12] Generic Methods for Optimization-Based Modeling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-21-2048.jpg)
![Differentiable LM layer
● Coarse-to-fine optimization
○ LSD-SLAM [J.ENgel+,ECCV14] や DSO
[J.Engel+,TPAMI17] と同様,Coarse-to-fine BA を適用
○ feature pyramid の各 layer で 5-iteration
○ 計 15-iteration を 1回の forward-pass で反復
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-24-2048.jpg)
![関連:CRF as RNN
● Semantic Segmentation において, 後段に平均場近似
(mean-field approximation)の手続きをRNNで実装
○ CRFの最適化は post-processing として当初分離されていた
○ RNN で 平均場近似を実装することにより,CRF の学習と最適化が1つのネッ
トワークで行えるようになった
25[S.Zheng+, ICCV15] Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Networks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-25-2048.jpg)
![Training Objective
● Camera Pose Loss
○ 普通の rotation (quaternion), translation loss
● Depth Map Loss
○ berHu Loss [L.Zwald+,arXiv12] が単純なL2ノルムよりも良い
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-26-2048.jpg)

![Quantitative Evaluation (on ScanNet)
● outperformed DeMoN[B.Ummenhofer+,CVPR17]
○ ours*, DeMoN* : trained on SUN3D dataset
○ 別データ(SUN3D)で trained したモデルでも DeMoN を上回る
● outperformed also geometric/photometric BA
○ geometric BA が苦手な indoor scenes (テクスチャが貧しい) に有効な特徴
を学習できた
○ photometric BA よりも凸性の高い特徴が有効だった
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-28-2048.jpg)
![Qualitative Evaluation (on ScanNet)
● DeMoN [B.Ummenhofer+,CVPR17] よりdepth が再現
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-29-2048.jpg)
![Qualitative Evaluation (on KITTI)
● unsupervised [Wang+,CVPR18], supervised
[Godard+,CVPR17] 両方を outperformed
30
[Wang+,CVPR18] Learning depth from monocular videos using direct methods.
[C. Godard+,CVPR17] Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-30-2048.jpg)
![Ablation Studies
● Differentiable LM vs Damped gauss newton
○ λ=prefixed な damped gauss newton 法との比較
■ CodeSLAM[CVPR18] で利用
○ λが固定な方法に比べて,λを推論しつつ update する BA-Net の結果が大き
く上回る
● Again, for fair comparison,
○ 両方で learned-feature F を利用
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-33-2048.jpg)

![Learning to solve NLLS [R.Clark+,ECCV18] との比較
● LS-Net: Learning to Solve Nonlinear Least Squares for Monocular Stereo
○ CodeSLAM [R.Clark+,CVPR18] グループの成果
○ gauss-newton の optimizer 自体を学習する(meta-learning)
● BA-Net: Dense Bundle Adjustment Network
○ LM法をNNで実装
35
Appendix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-35-2048.jpg)
![Meta-learning
● Learning to learn gradient descent by gradient descent [NIPS16]
○ https://github.com/deepmind/learning-to-learn
○ Optimizer を用いて(SGDとか)Optimizer 自体を学習する
36
Appendix
データに応じて,最適な g を学習できる!(はず)
なんだこの絵は...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-36-2048.jpg)
![Learning to solve NLLS [R.Clark+,ECCV18] との比較
● LS-Net: Learning to Solve Nonlinear Least Squares for Monocular Stereo
● BA-Net: Dense Bundle Adjustment Network
37
Appendix
Jacobian,残差を入力とする optimizer 自体をRNN-LSTM で学習
λのみNNで表現し,LM法は計算グラフとして実装](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ba-netpub-181207190341/75/BA-Net-Dense-Bundle-Adjustment-Network-3D-37-2048.jpg)