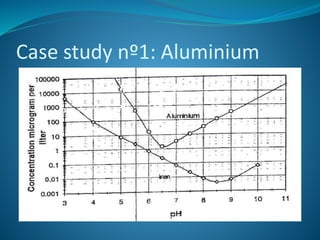
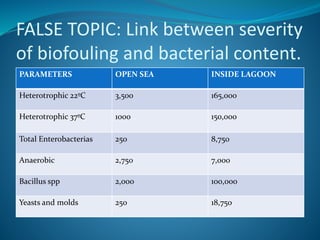
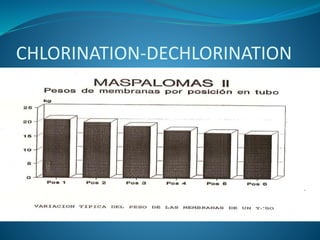
This document discusses various case studies of fouling issues in reverse osmosis plants. It examines cases where fouling was incorrectly diagnosed as biological when it was actually due to inorganic causes like aluminum or iron. It also explores the link between bacterial content and biofouling severity, finding no clear relationship. The document advocates avoiding chlorination and other chemical additions, and stresses keeping water flowing during shutdowns to prevent fouling issues.