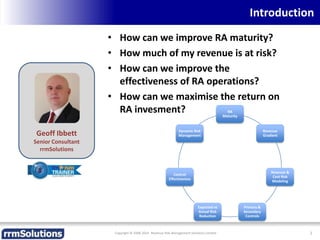
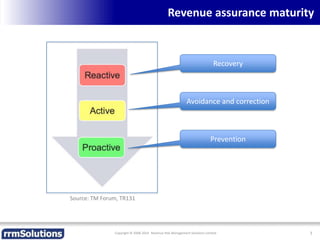
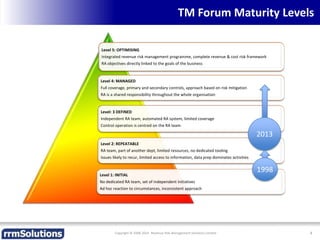
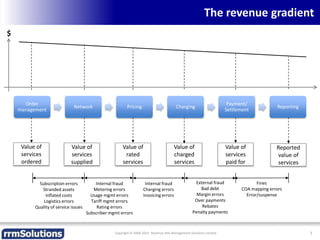
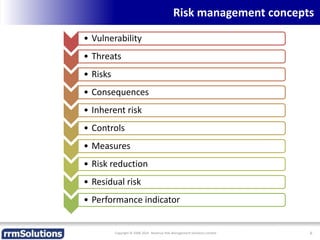
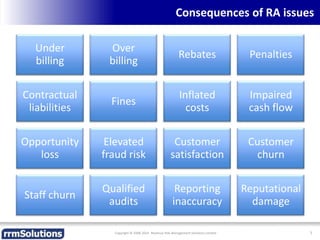
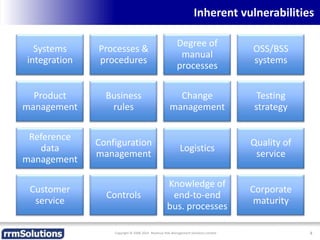
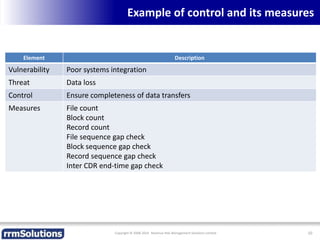
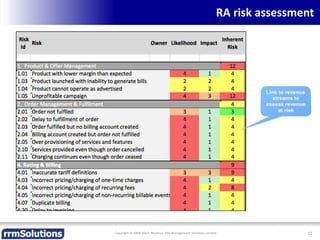
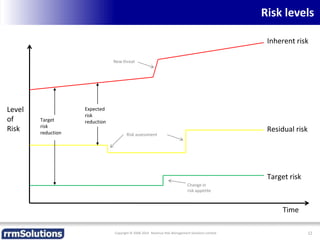
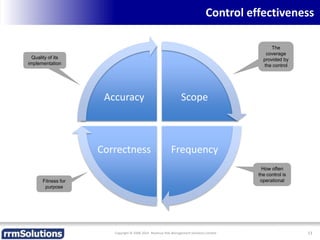
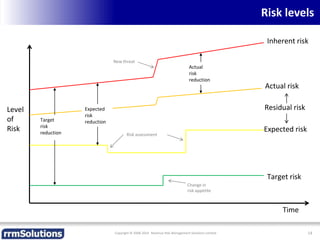
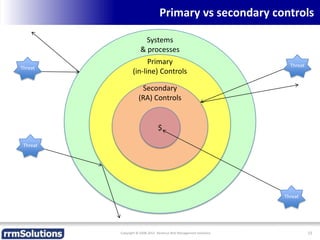
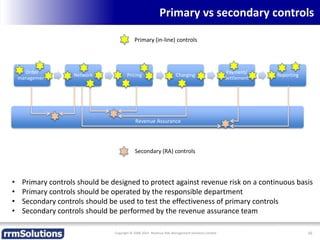
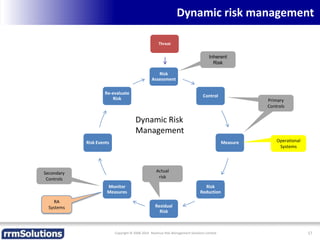
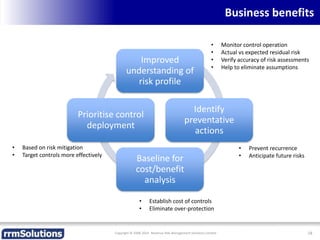
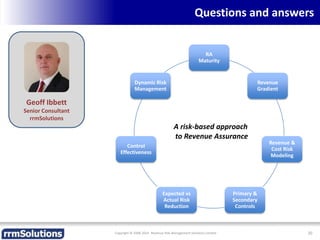
The document discusses the importance of enhancing revenue assurance (RA) maturity by implementing risk management techniques. It outlines various maturity levels of revenue assurance and emphasizes a shift towards preventative actions and dynamic risk management, where both primary and secondary controls are crucial. The document concludes that more effective automation and targeted investment in RA initiatives are necessary for improved performance and effectiveness.