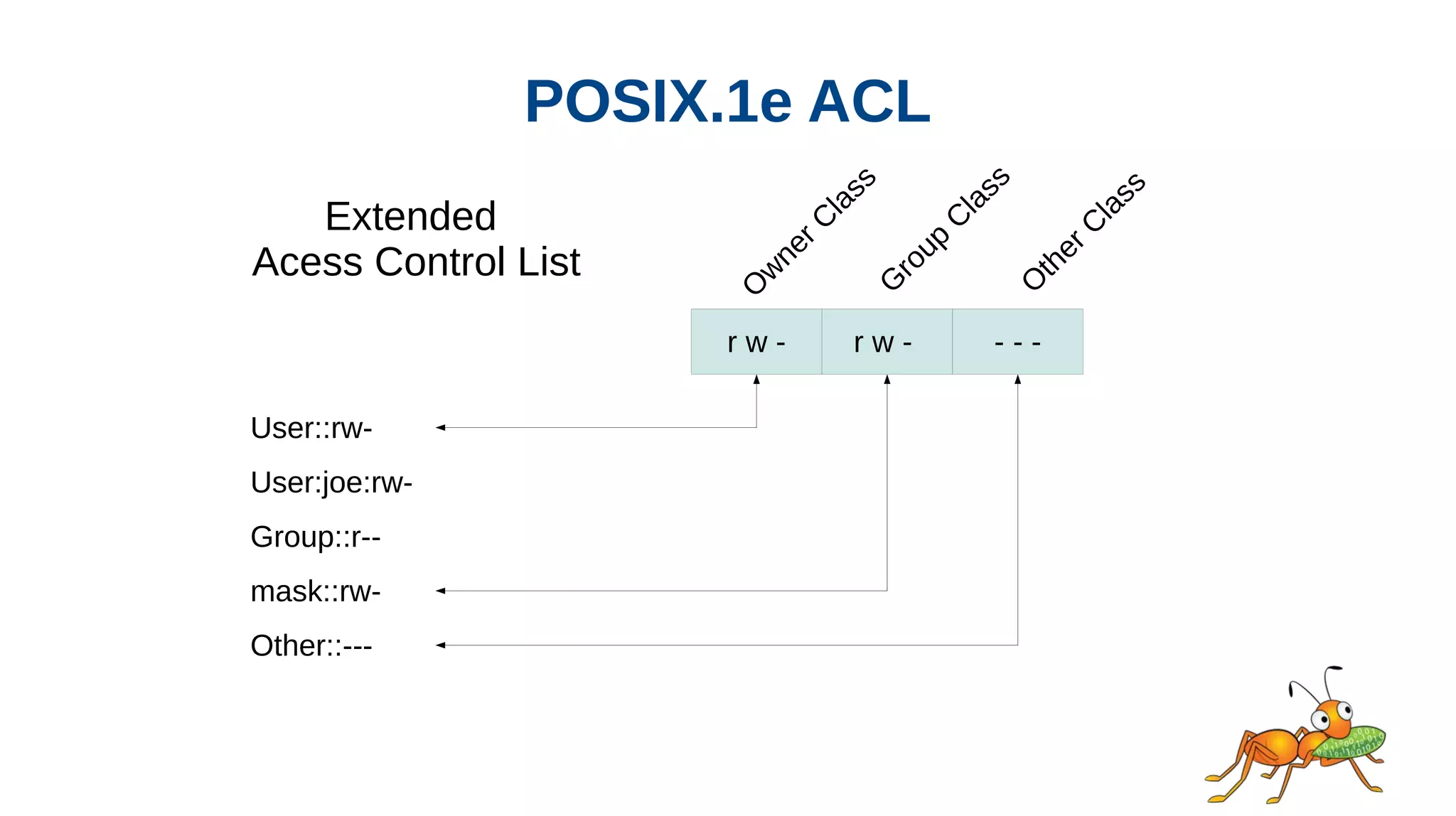
This document discusses access control lists (ACLs) and how GlusterFS supports them. It describes Unix permissions, POSIX ACLs, Windows ACLs, NFSv4 ACLs, and RichACL. RichACL supports more granular permissions than POSIX ACLs and can represent NFSv4 and Windows ACLs. The document outlines challenges for GlusterFS in supporting RichACL, such as needing to convert existing ACLs and limited extended attribute size. It was presented by Rajesh Joseph from the GlusterFS development team.