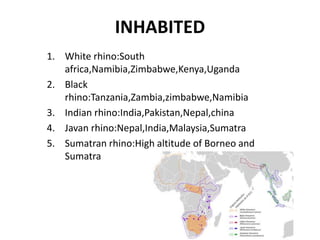
This document summarizes information about rhinos. It describes the 5 species of rhino, their habitats in Africa and Asia, physical characteristics like thick skin and one or two horns, and solitary behavioral patterns with territorial aggression. Diet is described as herbivorous with grazing on grass and leaves. Breeding involves long gestation, and males mature later than females. Threats include poaching for horns and infectious diseases like tuberculosis. The document provides scientific classifications and compares male and female physical attributes. Restraining techniques and tools are also outlined.