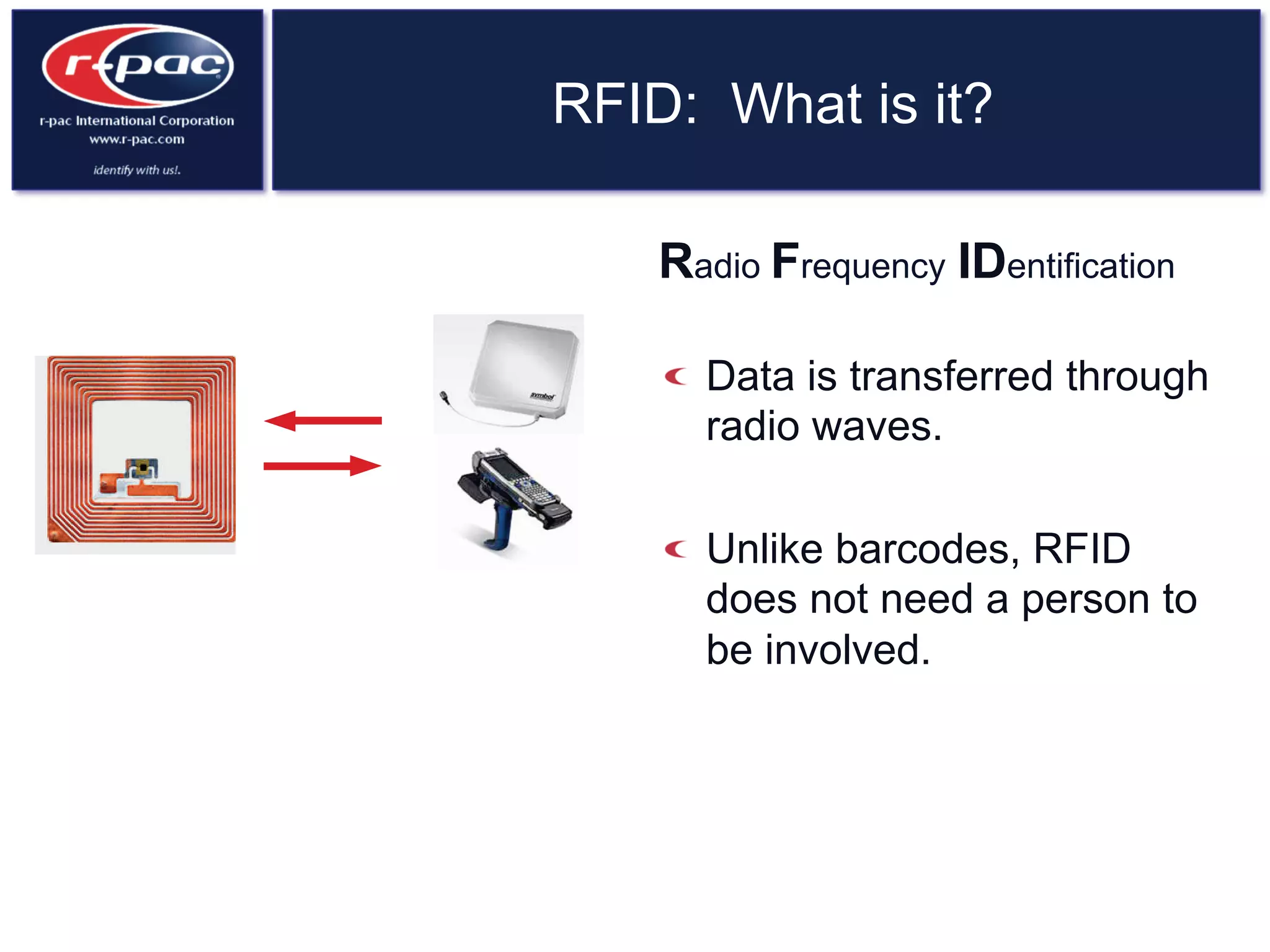
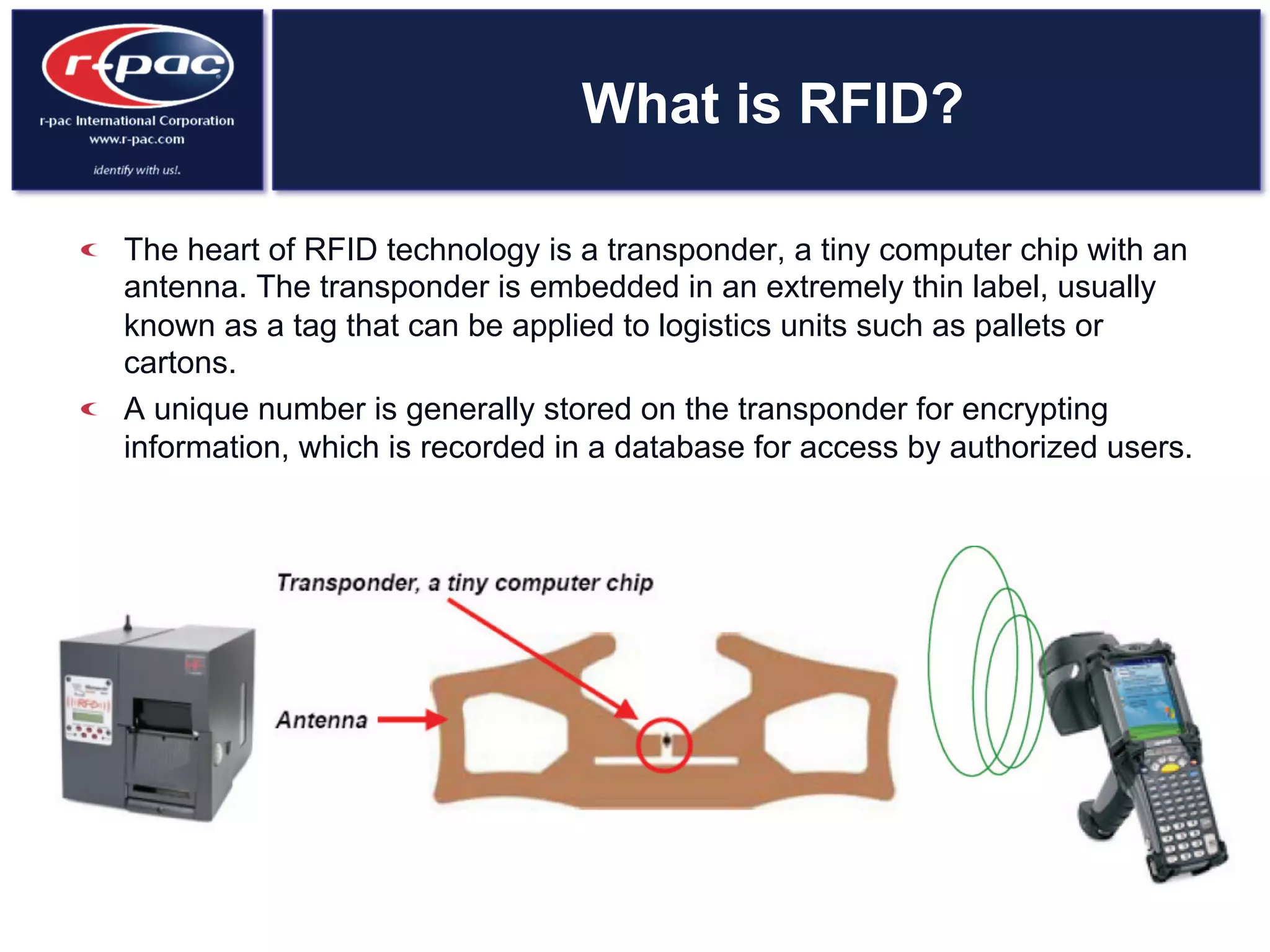
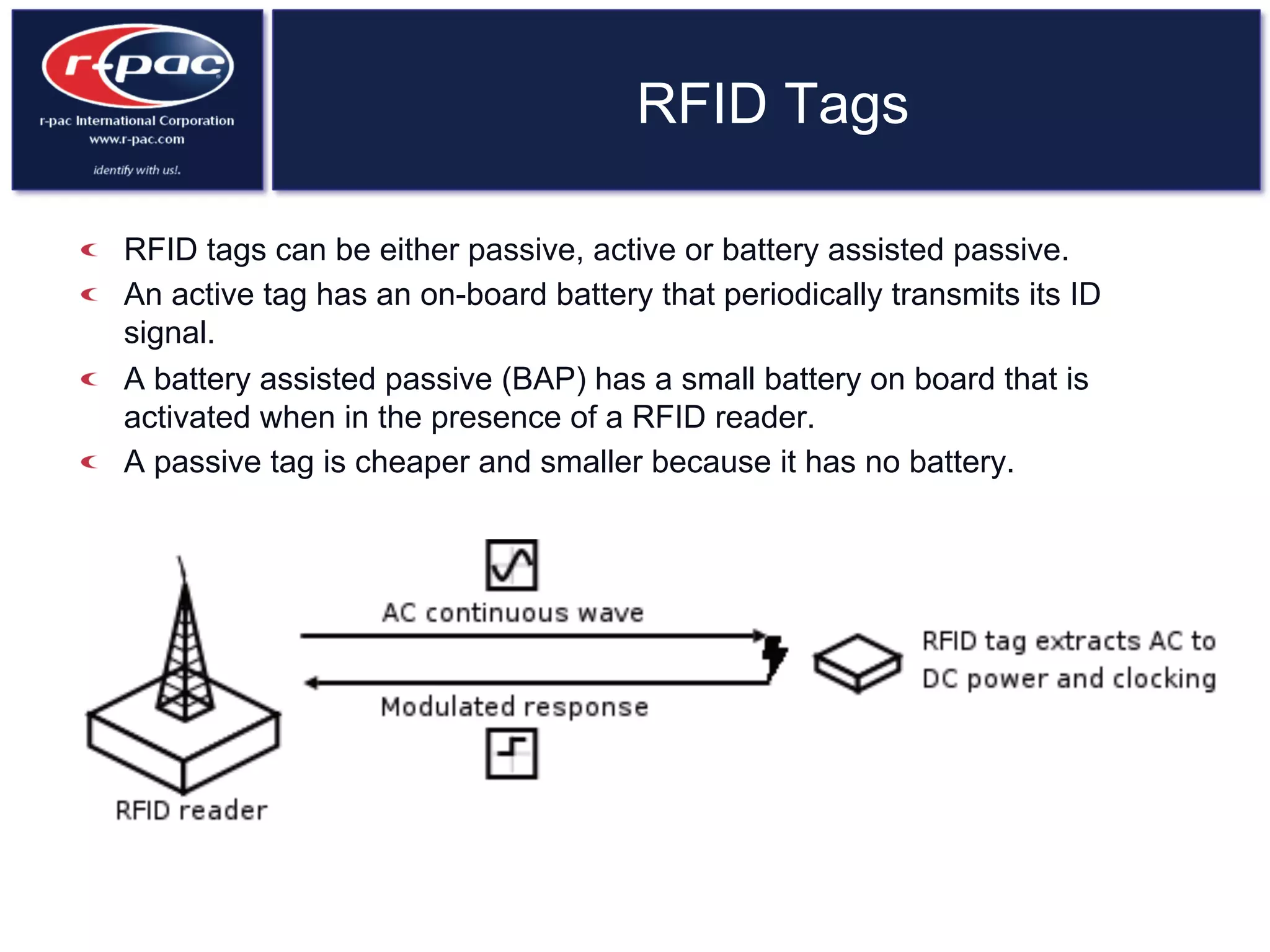
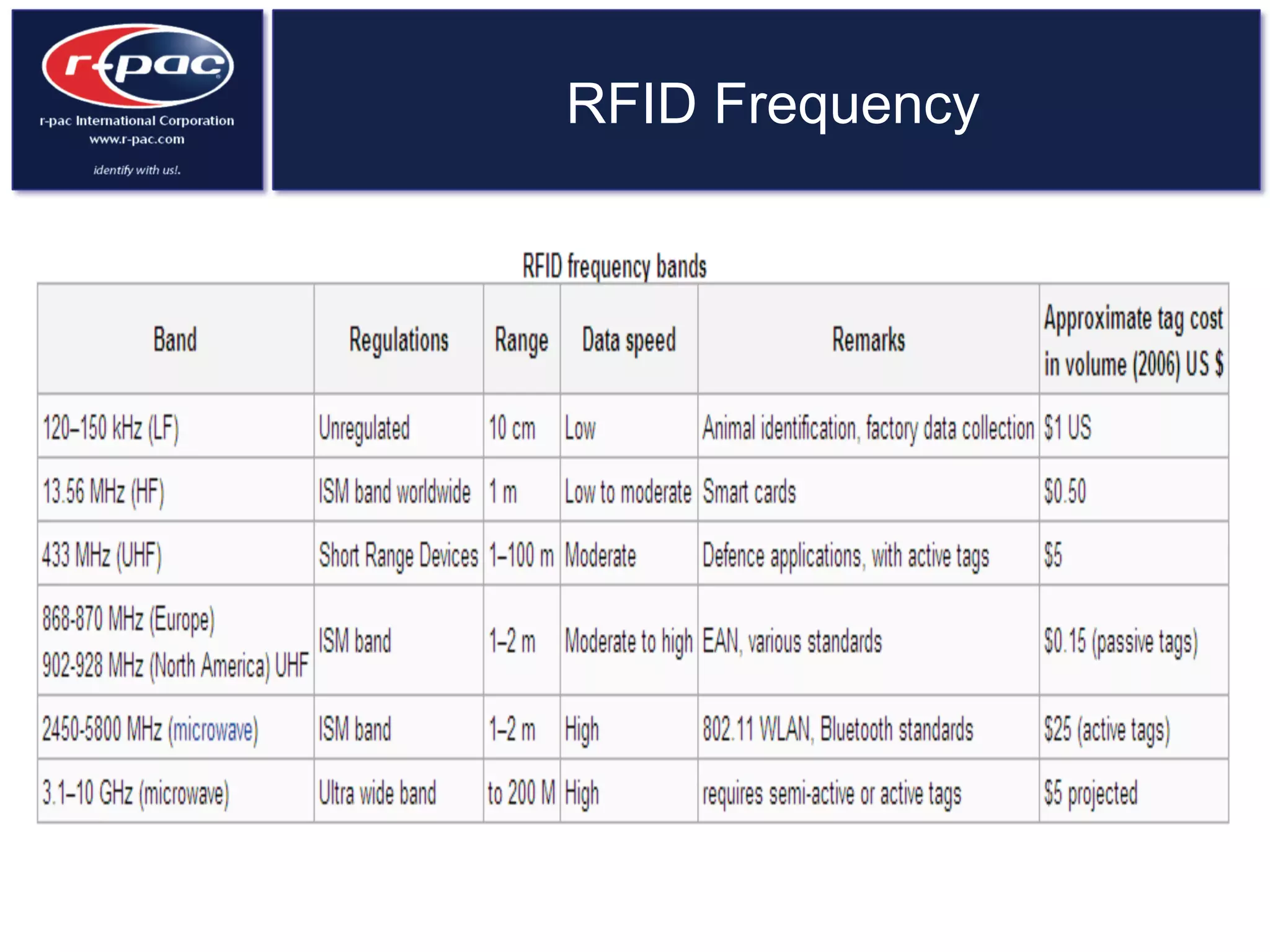
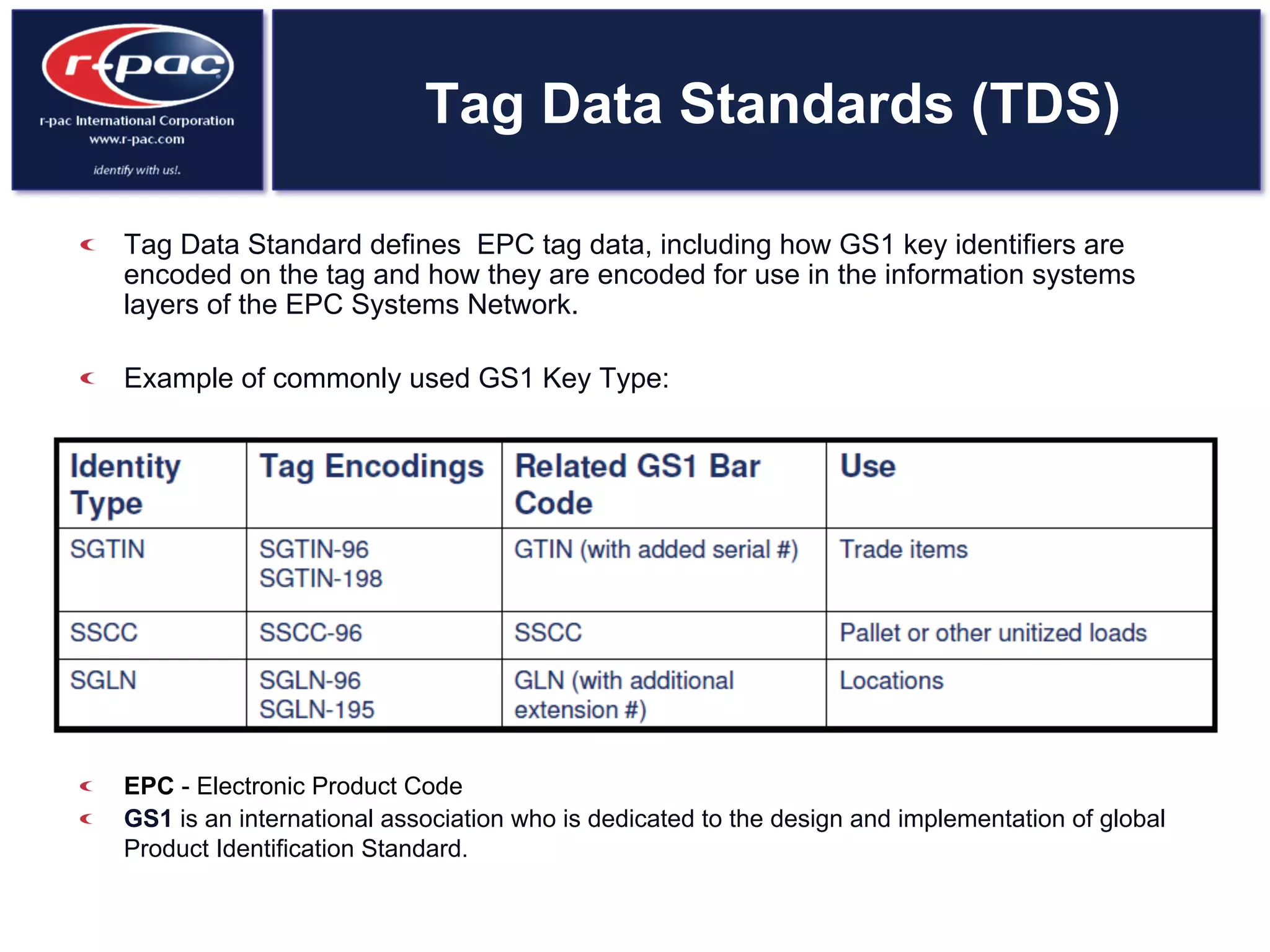
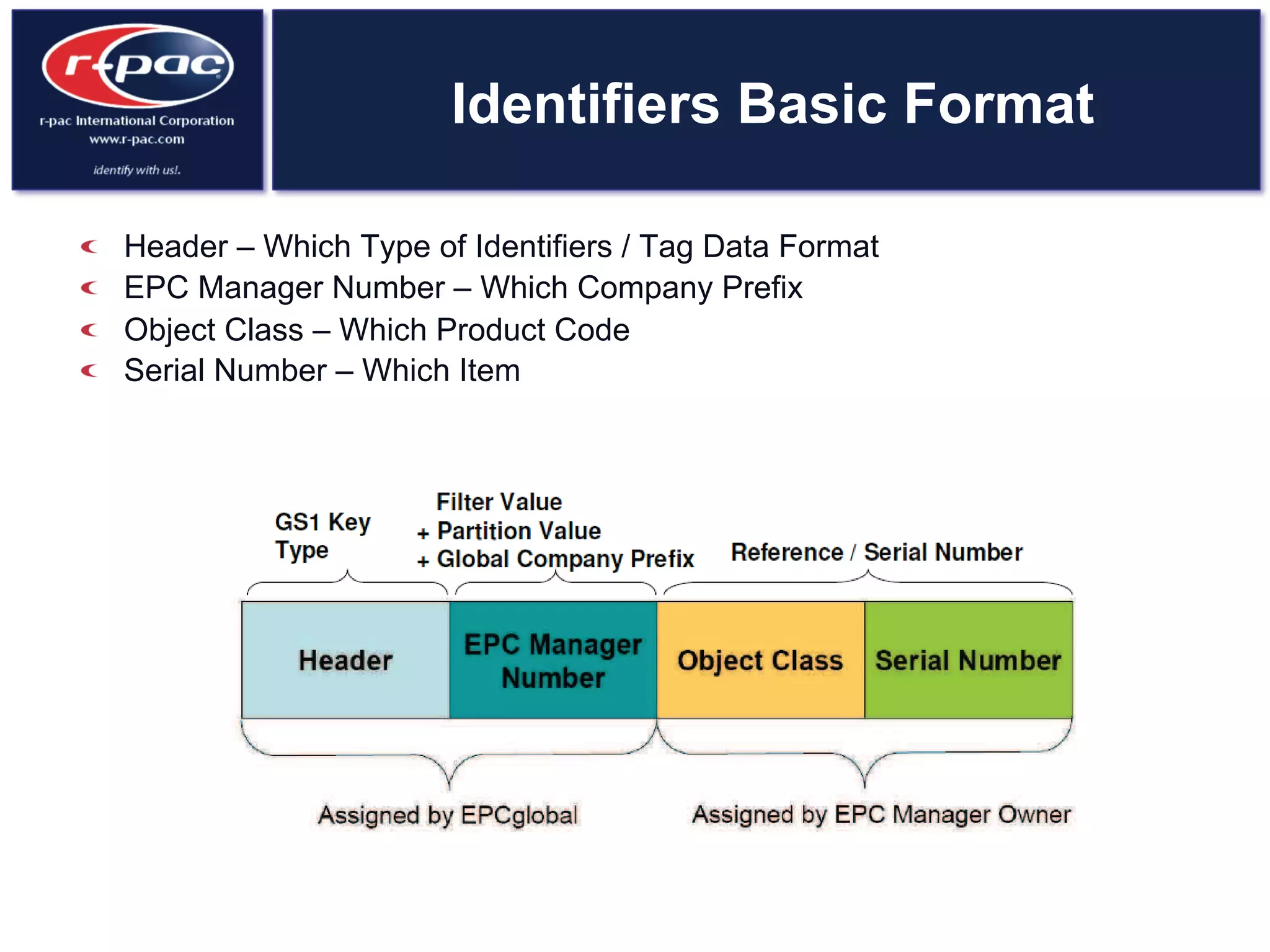
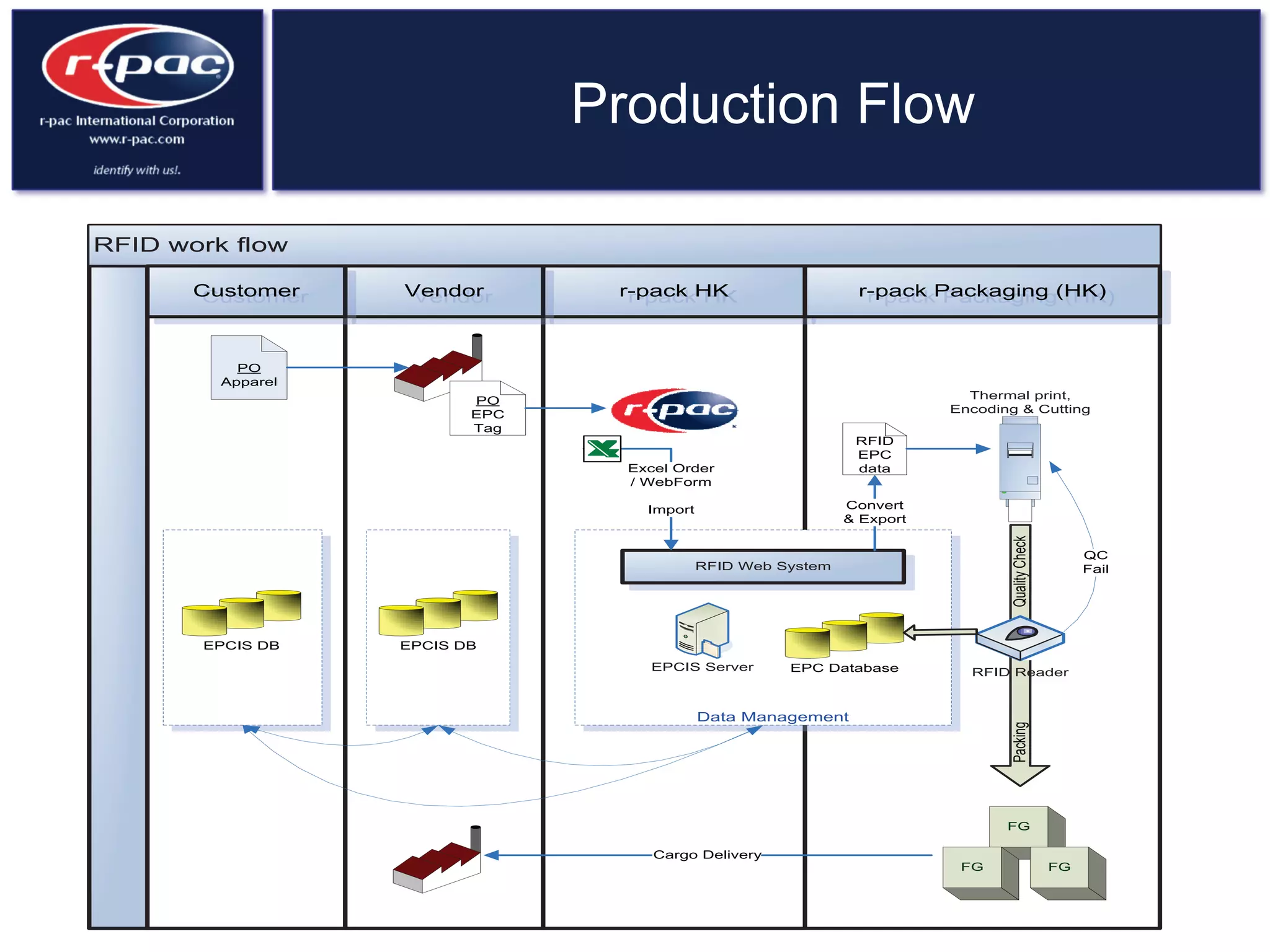
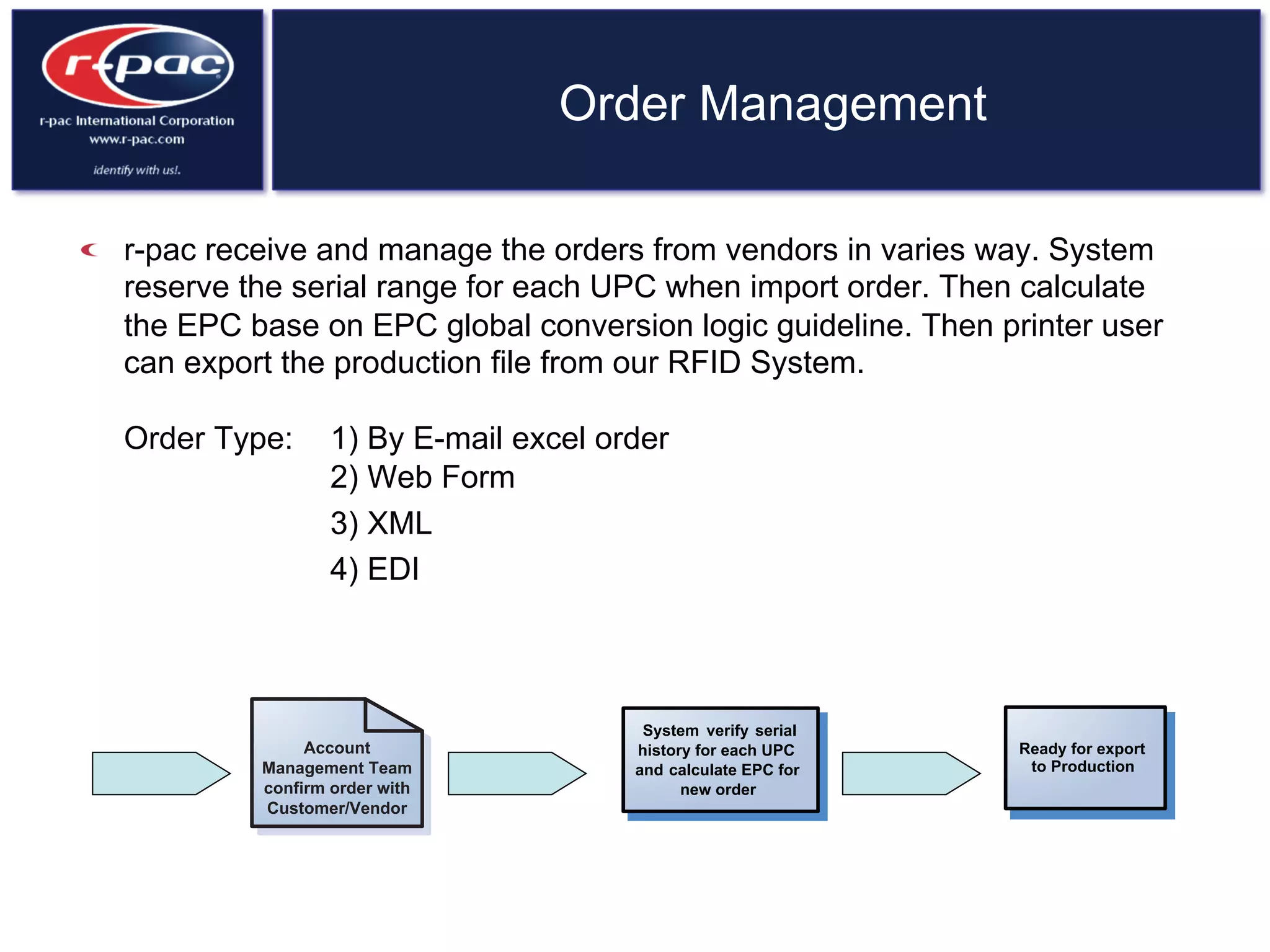
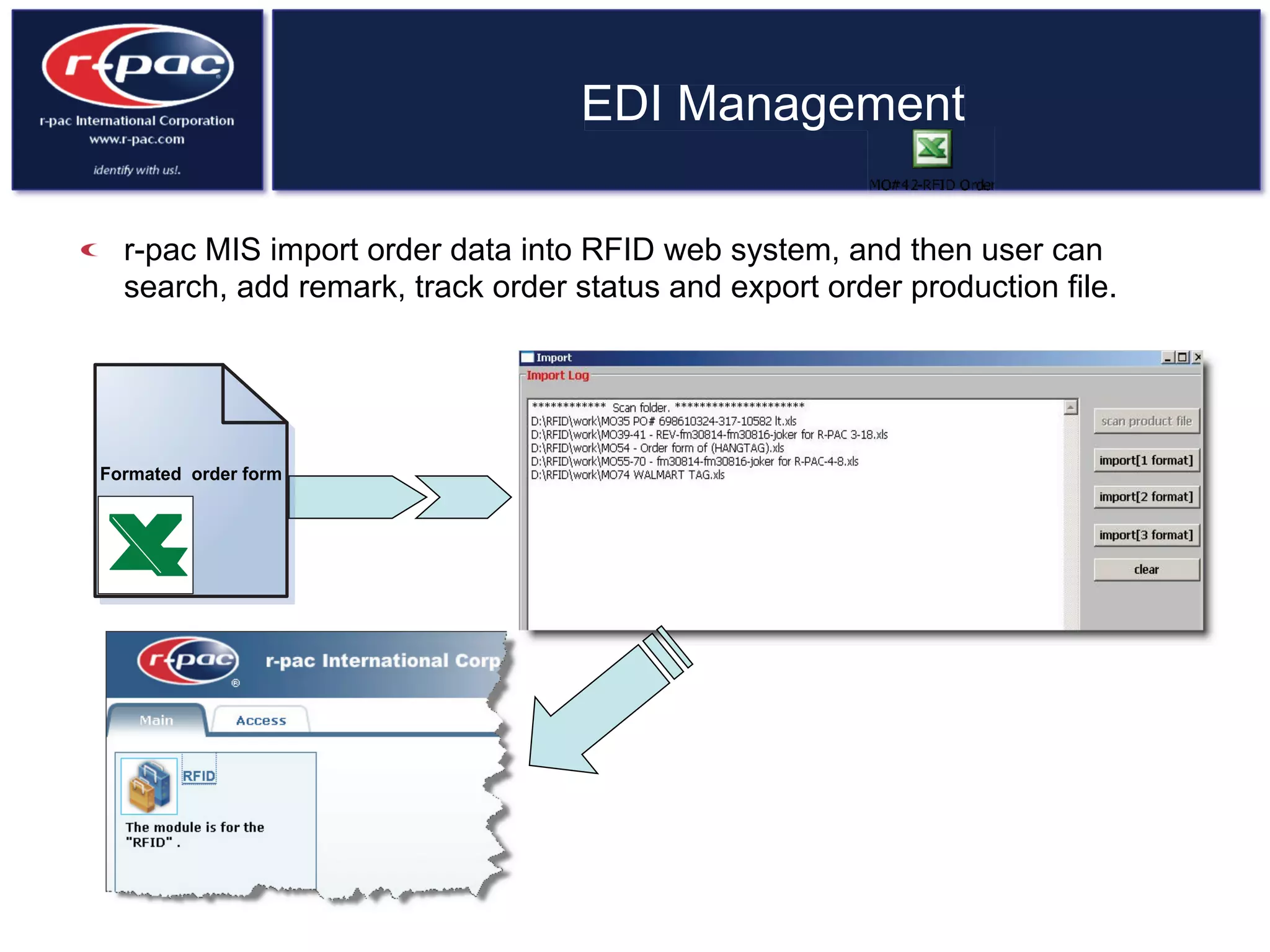
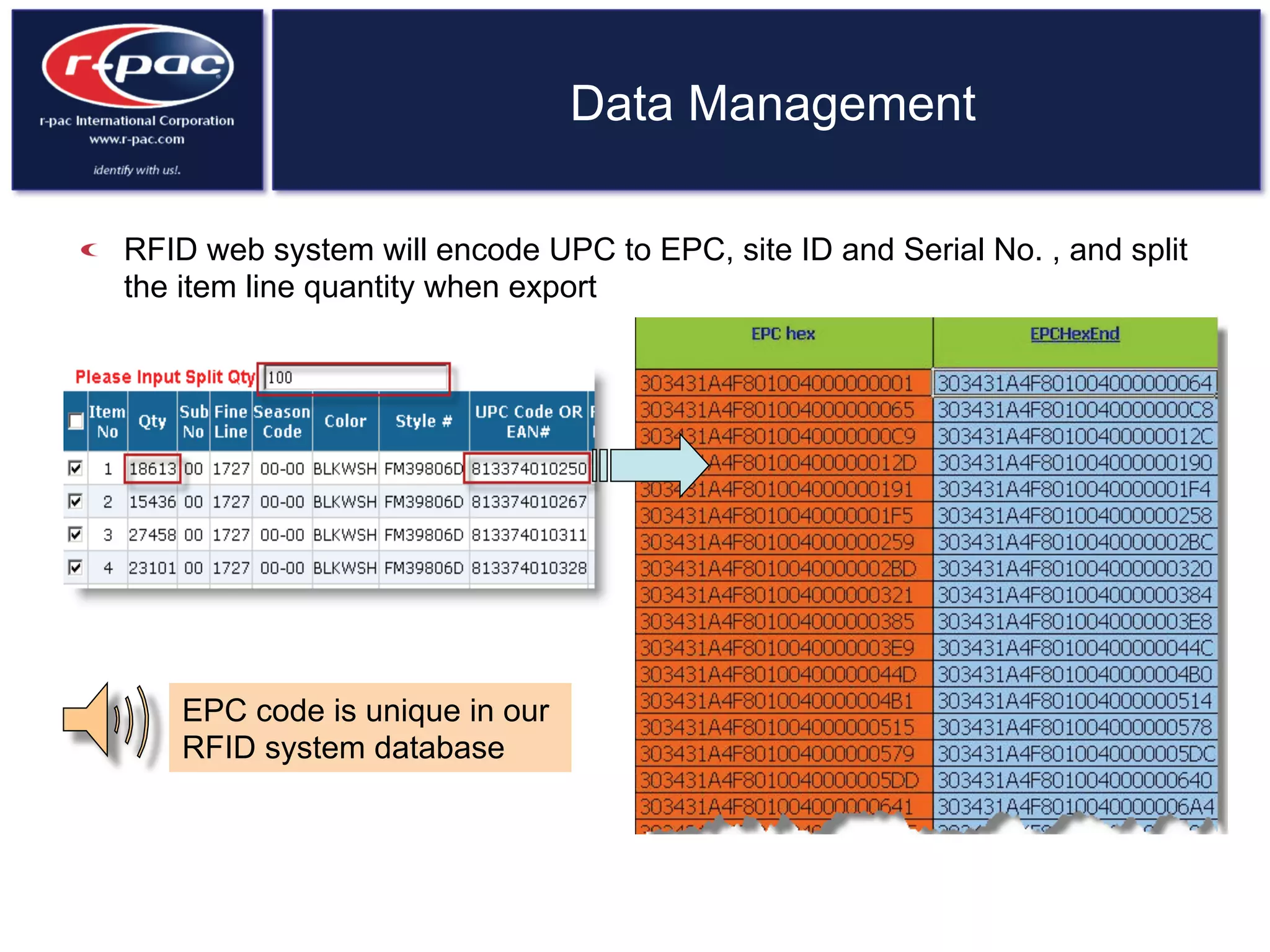
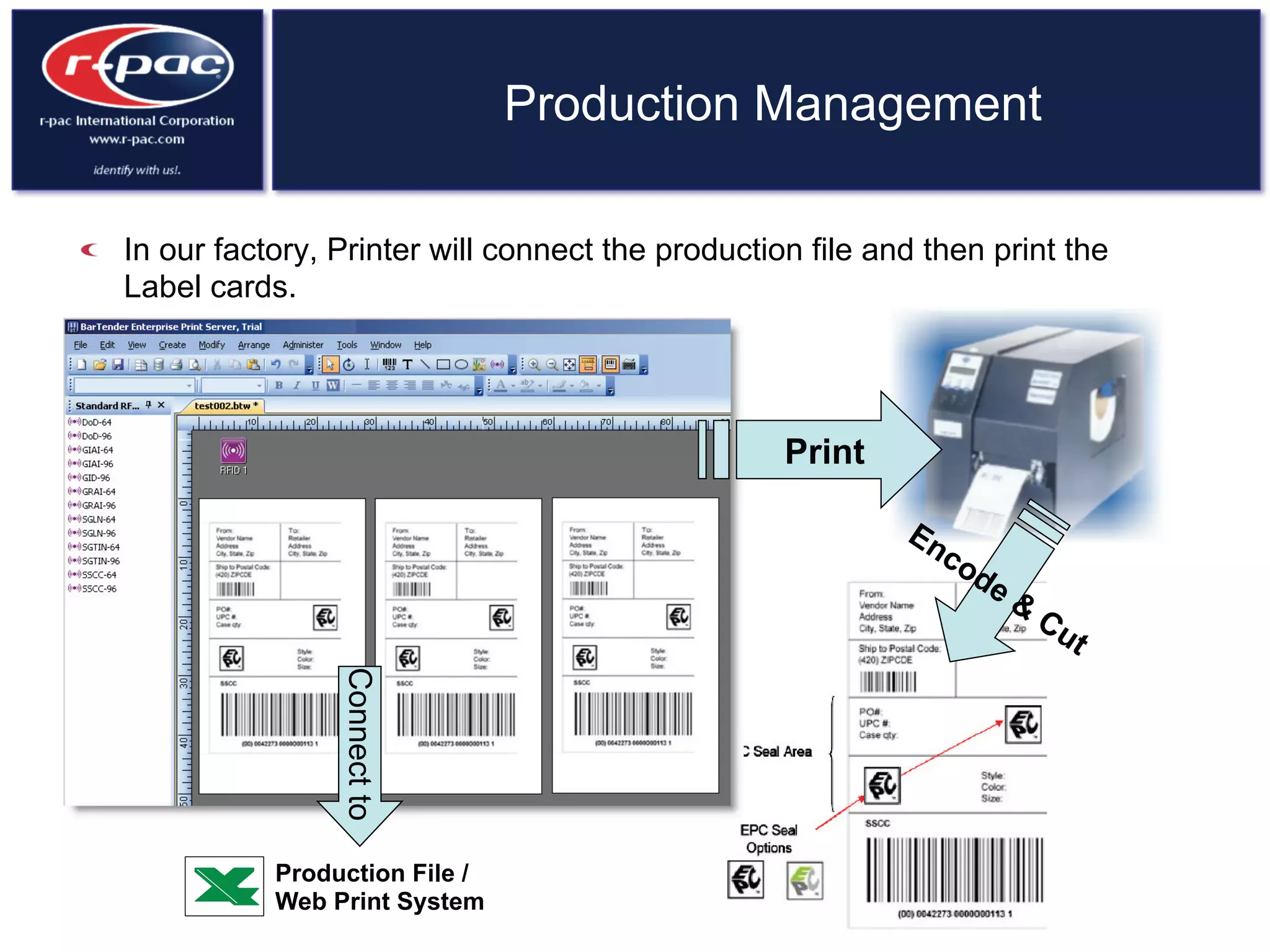
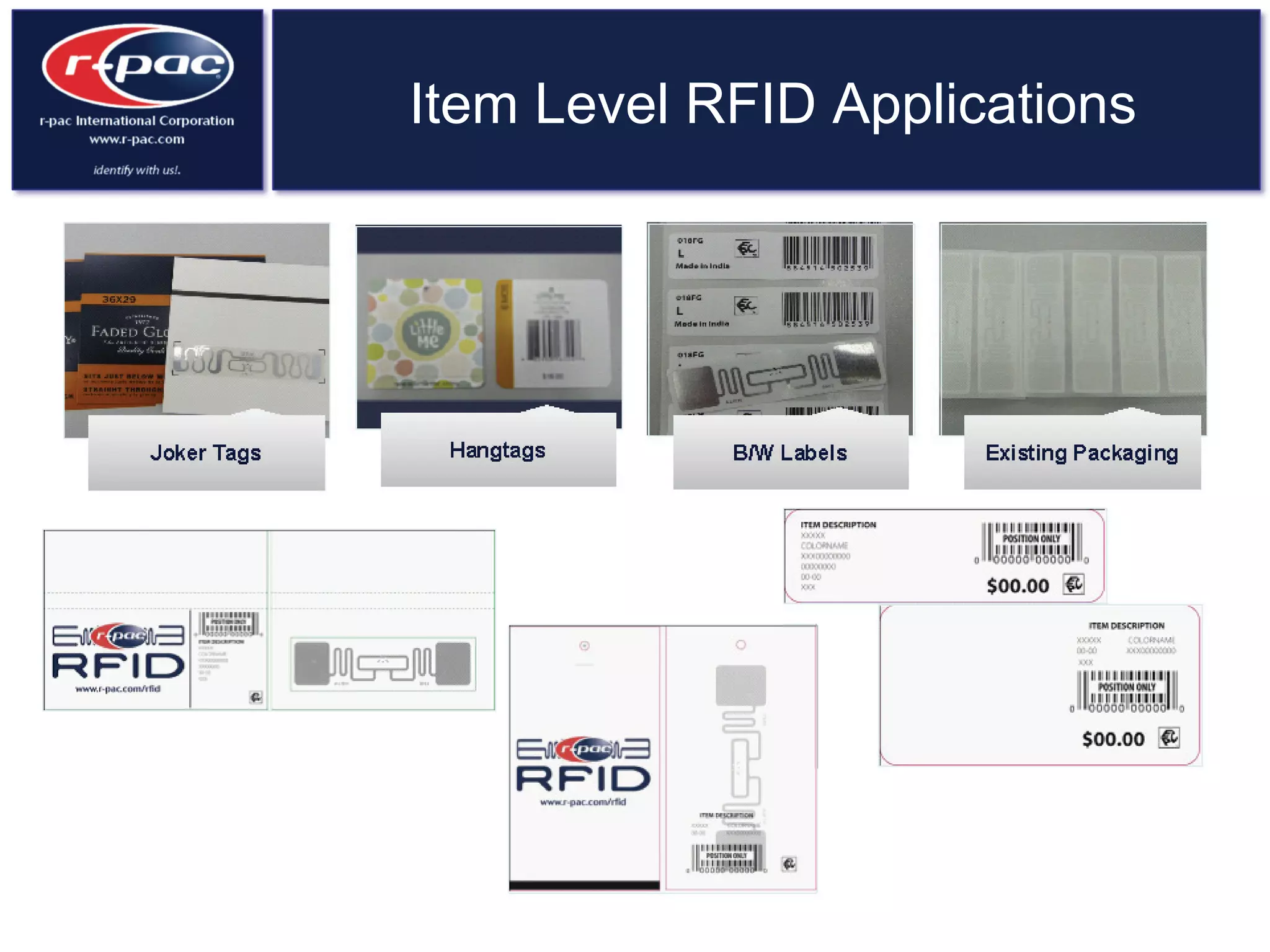
This document provides an overview of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology. It discusses how RFID works by transferring data through radio waves without needing direct contact, unlike barcodes. The document traces the history of RFID from its origins in tracking airplanes in World War 2 to its increasing use by businesses and governments from the 1980s onward to track inventory. Finally, it describes how RFID is used now across various industries to track assets, equipment, materials, products, personnel and more through the use of RFID tags and readers.