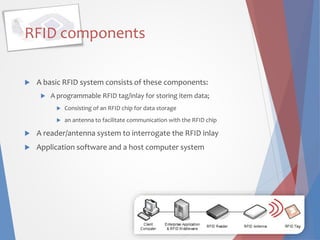
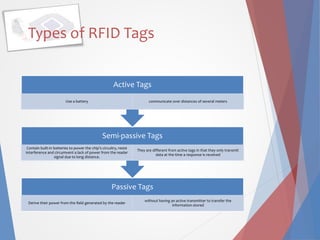
This document discusses RFID (radio frequency identification) technology, including its components, types of tags, and applications. The key components of an RFID system are RFID tags/inlays containing chips and antennas, readers/antennas, and application software. There are three main types of tags: passive tags which have no power source, semi-passive tags with batteries, and active tags with longer read ranges. Common applications mentioned include credit cards, electronic toll collection, supply chain/logistics tracking, and access control. The document also references an online survey about opinions on RFID and its further potential uses.