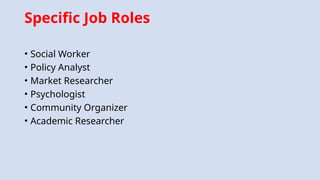
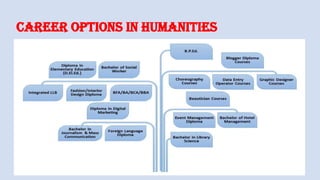
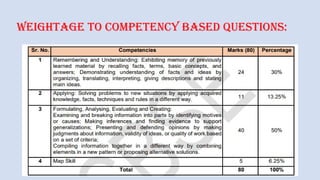
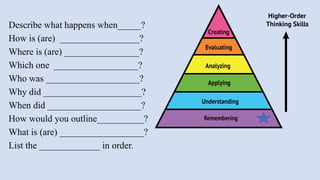
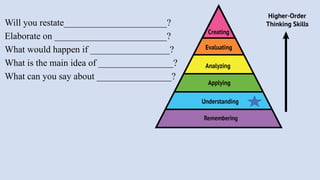
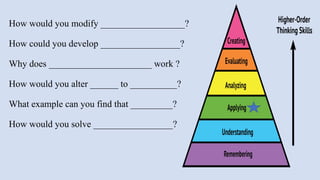
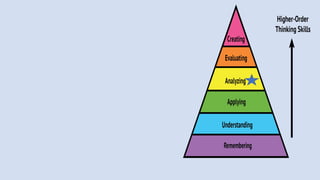
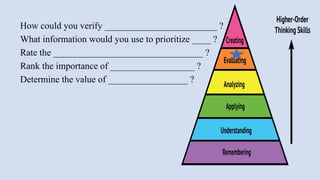
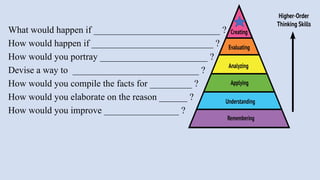
The document outlines a workshop on career guidance in social science aimed at secondary level educators in Bihar, scheduled for September 2024. It covers various career opportunities, job roles, and emerging fields in social science, as well as detailed strategies for competency-based assessments using Bloom's Taxonomy. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding the interconnection between biological diversity loss and cultural identity while suggesting methods for creating effective assessment questions.