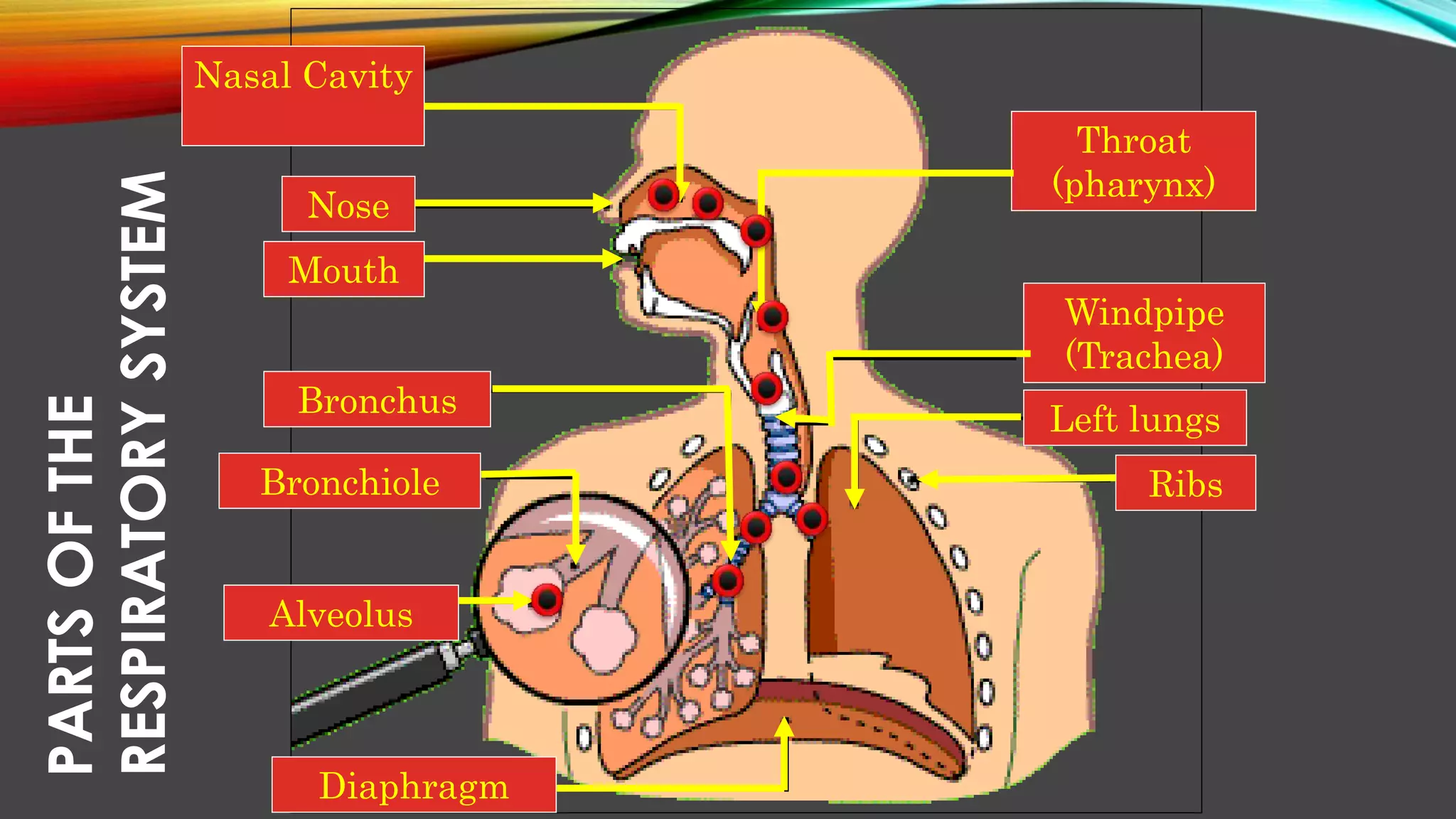
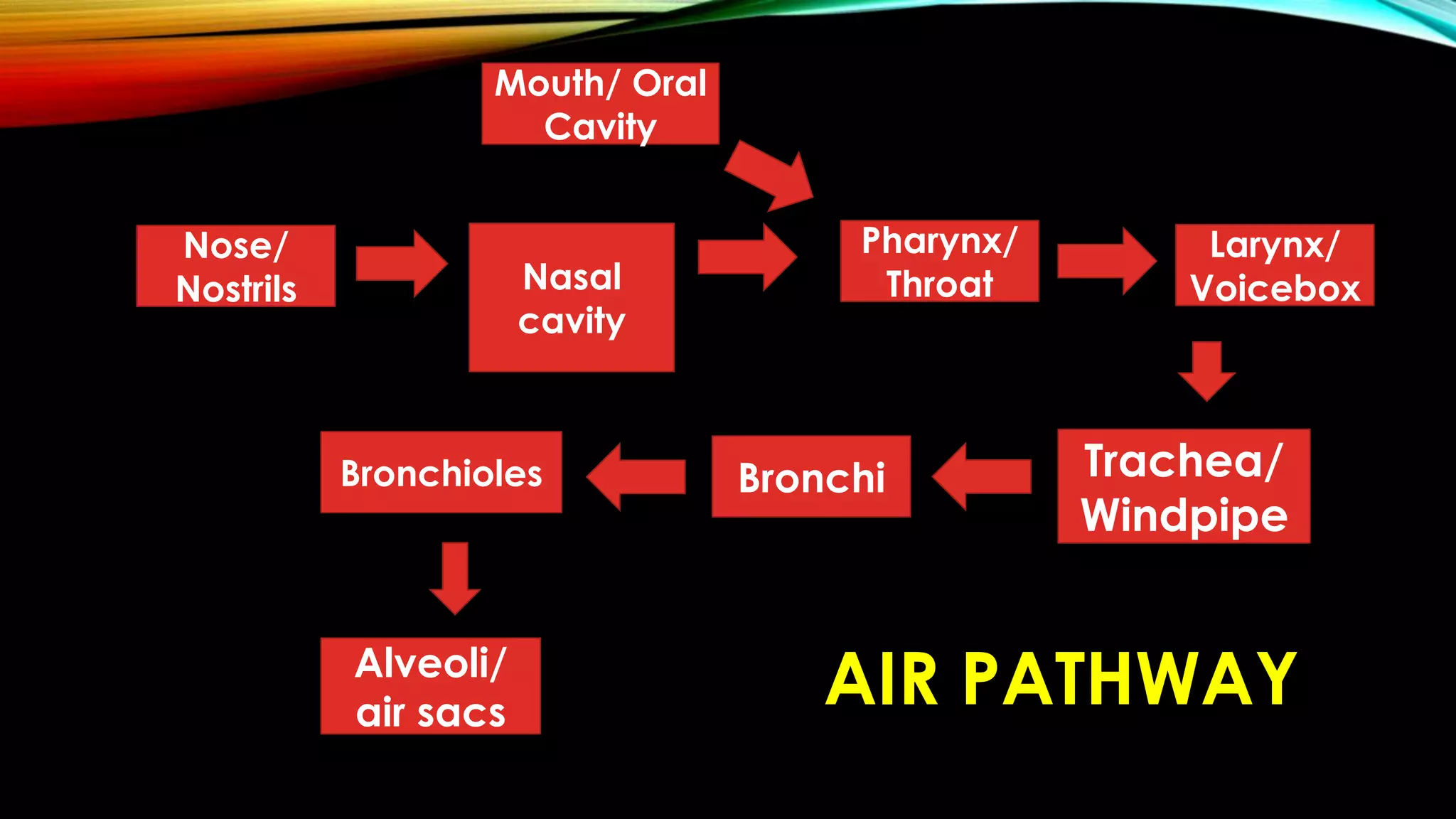
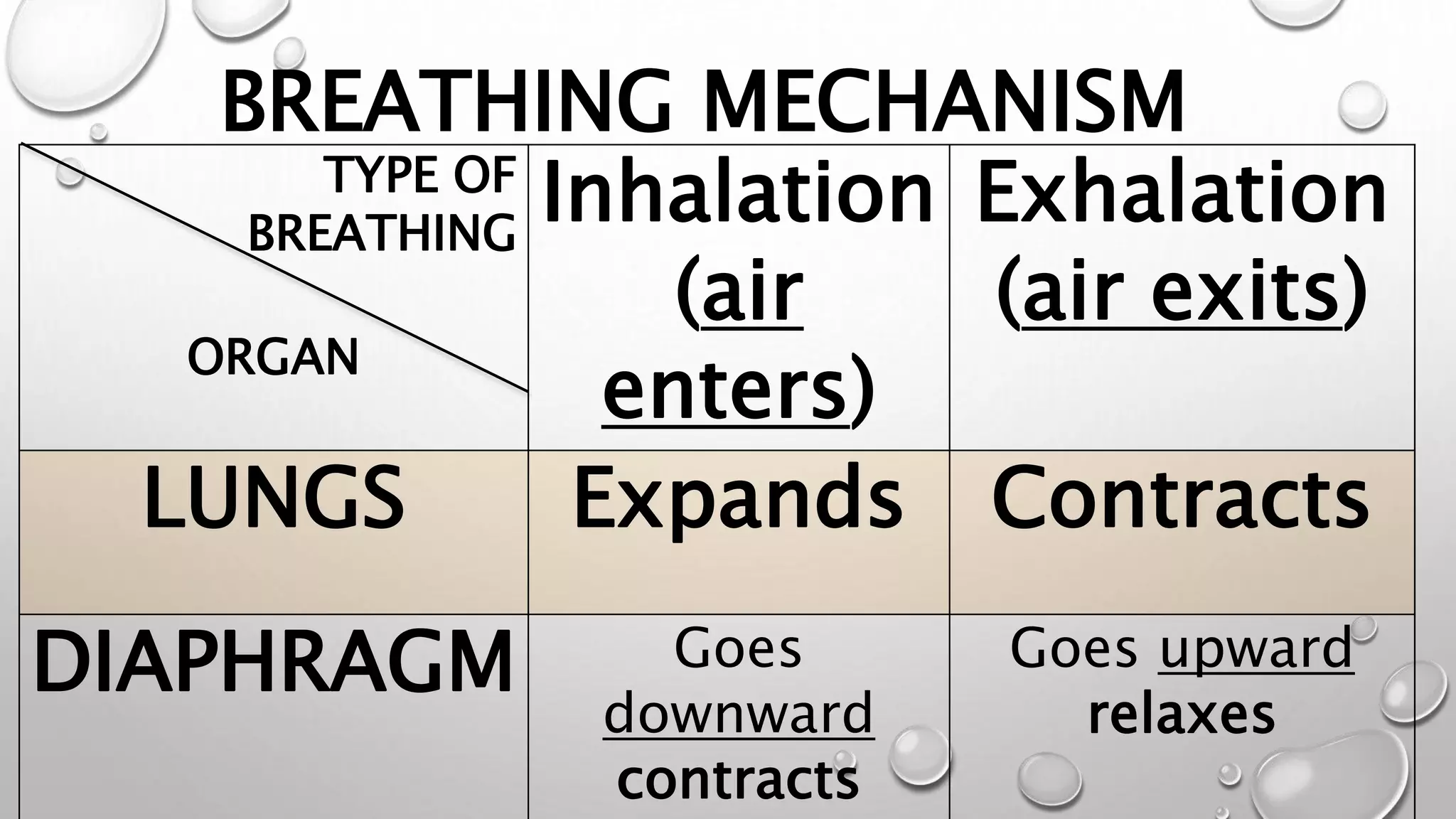
The main components that cause air to go in and out of the lungs are the diaphragm and rib muscles. When you inhale, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, and the rib muscles expand the rib cage outward and upward. This increases the volume of the chest cavity and causes the lungs to expand and draw air in through the airways. When you exhale, the diaphragm and rib muscles relax and move in the opposite direction, decreasing the chest cavity volume and causing the lungs to expel air out through the airways.