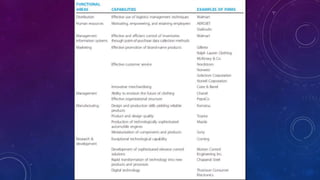
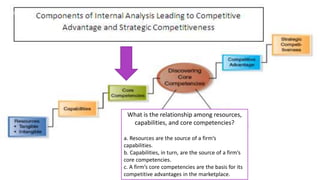
This document discusses resources, capabilities, and core competencies in companies. It defines resources as a firm's assets including tangible resources like capital equipment and intangible resources like brand value. Tangible and intangible resources combined create capabilities. Capabilities are how a firm uses its resources to achieve goals and compete. Core competencies are the source of competitive advantage, involving deep proficiencies that create unique customer value. The relationship is that resources create capabilities, which then form the basis for core competencies that differentiate the firm in the market.