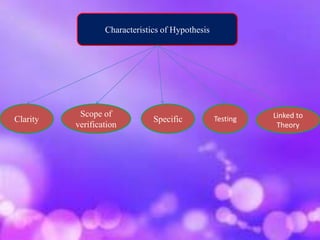
This document discusses research methodology and processing of data. It covers editing, coding, classification, and tabulation as important steps in processing data collected during research. Editing involves correcting errors and omissions in the data. Coding assigns standardized codes to responses for efficient analysis. Classification groups the data based on common characteristics. Tabulation arranges the classified data in an organized table for analysis. The document also defines hypothesis and discusses types of hypotheses, characteristics of a good hypothesis, and the procedure for testing hypotheses using statistical techniques. Finally, it defines interpretation as drawing inferences from analyzed data and discusses techniques for proper interpretation.