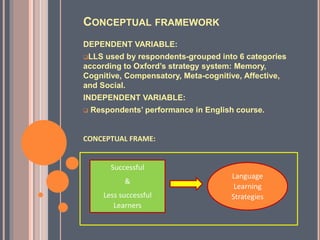
This document discusses a research study on language learning strategies used by English as a Second Language learners and their course performance at Kolej Poly-Tech MARA Ipoh. The study aims to identify the most frequent strategies used, compare strategies used by more and less successful learners, and determine which strategies are most frequently used by successful learners. A questionnaire based on Oxford's Strategy Inventory for Language Learning will be used to collect data, which will then be analyzed using descriptive statistics to identify relationships between strategies used and course performance. The findings could help make students aware of how language learning strategies may enhance their language acquisition.