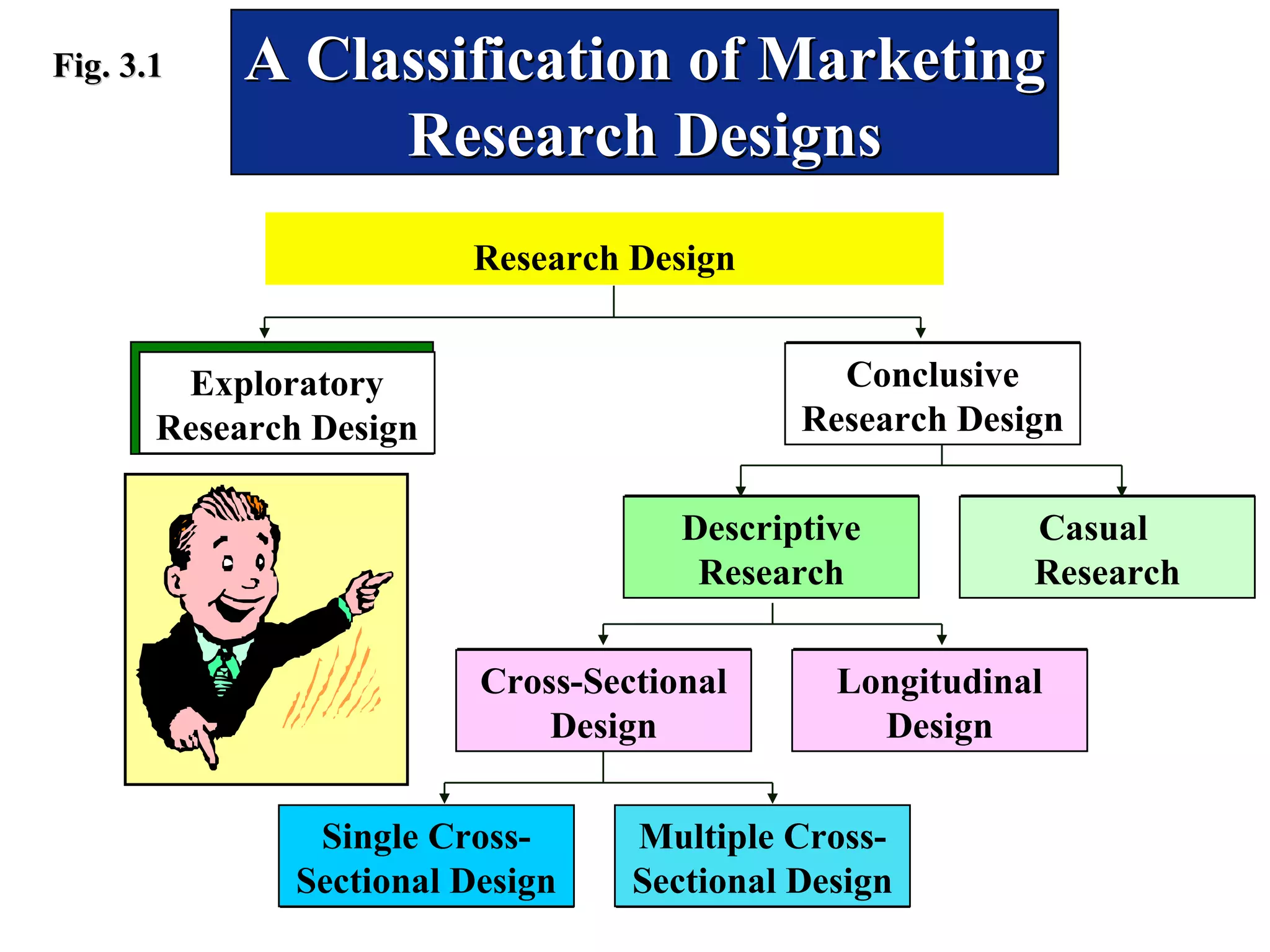
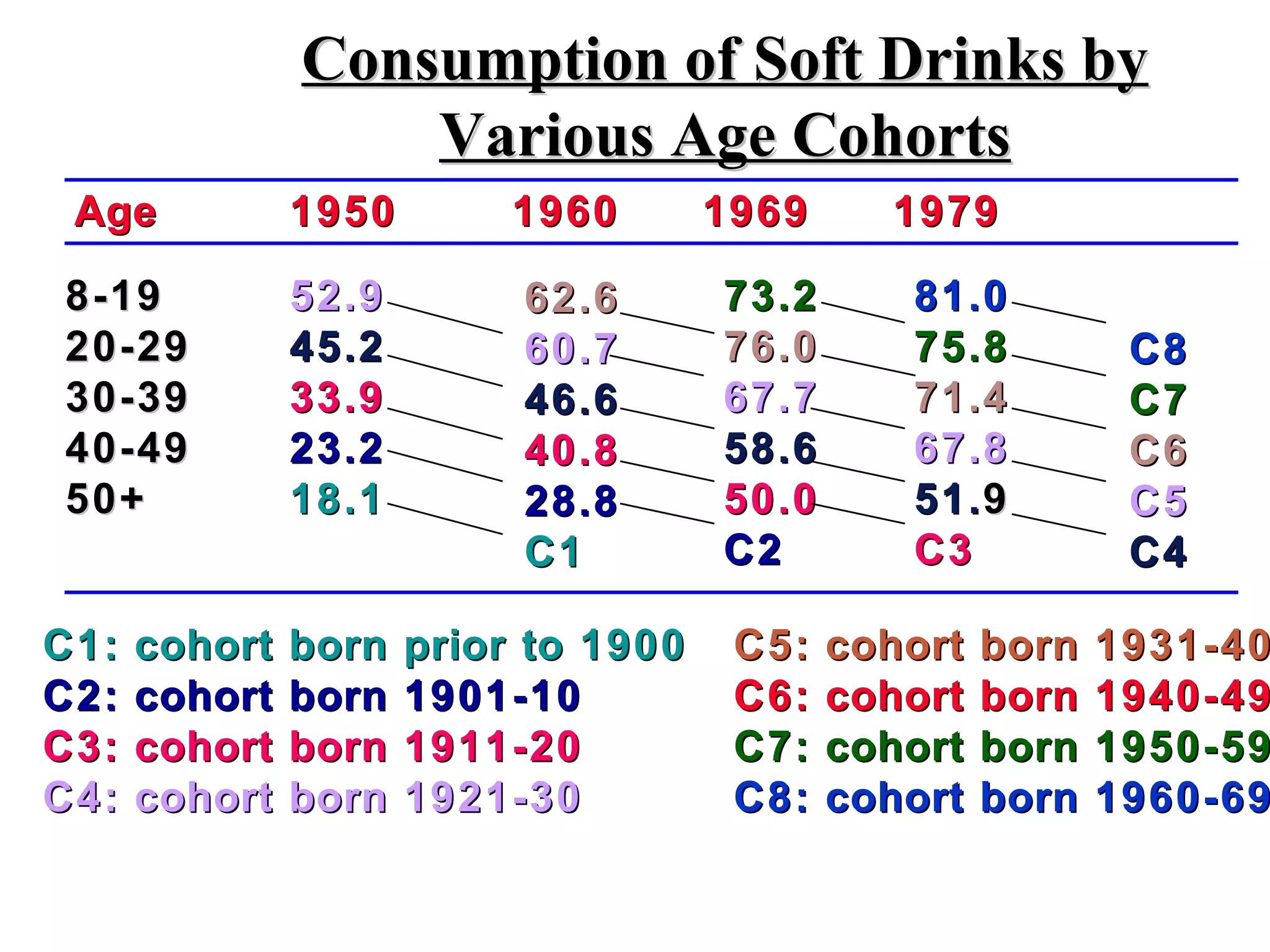
NASCAR conducted exploratory and descriptive research to understand how to expand its audience beyond its stereotypical rural Southern fan base. Extensive focus groups revealed NASCAR had a rural sports image that was generally viewed positively. Descriptive surveys showed many fans had higher incomes and education levels than stereotypes suggested. NASCAR then used this research to develop a marketing plan emphasizing its broad rural sports appeal across America rather than just the South. Citicorp also uses exploratory, descriptive, and causal research including focus groups, surveys, and test marketing when developing new products like one targeted at senior citizens. Greenfield Online Research Center recruits internet users to participate in its online research through exploratory sign-up surveys then matches participants to suitable descriptive