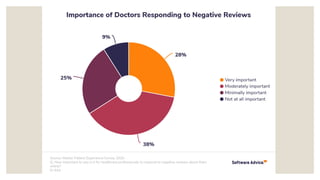
The document discusses understanding reputation management and the reputation economy. It defines reputation management as shaping public perception of an individual or institution, particularly regarding their digital presence. The reputation economy refers to how a person or organization's standing is shaped by user contributions online. It also discusses how Google works through algorithms that determine search rankings, and how individuals and organizations can establish reputation management plans to positively influence their online presence and respond if reputation is damaged.