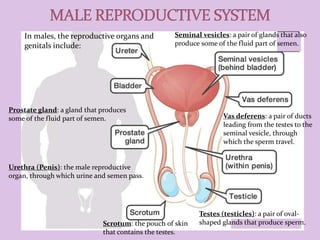
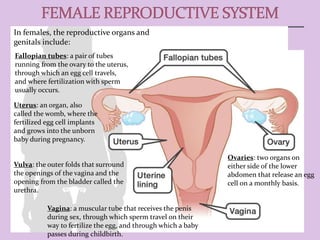
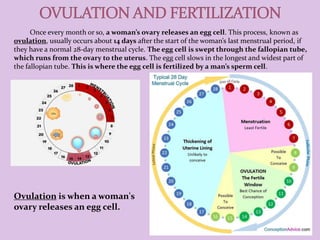
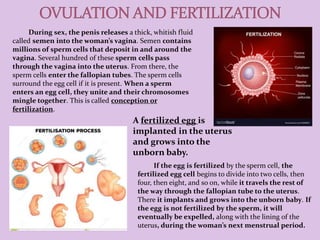
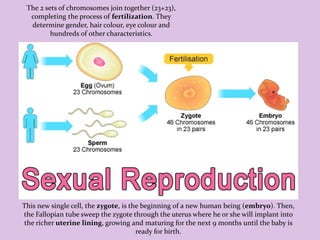
Male and female reproductive organs work together to allow for reproduction. In females, eggs are produced in the ovaries and travel through the fallopian tubes. In males, sperm are produced in the testes. During sex, sperm from a male are deposited into the female's vagina and travel to meet an egg. If a sperm fertilizes an egg, they unite and begin dividing, traveling through the fallopian tube to implant in the uterus, where it will grow into a baby over 9 months. The placenta and amniotic sac in the uterus provide nutrients and protection to the developing fetus.