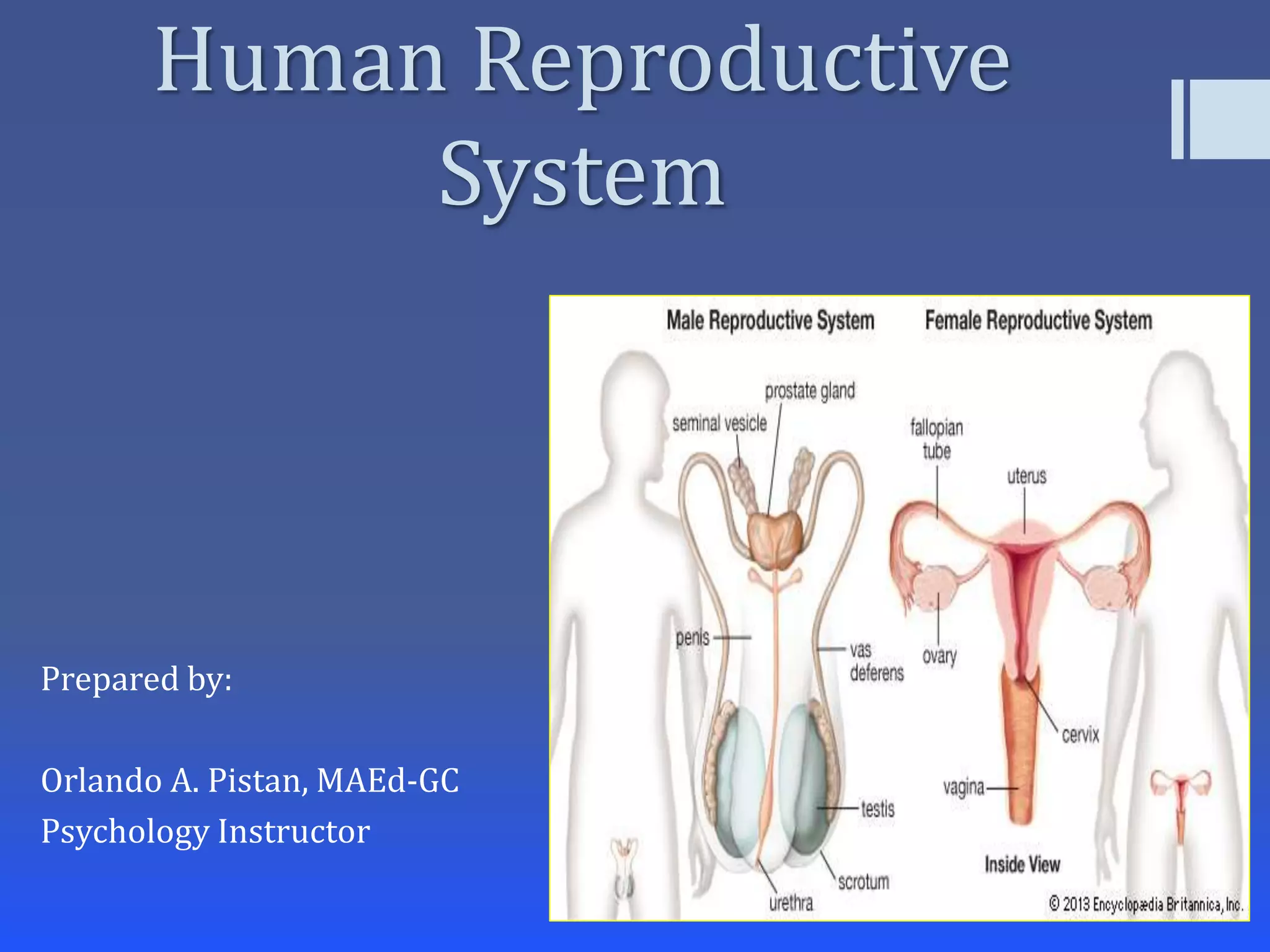
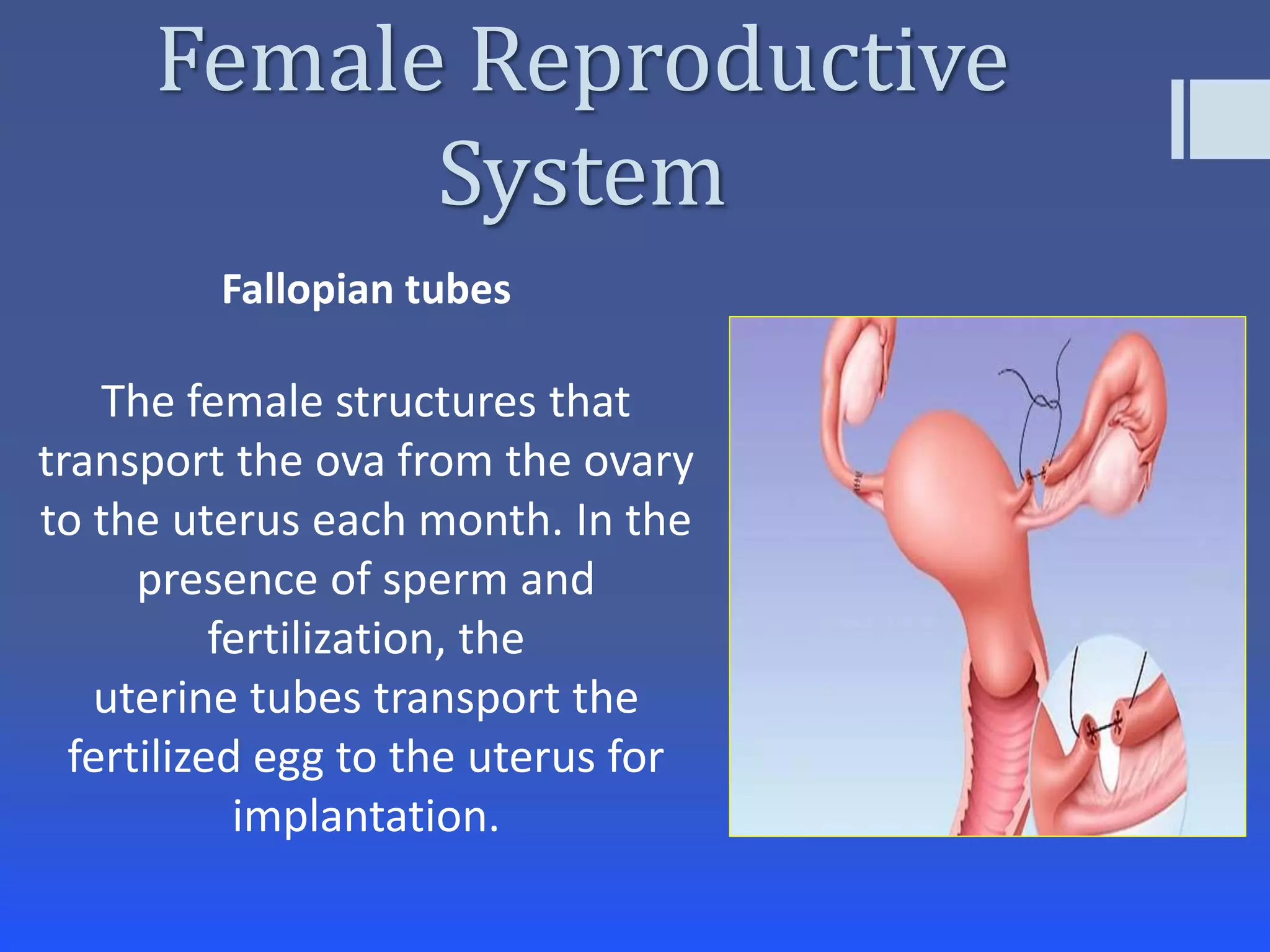
The document summarizes the key components of the human reproductive systems for both males and females. It describes the main organs involved in reproduction for each gender, including the vagina, uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, scrotum, testes, epididymis, sperm ducts, seminal vesicles, prostate gland and penis for males. It also outlines some facts about puberty and the development of secondary sexual characteristics during adolescence that signal the reproductive systems becoming functional.