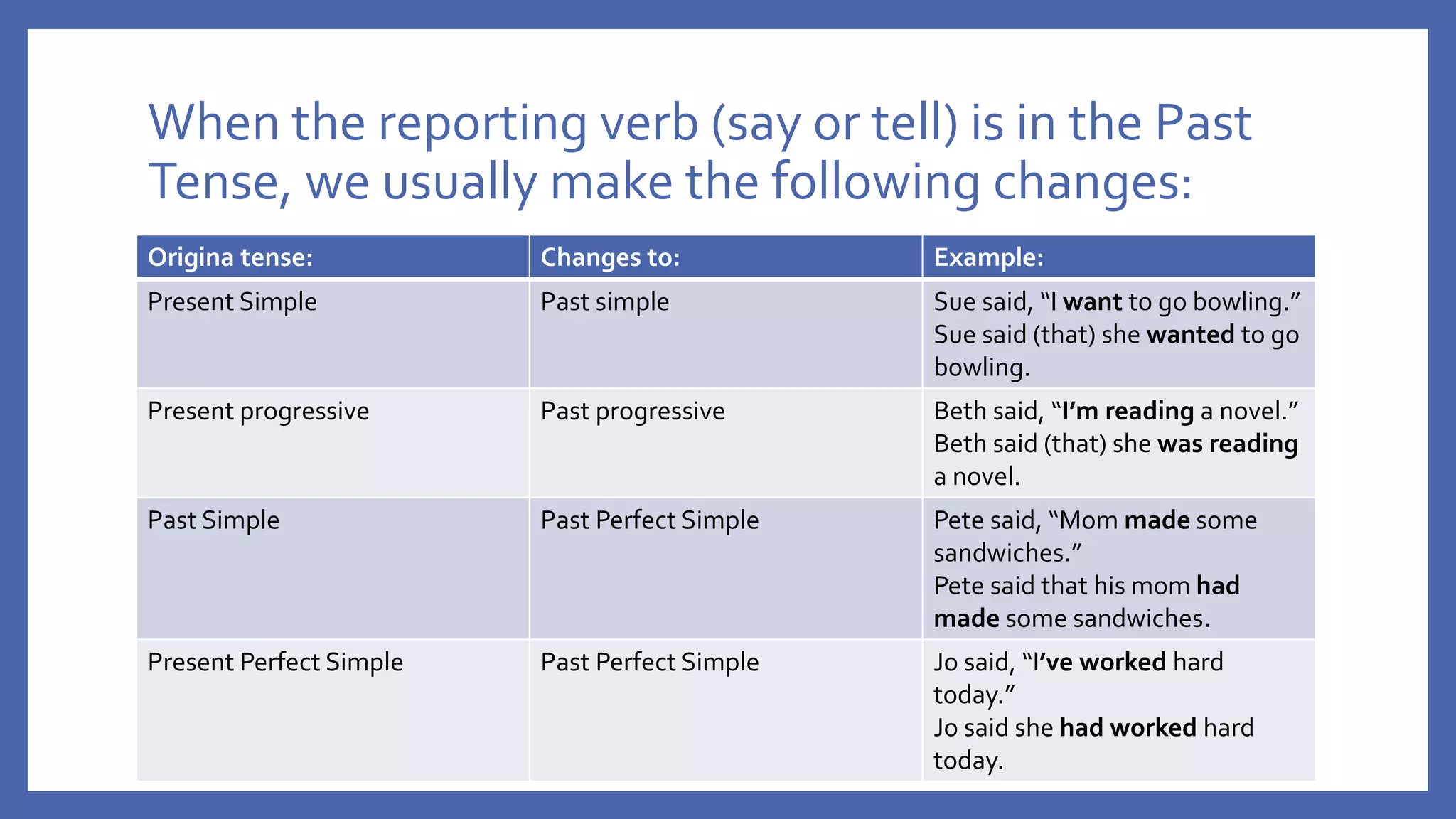
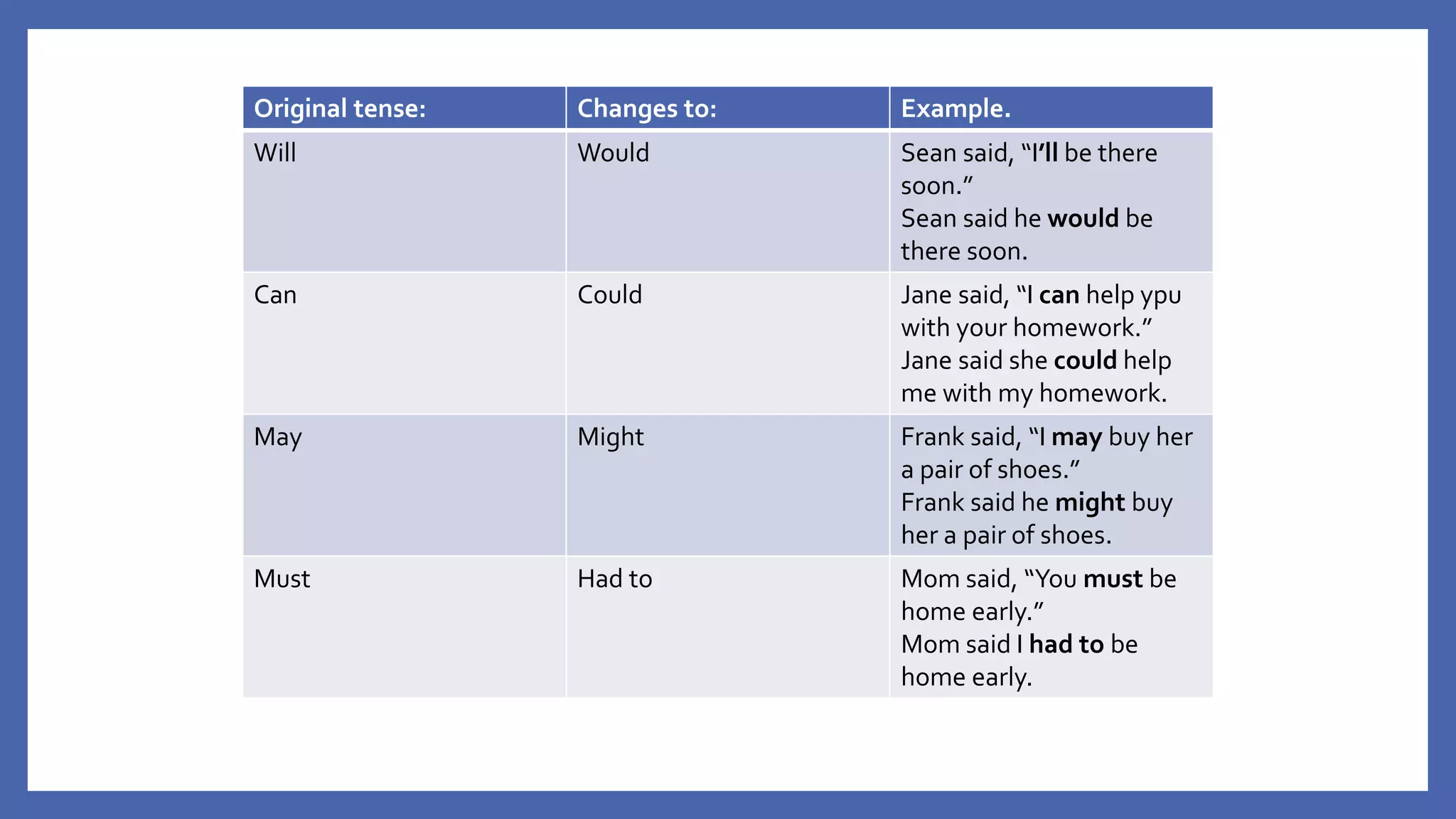
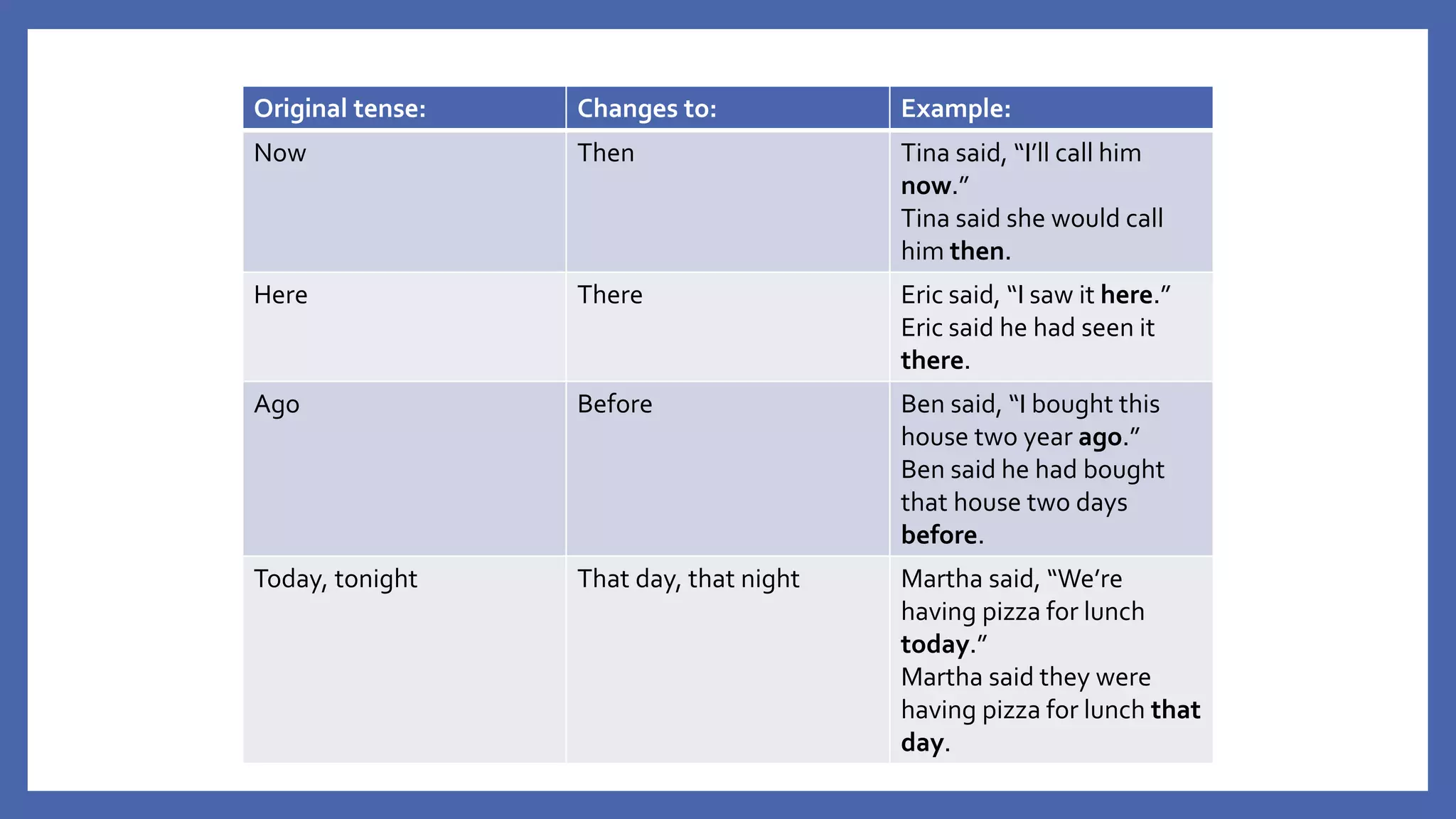
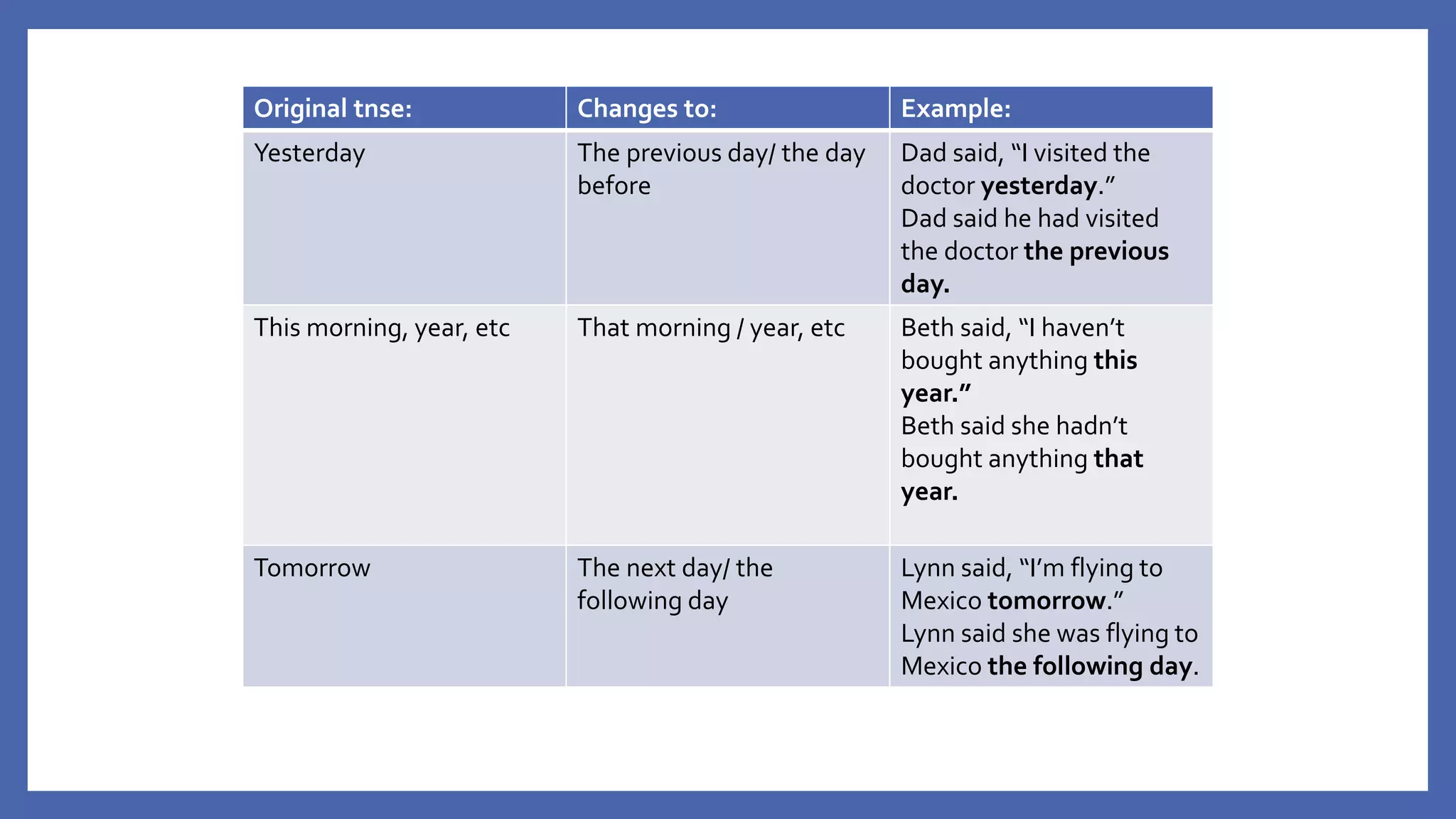
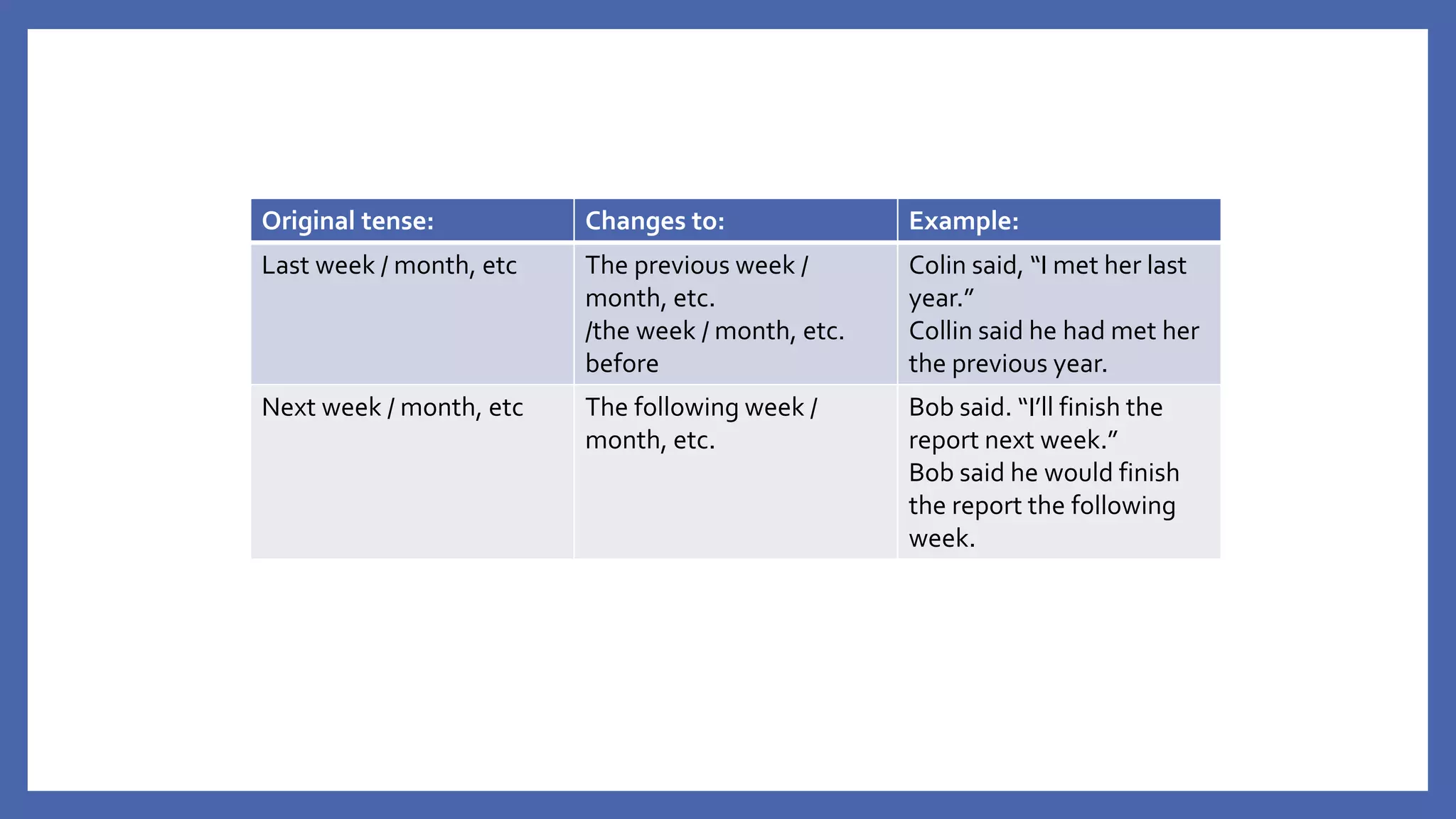
The document discusses how to change direct speech into reported speech in English. It provides rules for changing pronouns, tense, time and place adverbs, and word order when converting statements, questions, commands and requests from direct to reported speech. For statements, a reporting verb like "said" is used, followed by "that" and the reported statement. For questions, the reporting verb is usually "asked" and word order changes. Commands become "told to" do something and requests become "asked to" or "asked if/whether" plus the base form of the verb.