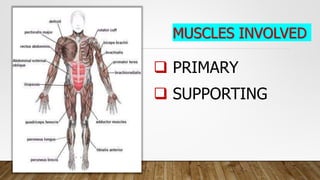
This document discusses basketball as a sport and the anatomy involved in playing basketball. It begins with a brief history of basketball, describing how the game was invented in 1891. It then outlines the basic skills in basketball. The document focuses on the primary and supporting muscles used in basketball, describing the function and role of muscles like the trapezius, deltoid, biceps, abdominal muscles, and more. It provides details on how these muscles are involved in the movements required to play basketball.