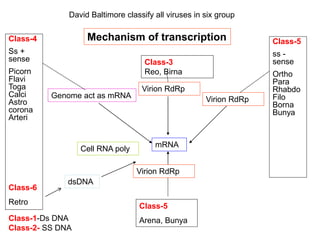
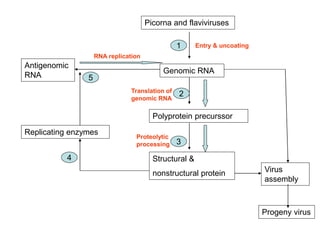
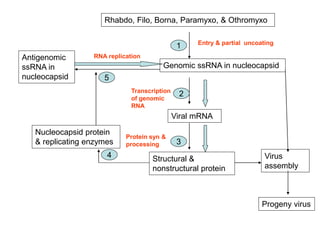
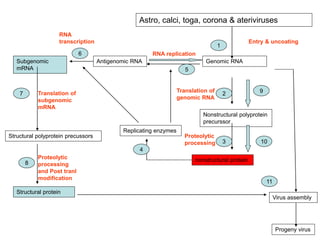
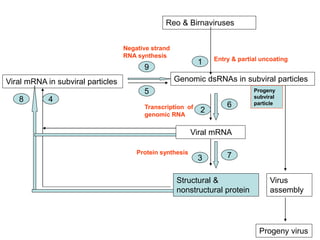
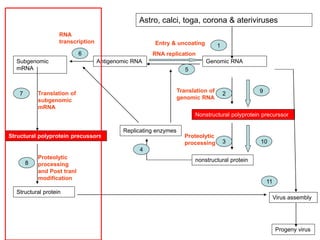
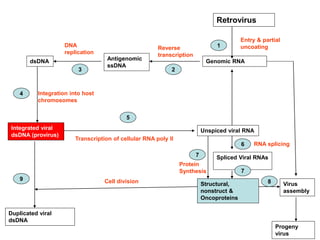
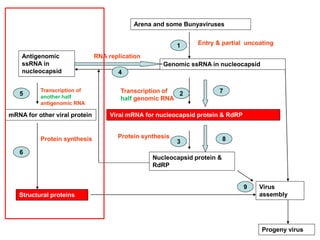
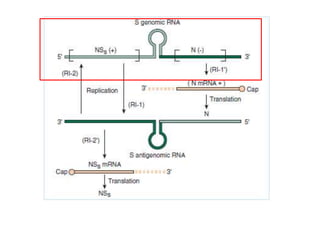
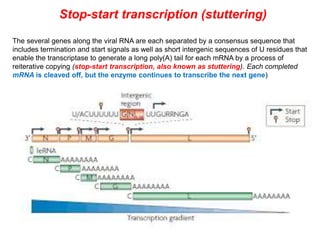
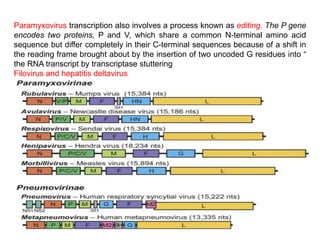
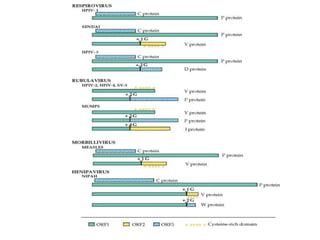
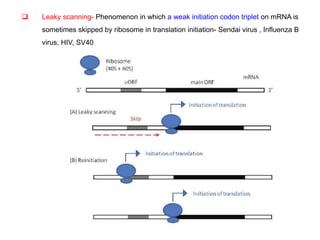
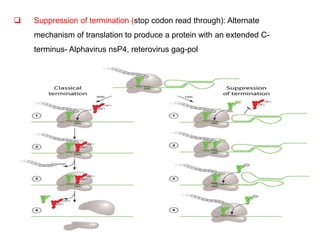
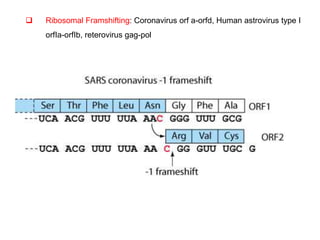
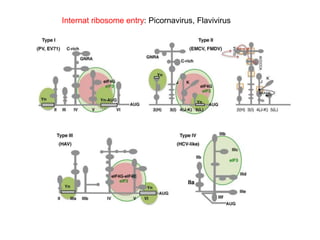
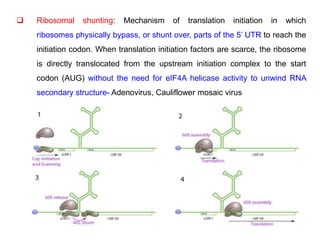
The document discusses the classification and replication mechanisms of various RNA viruses, categorizing them into different classes based on their genetic structure. It outlines the processes involved in transcription, translation, and assembly of viral particles, highlighting key enzymes and proteins involved in these mechanisms. Additionally, it addresses unique transcription phenomena such as stop-start transcription, editing, leaky scanning, and ribosomal shunting observed in virus biology.