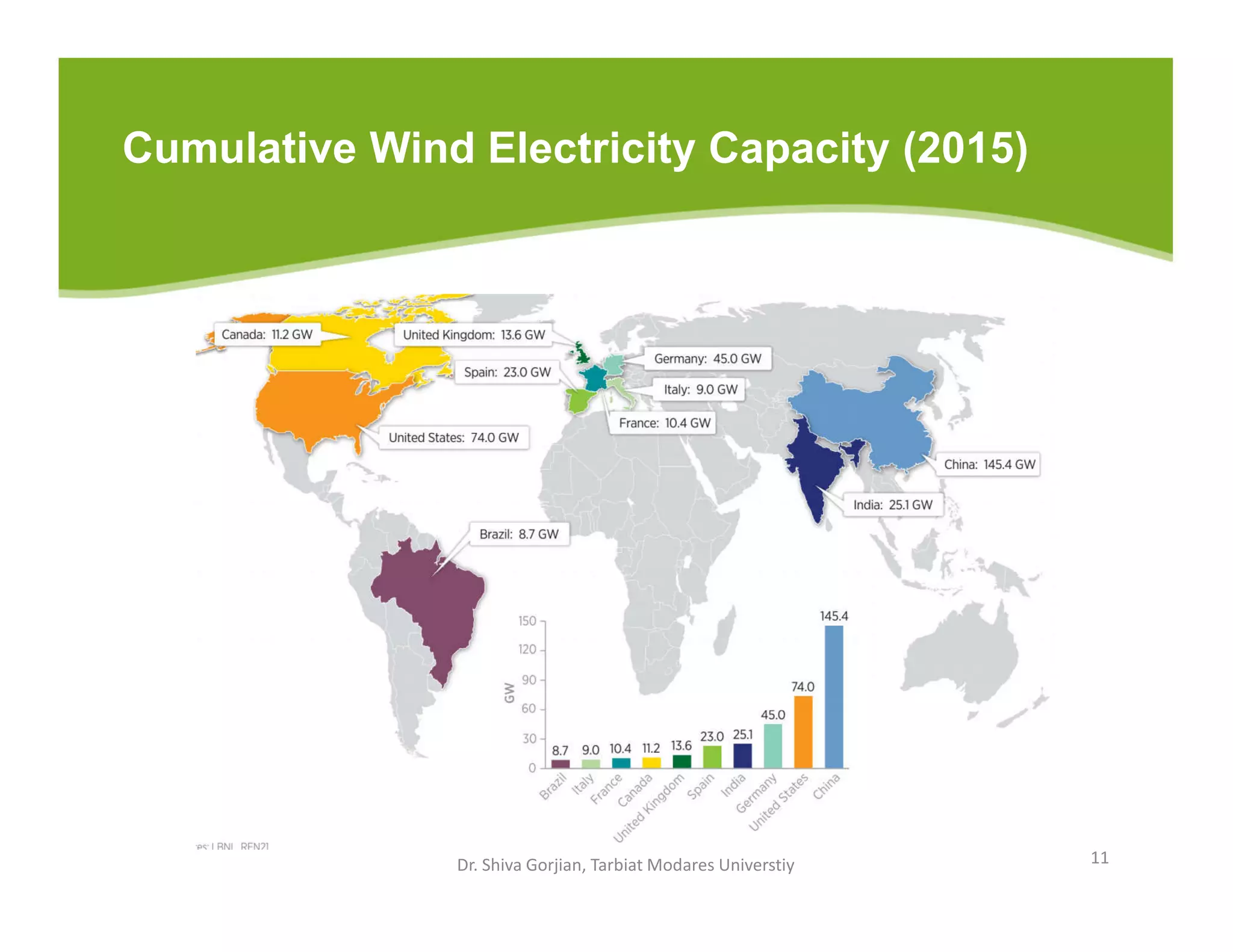
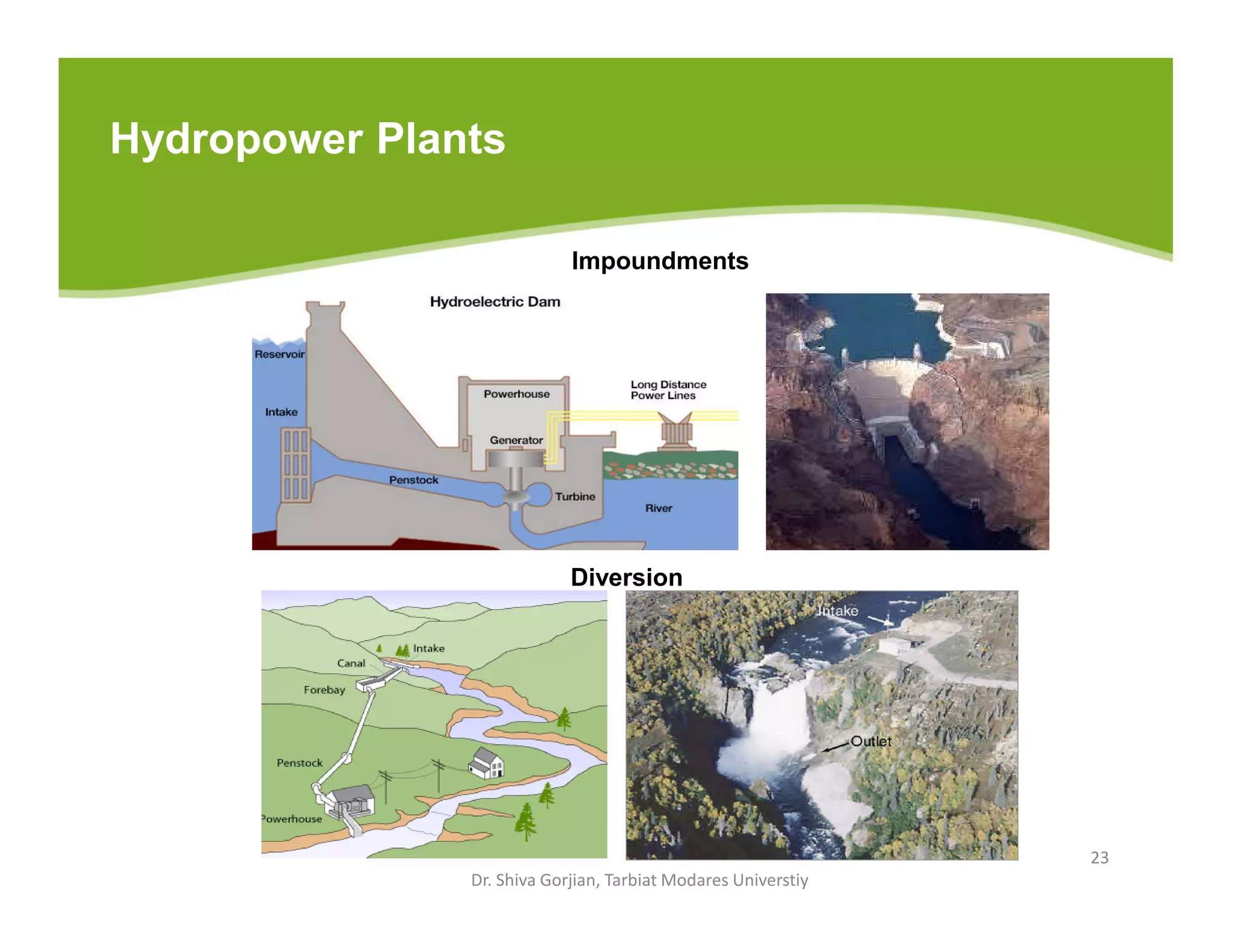
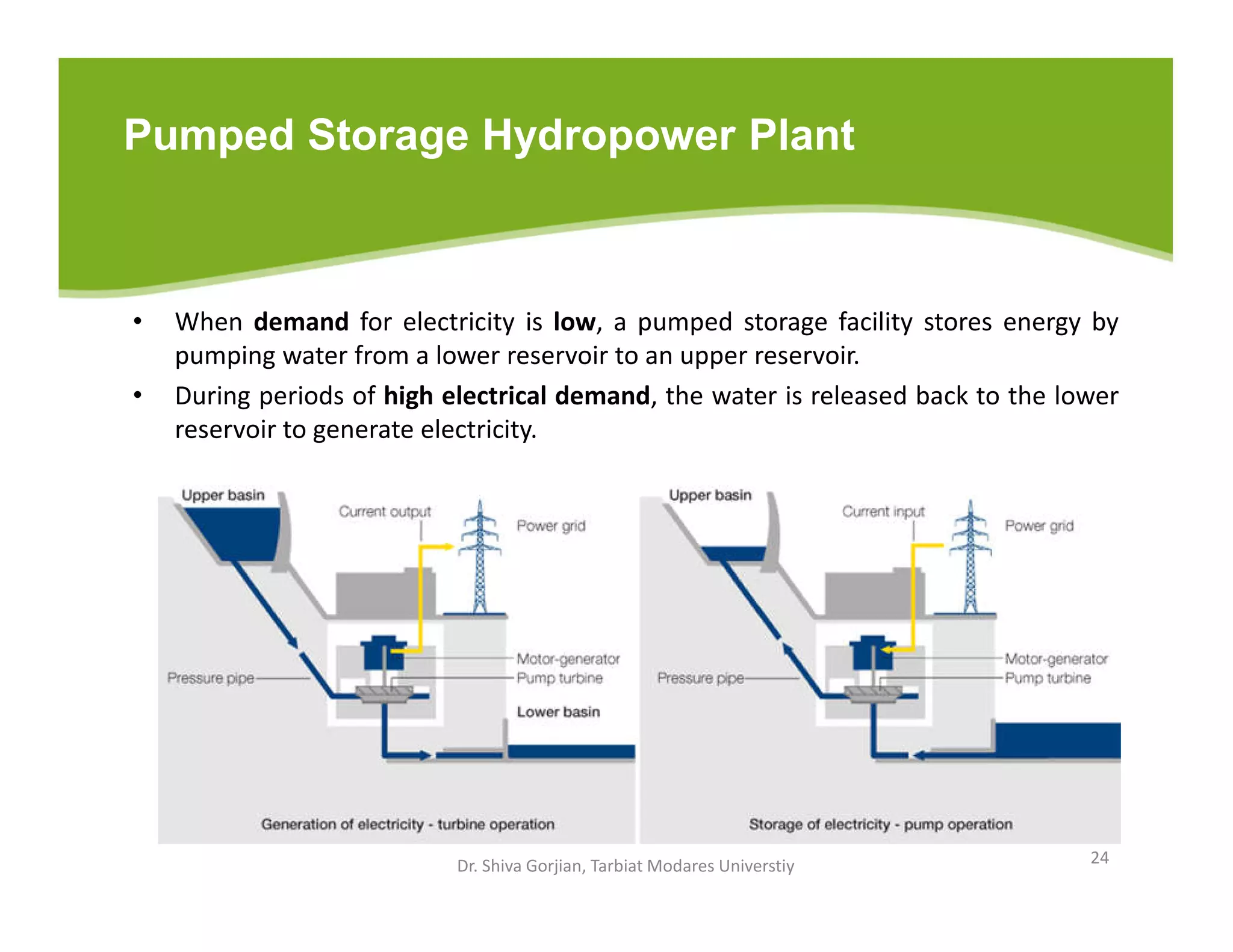
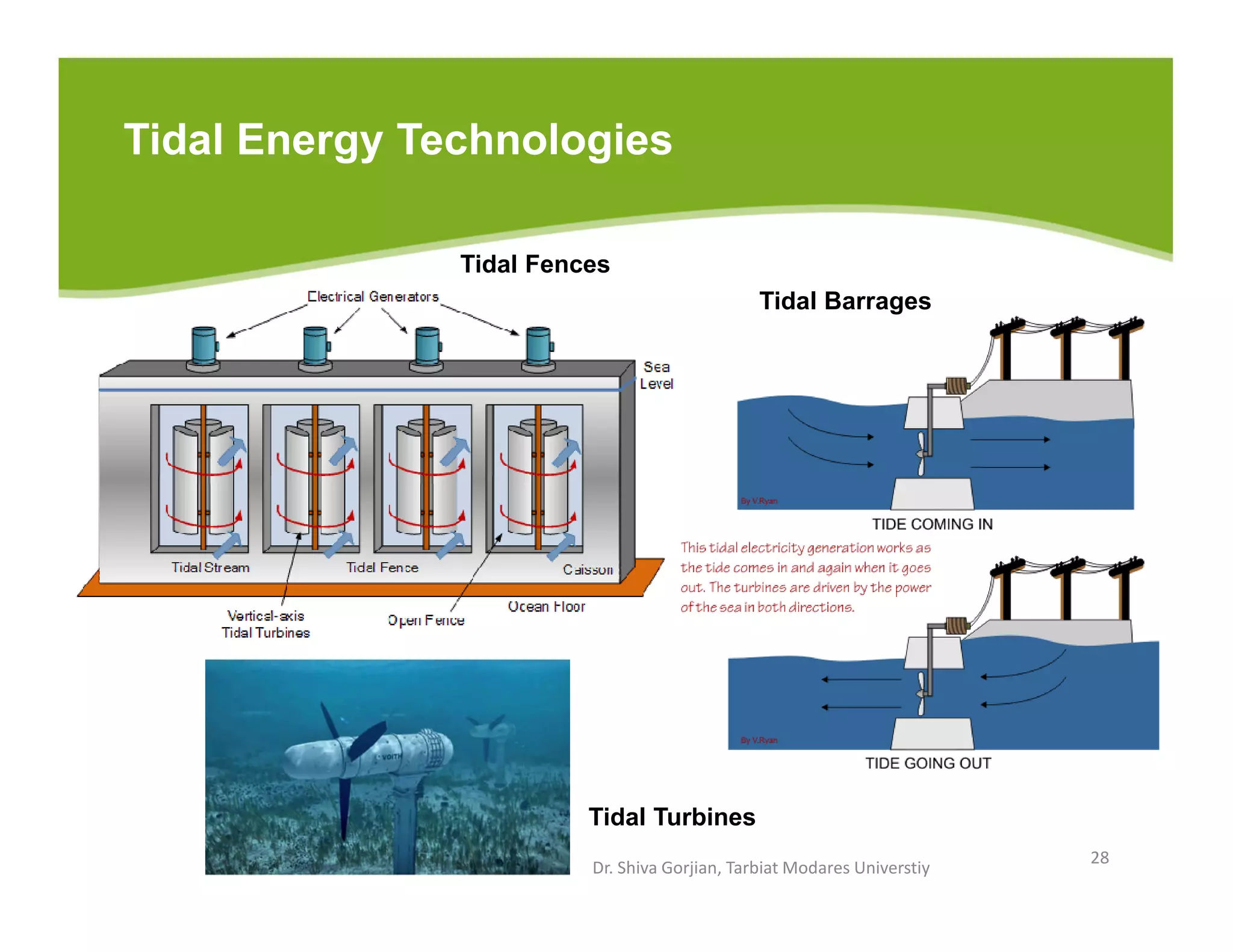
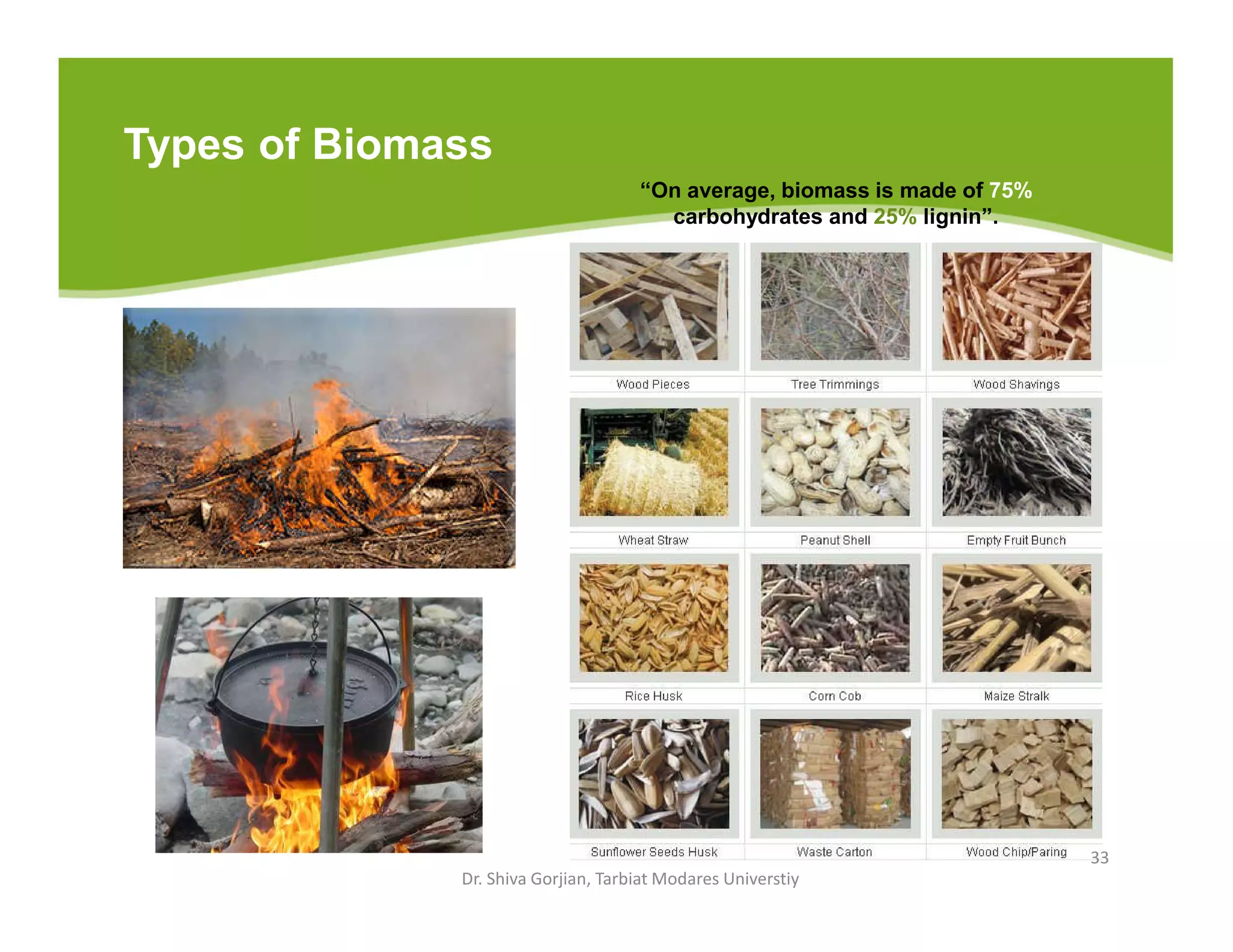
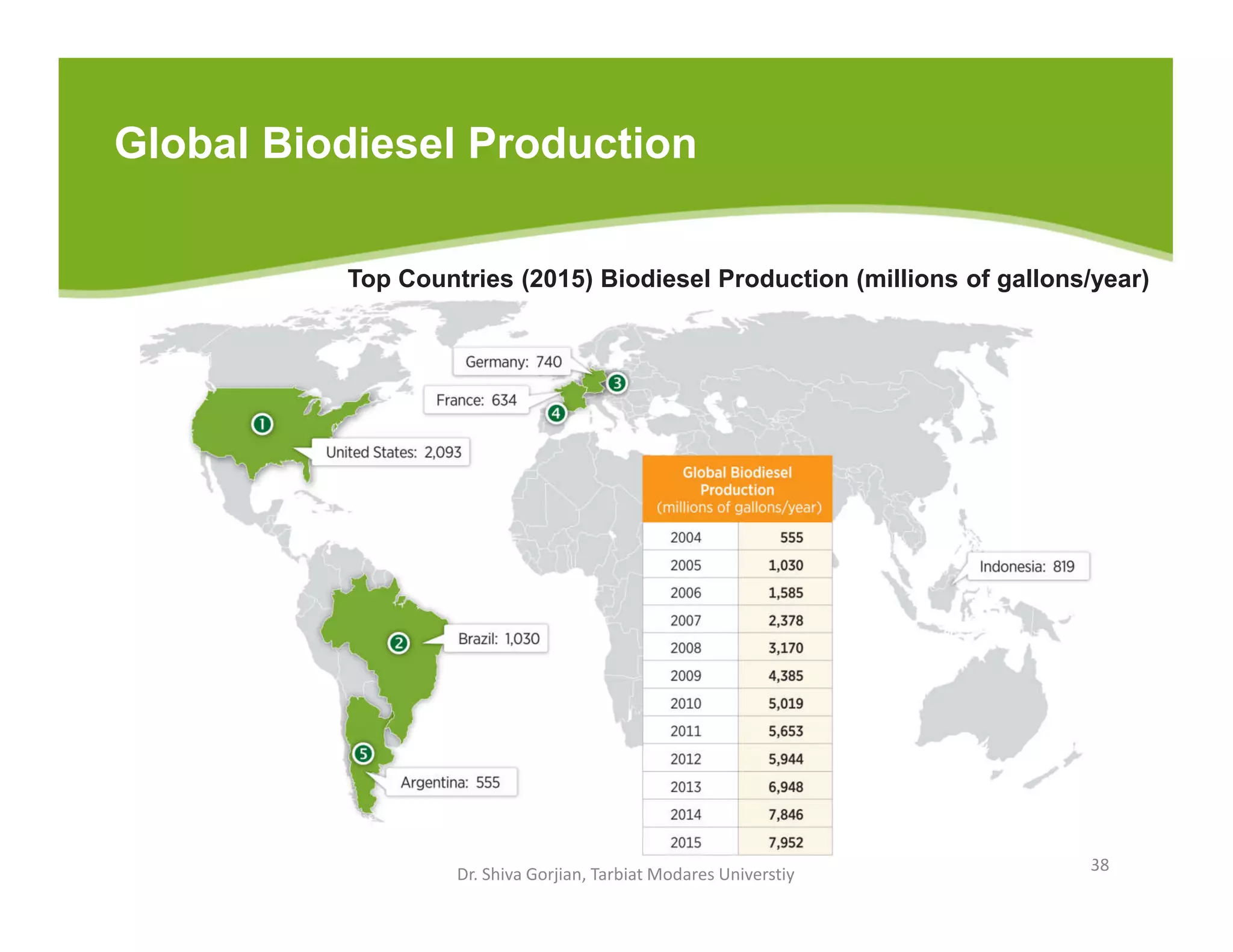
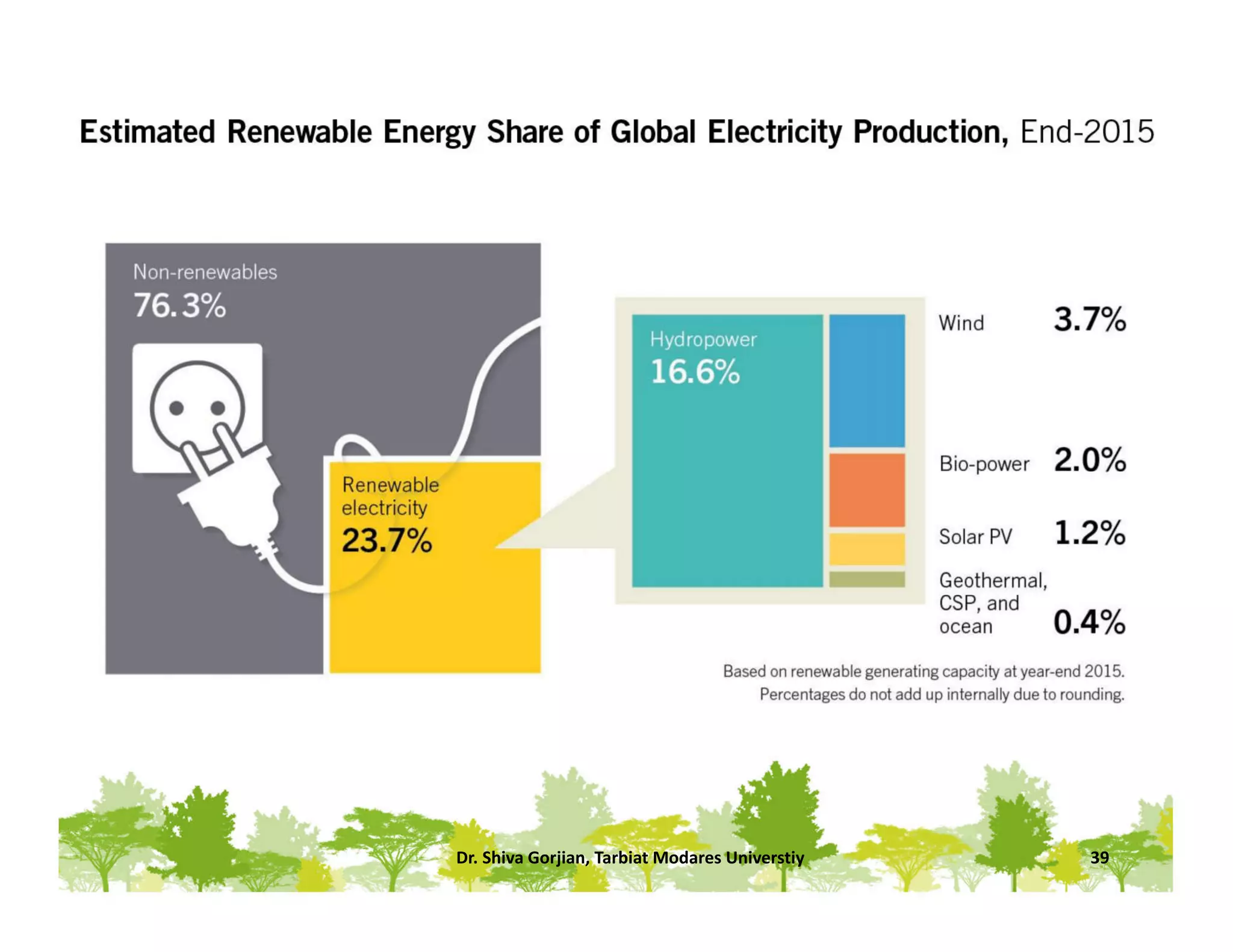
The document discusses various renewable energy technologies, including solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, and biomass. It highlights the importance of renewable energy sources in reducing dependency on fossil fuels, their environmental benefits, and their potential for electricity generation. Additionally, it covers specific technologies and processes associated with each type of renewable energy, including solar power conversion methods, wind energy generation, and biomass production techniques.