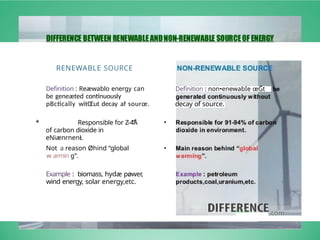
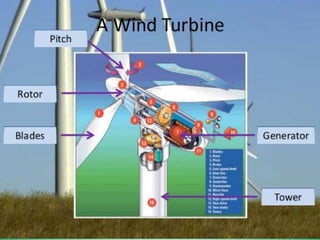
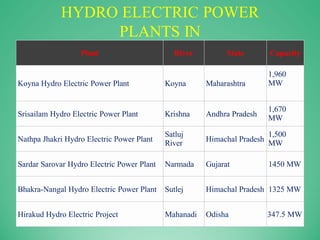
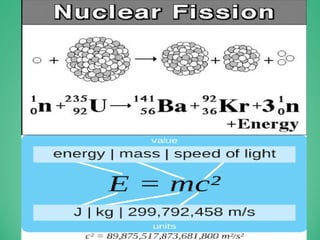
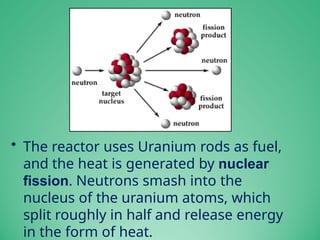
The document discusses various renewable energy sources in India, including solar, wind, hydro, tidal, biomass, nuclear, and geothermal energy, along with their advantages and disadvantages. It emphasizes the significance of renewable energy in reducing carbon emissions and highlights existing facilities and future opportunities for their development in India. Furthermore, it includes specific capacity statistics and examples of energy plants across different states.