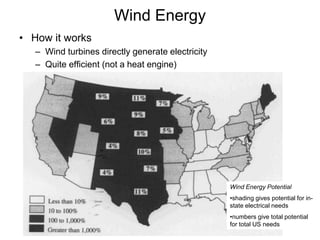
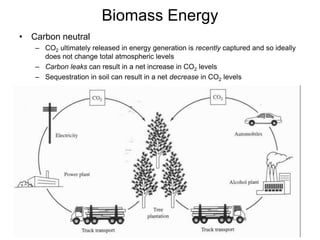
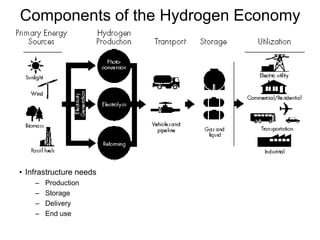
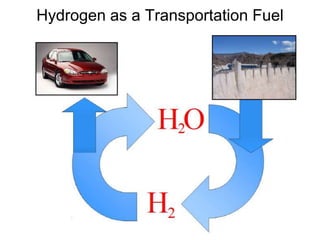
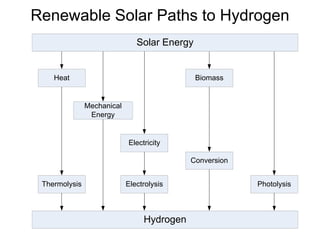
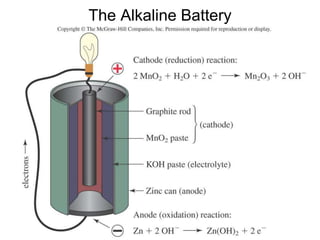
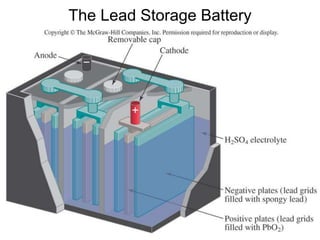
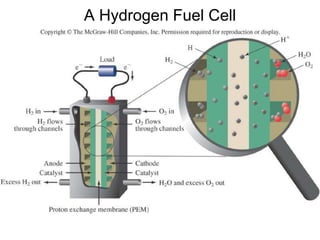
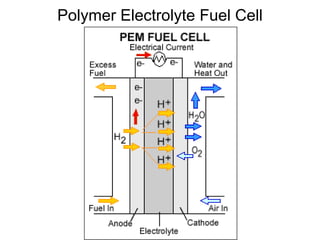
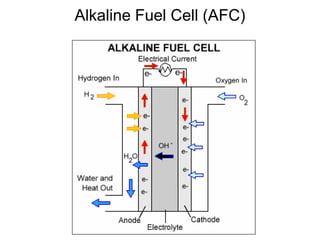
This document discusses various renewable energy sources including solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass. It provides details on how each works, their advantages, and disadvantages. Hydroelectric energy is highlighted as being cheap to operate with low emissions, but can displace populations and negatively impact ecosystems. Wind energy is free and clean but intermittent. Biomass has potential to be carbon neutral but often has low energy yields and agricultural impacts. The hydrogen economy is also introduced as a hypothetical future system where hydrogen plays a central role, especially in transportation.