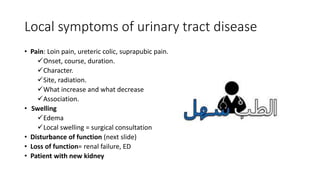
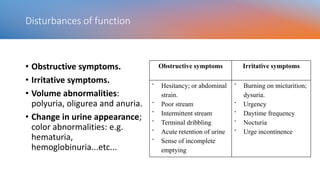
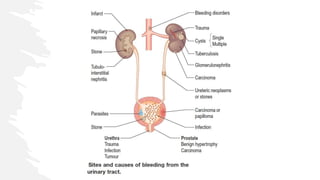
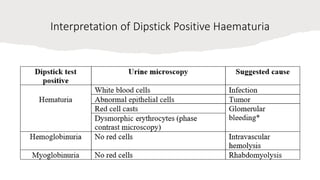
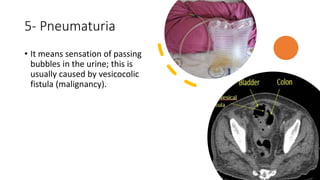
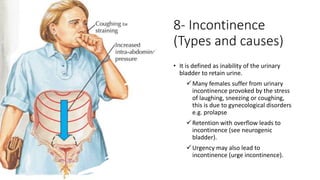
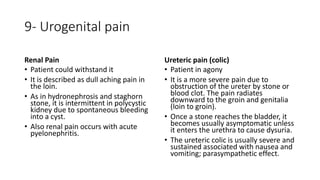
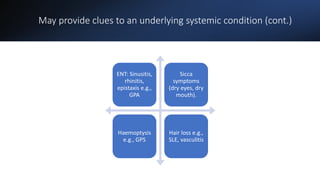
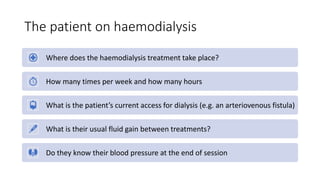
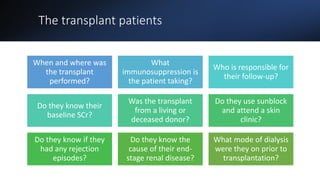
This document covers a detailed clinical assessment approach in nephrology, emphasizing the importance of patient history, symptomatology, and various urinary dysfunctions. It highlights key symptoms such as dysuria, polyuria, hematuria, and their potential causes, alongside considerations for past medical history, risk factors, and treatment approaches. Moreover, it discusses the management of patients on renal replacement therapy, outlining specific questions to facilitate effective patient care.