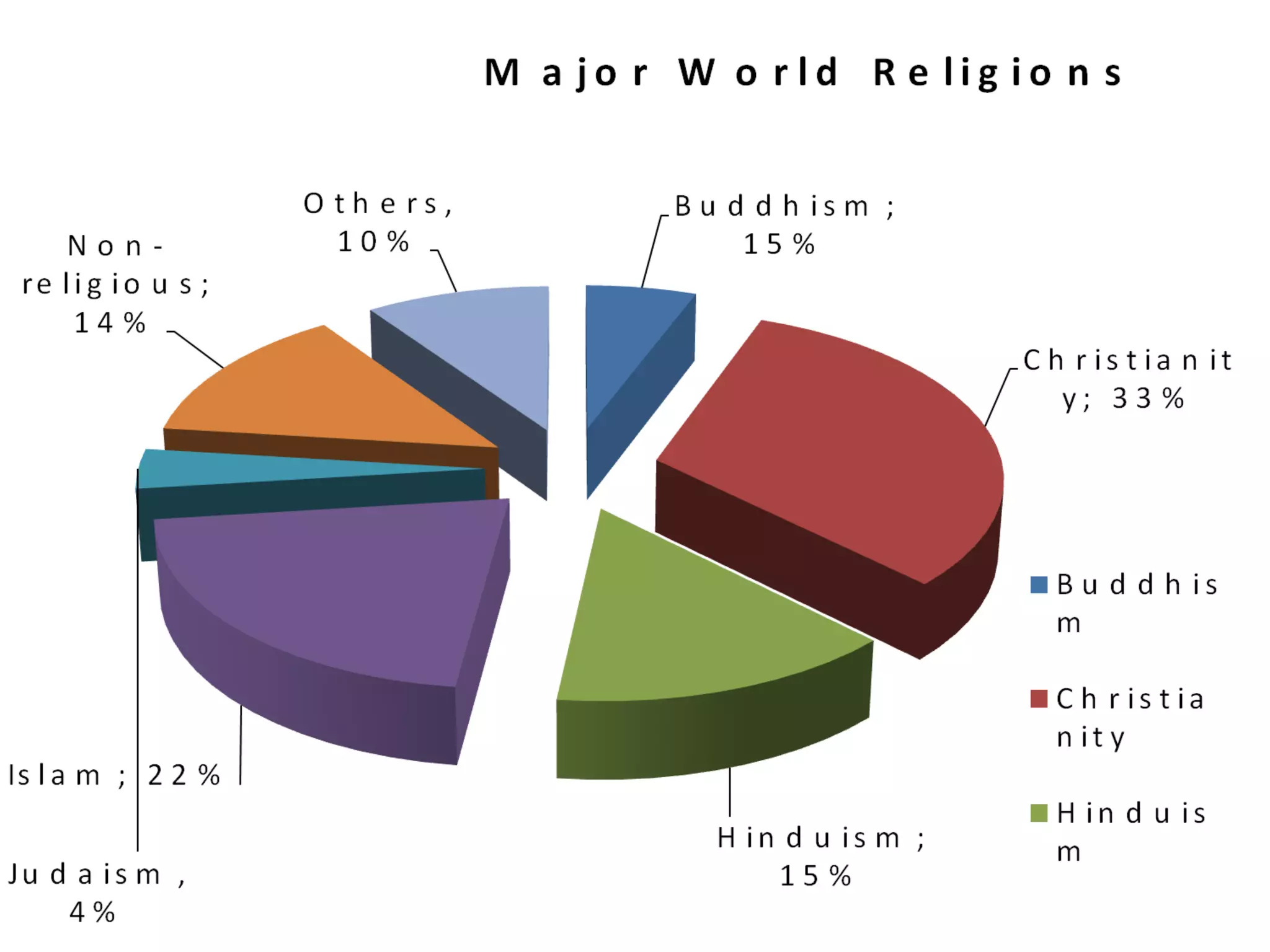
Religion is an organized system of beliefs, ceremonies, and practices centered around a deity or supreme being. Most religions involve a belief in God or gods, codes of conduct, sacred stories and texts, rituals, and doctrines of salvation. The eight major world religions are Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, Sikhism, Taoism, and Jainism. People practice religion for reasons such as culture, security, fellowship, and meaning in life.

![*REASON
why peoplepracticereligion?
* It is a part of heritage or their culture, tribe, or family.
* It gives many people a feeling of security because they believe that a divine
power watches over them.
* For help or protection.
* It promises them salvation and either happiness or the chance to improve
themselves in a life after death.
* Brings a sense of individual fulfillment and gives meaning to life.
* It provides answers to questions of life such as:
[a] What is the purpose of life?
[b] What is the final destiny of man?
[c] What is the difference between right and wrong?
* They enjoy a sense of kinship with their fellow believers (fellowship).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-3-2048.jpg)

![*CHIEF
CHARACTERISTICS
of religion
[I.] BELIEF IN THE EXISTENCE OF A GOD OR A DEITY
Most religions are theistic. They teach that deities govern or greatly
influence the actions of human beings as well as events in nature.
A. Forms of Beliefs
[1] THEISM- generally believes in the existence of a God.
[2] ATHEISM- believes that there is no God that exists.
[3] AGNOSTICISM- say that the existence of a deity cannot
be
proven or disproved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-5-2048.jpg)
![*CHIEF
CHARACTERISTICS
of religion
B. Forms of Theism
[1] PANTHEISM- believes that everything is God, everything is a
divine manifestation of God, and finally that nothing really exists that is not
God.
[2] PANENTHEISM-believes that God is everywhere. God’s presence
can be felt anywhere if only we open our eyes to this reality. God is present
in His creation but Creation is not God.
[3] POLYTHEISM- those who believe in two or more Gods. The
ancient Greeks and Romans have Polytheistic religions.
Examples: Aphrodite- Goddess of Love; Mars- Roman God of War
[4] HENOTHEISM- worships a supreme God but does not deny the
existence and power of the other Gods.
[5] MONOTHEISM- teaches that there is only one God.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-6-2048.jpg)
![*CHIEF
CHARACTERISTICS
of religion
[II.] DOCTRINE OF SALVATION
Most religions stress that salvation is the highest goal of the faithful
and that all followers should try to achieve.
A doctrine of salvation is based on the belief that individual are in
some form of danger from which they must be saved.
[III.] CODE OF CONDUCT
Code of conduct is a set of moral teachings and values that all
religions have in some form. It tells believers how to conduct their lives. It
teaches them how to act toward the deity and towards one another.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-7-2048.jpg)
![*CHIEF
CHARACTERISTICS
of religion
[IV.] THE USE OF SACRED STORIES CONTAINED IN THE SACRED BOOKS
Sacred stories or myths are often used by religious leaders to
dramatize the teaching of their faith.
[V.] RELIGIOUS RITUALS
Rituals include the acts and ceremonies by which believers appeal
to and serve God, deities, and other sacred powers. The performance of a
ritual is often called “service”, the most common form of ritual is prayer.
Through prayer, a believer addresses worship and thoughts to an
object of worship.
Prayer includes request, expressions of thanksgivings, confession of
sins, and praise.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-8-2048.jpg)


![B
U
D
- Buddhism offers clear rules for its followers
D
- Four Noble Truths
H - [1] Life involves suffering (dukkha); [2] The cause of suffering is craving
I and desire (tanha); [3] To cease suffering is to renounce craving and
S desire; [4] Desire can be eliminated by following the Eightfold Path
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-11-2048.jpg)
![B
U
D
D - The Eightfold Path to liberation involves:
H [1] Right viewpoint, [2] Right aspiration, [3] Right speech,
I [4] Right behavior, [5] Right occupation, [6] Right effort,
S [7] Right mindfulness, [8] Right meditation
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-12-2048.jpg)
![B
U
D -CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
D [1] Interrelatedness rather the Individualism
- Greed and self-centeredness is the cause of much suffering in
H our world. Not happy- compete against each other. Ergo, live and act and
I be together, in a relationships of care and concern.
S - A nation that is not based on competition, but based on
M compassion (being with).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-13-2048.jpg)
![B
U
D -CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
D [2] The Need for Possibility of Personal Transformation
- “Your efforts and plans are very important. But, you will not be
H able to bring about peace in the world, unless you bring about peace
I within yourself. And to do that, you have to meditate.
S - Meditation is the key to mind cleansing and thought clarity.
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-14-2048.jpg)
![[FOUNDER] Gautama Buddha, Siddhartha Gautama (Real Name)
B [PLACE OF ORIGIN] India
U [BOOKS/SACRED TEXTS]Tripitaka- known as the Three Baskets divided
D into three parts namely:
D The Book of Discipline (VinayaPitaka)
The Discourses of Lord Buddha (SutthaPitaka)
H
The Book of Psychological Analysis & Synthesis
I (AdhidhammaPitaka)
S [GOD/S] Dharma
M [BRANCHES]Hinayana (Lesser Vehicle; Conservative), Mahayana (Greater](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-15-2048.jpg)




![H
I
N -CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
D [1] The Sacredness of Creation
- The world is a sacred reality. They see the world as God’s body.
U [2] The Value of Diversity
I - Diversity is as essential as unity. The one Divine is expressed in
S millions ways. Variety is not only the spice of life; it is also the source of
M life.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-20-2048.jpg)
![H
I
N -CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
D [3] The Challenge of Nonviolence
- Nonviolence comes from Hinduism through Mahatma Gandhi.
U Our shared oneness with the divine forbids us to be violent to others or
I to one another.
S
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-21-2048.jpg)
![H
I [FOUNDER] No
[PLACE OF ORIGIN] Indus Valley, India
N [BOOKS/SACRED TEXTS] Vedas (Eternal Truth), Sama Veda (Verses for
D Chanting) Yajur Veda (Ritual Instructions), Atharva Veda (Mystical Verse
U on Healing Matters), Epics (Mahabharata, BhagavadGita)
I [GOD/S] Brahma (The Creator), Vishnu (The Sustainer/Preserver), Shiva
S (The Destroyer)
[BRANCHES] Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, Hari Krishna
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-22-2048.jpg)


![I
S - Their basic beliefs are contain in the Five (5) Pillars
L [1] There is no God but Allah and Muhammed is his prophet (Shahadah)
A [2] Pray five times a day (Salat)
[3] Almsgiving (Zakat)
M
[4] Fasting during the day of Ramadan (Sawm)
[5] Pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-25-2048.jpg)
![-CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
[1] Realistic Optimism
I
- In the face of global poverty, violence, and injustice, Islam offers
S the world a message of what we might call R.O.
L [2] Religion and Politics
A - Religion must influence politics. Religion has something to say
M to the state. According to Qur’an, it is meant not just to change one’
heart but also to change one’s society. “Religion is “something between
God and the government.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-26-2048.jpg)
![I [FOUNDER] Mohammed
S [PLACE OF ORIGIN] Mecca,Saudi Arabia
L [BOOKS/SACRED TEXTS]Qu’ran (The Words of Allah), Hadith (A Collection
A of the Sayings of Mohammed)
M [GOD/S] Allah
[BRANCHES] Sunni Muslims (Mainstream)- Traditionalists, Shi’ite Muslims
(dispute over the succession)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-27-2048.jpg)



![J
U
D
A - The “Six (6) Rights”: *1+ Right to life; *2+ Right to possessions; *3+ Right to
I clothing; [4] Right to shelter; [5] Right to work; [6] Right to liberty
-The Old Testament Bible is their official book specially the Torah or the
S
“five books of Moses”- Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Deuteronomy and the
M book of Numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-31-2048.jpg)
![J -CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
U [1] Hope
D - Judaism keeps a message of optimism and hope alive. No
A matter the suffering maybe, things can be solved.
I [2] Human Responsibility
- Jews remind us that we can rely on the presence of God, it also
S reminds us that God is relying on us. The Torah constantly calls Jews to
M act responsibly as coworkers of God in bringing creation to even greater
beauty.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-32-2048.jpg)
![J
U
D -CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
A [3] Centrality of Justice
- Yahweh is not only a God who created the world but also a God
I who calls for justice within this world. Humanity will never attain shalom
S (peace) without humans who act for justice.
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-33-2048.jpg)
![J
U
D [FOUNDER] Abraham
A [PLACE OF ORIGIN] Palestine, Israel
I [BOOKS/SACRED TEXTS] Bible (OT), Torah (5 Books of Moses), Mishnah
(Ethical and Ritual teachings), Talmud (Collection of Traditions)
S [GOD/S] YHWH (Too holy to be spoken)
M [BRANCHES] Conservative Judaism, Humanistic Judaism, Orthodox
Judaism, Reform Judaism, Mystical Judaism, Zionism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-34-2048.jpg)



![C
H
R
I
S
T
-CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
I [1] Jesus’ Ethic of Love
A - Jesus radically focused on “love of neighbors” as the central
N concern not only to Christianity but to all religions. The whole law is
I summed up in a single commandment: “You shall love your neighbors as
T yourself”. Jesus teaches us to care and to share, to be able to forgive and
to repent, to practice mercy and renunciation, and to give help.
Y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-38-2048.jpg)
![C
H
R
I
S -CONTRIBUTIONS TO GLOBAL RESPONSIBILITY
T [2] A House of all Nations
I - The Roman Catholic and the Protestant Churches are united in
A witnessing how the world can become one home for all nations.
N - Hopefully, his example will continue to inspire us, as we create a
home where all are welcomed because we can share with one another
I the light we all received from the one who received many names, like
T God, Allah, Brahman, and so many others.
Y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-39-2048.jpg)
![C
H
R
I
S
T
I
A
N [PLACE OF ORIGIN] Israel
[BOOKS/SACRED TEXTS] Bible & Tradition
I [GOD/S] Trinity (God the Father, Son J.C., Holy Spirit)
T [BRANCHES] Catholic, Protestant, Lutheran, Anglican, Methodist, and
Y Baptist](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theo-120718092905-phpapp02/75/Religions-Theology-40-2048.jpg)


