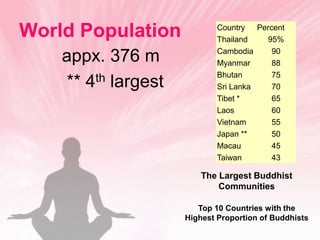
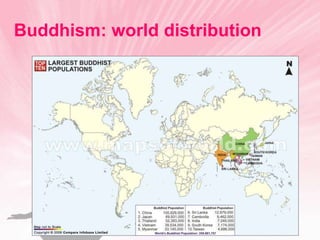
Buddhism originated in India over 2,500 years ago and was founded by Siddhartha Gautama. The religion's core beliefs are the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, which provide guidance for followers to end suffering by eliminating desire and reaching a state of nirvana. Buddhism spread from India and now has over 376 million followers worldwide, with most Buddhists living in countries like Thailand, China, Japan, and Sri Lanka. Key concepts include reincarnation, karma, and rejection of the caste system and gods.