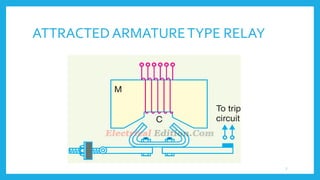
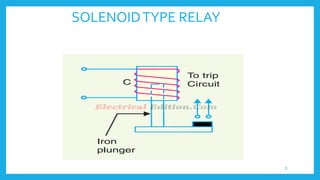
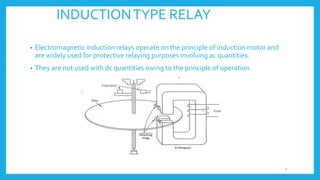
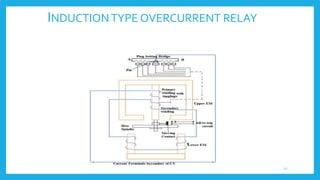
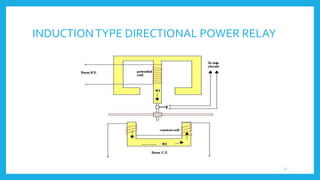
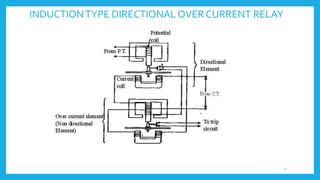
This document presents information on protective relays. It begins by stating why electrical systems need protection from faults, then defines what a relay is and its purpose of tripping circuit breakers when faults are detected. The operating principles of electromagnetic attraction and induction are described. Types of relays are discussed, including attracted armature, solenoid, induction overcurrent, and induction directional power and overcurrent relays. Examples of each type are shown. The presentation concludes by noting that protective relays are essential for isolating faults and protecting equipment.