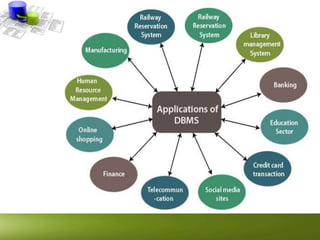
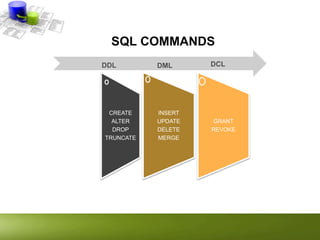
The document provides an overview of Data Manipulation Language (DML) within relational database management systems (RDBMS), highlighting key SQL commands such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE used for database modifications. It explains CRUD operations for managing data and differentiates between procedural and non-procedural programming. Additionally, it offers syntax examples and practical applications for each command type within the context of a relational database like MySQL.