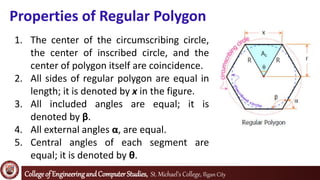
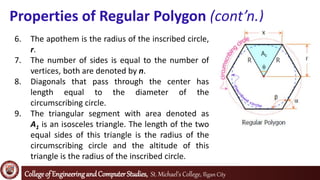
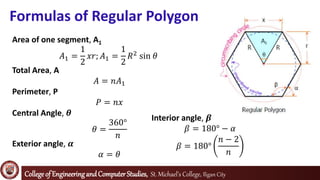
The document defines and explains properties of regular polygons. It states that regular polygons are polygons with all sides of equal length and all interior angles of equal measure, making them both equilateral and equiangular. It then lists nine properties of regular polygons, including that the center of the circumscribing circle, inscribed circle, and polygon coincide and that diagonals through the center are equal to the diameter. Formulas are provided for the area of each polygon segment, total area, perimeter, central angle, exterior angle, and interior angle of regular polygons. Examples are given to find the area of a regular pentagon and shaded region of an overlapping triangle configuration related to a regular hexagon.