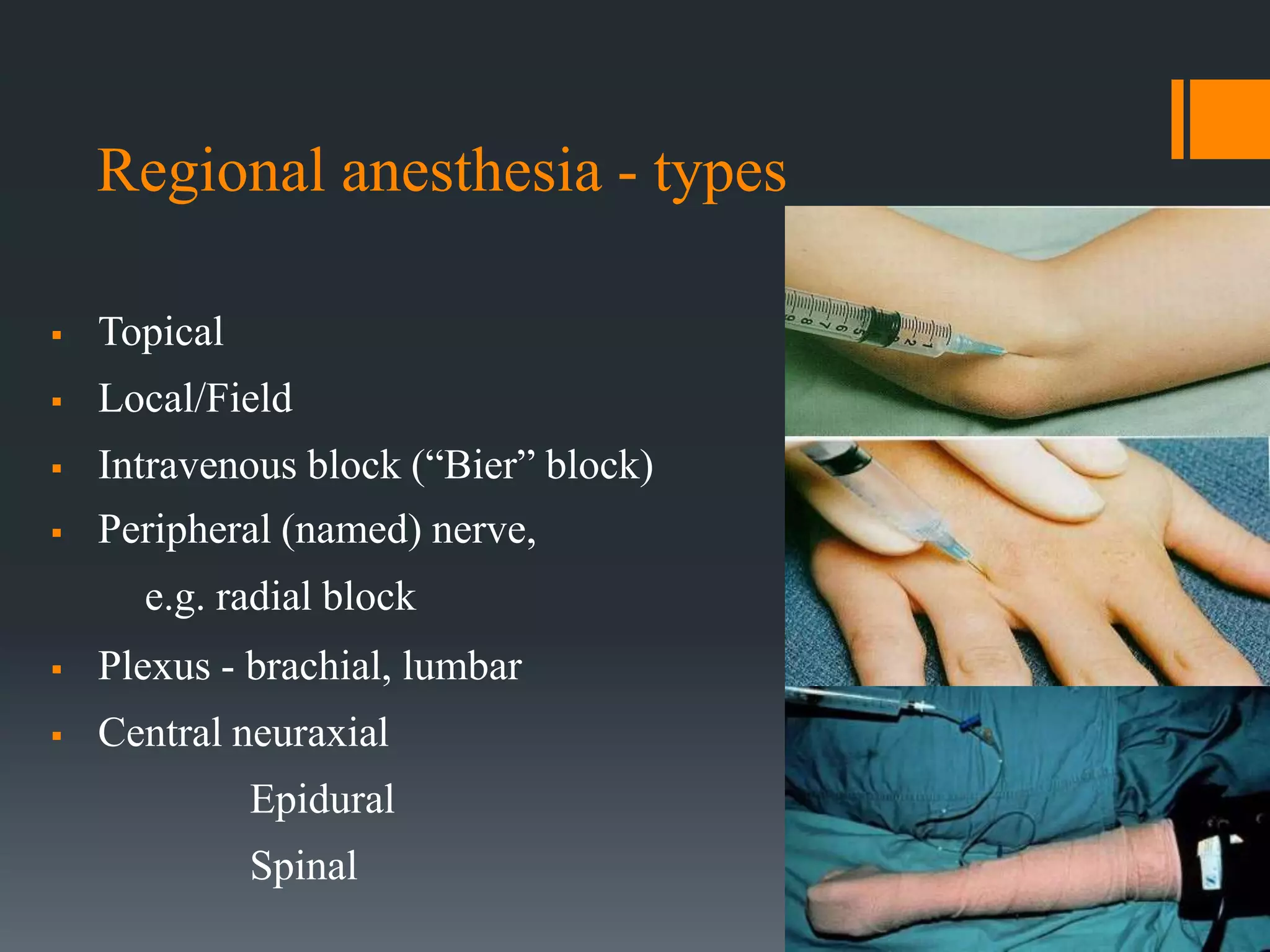
Local anesthetics work by blocking sodium channels in nerves, preventing the propagation of action potentials and sensation of pain. There are two classes: esters and amides. Lidocaine is a commonly used amide that has a quick onset and lasts several hours. Regional anesthesia involves administering local anesthetics to specific body areas and can be used for surgery, post-op pain relief, and other procedures. Potential complications include local tissue toxicity, allergy, and overdose. Proper administration and monitoring can help prevent complications.