The document discusses refractometry and the use of refractometers. It provides details on:
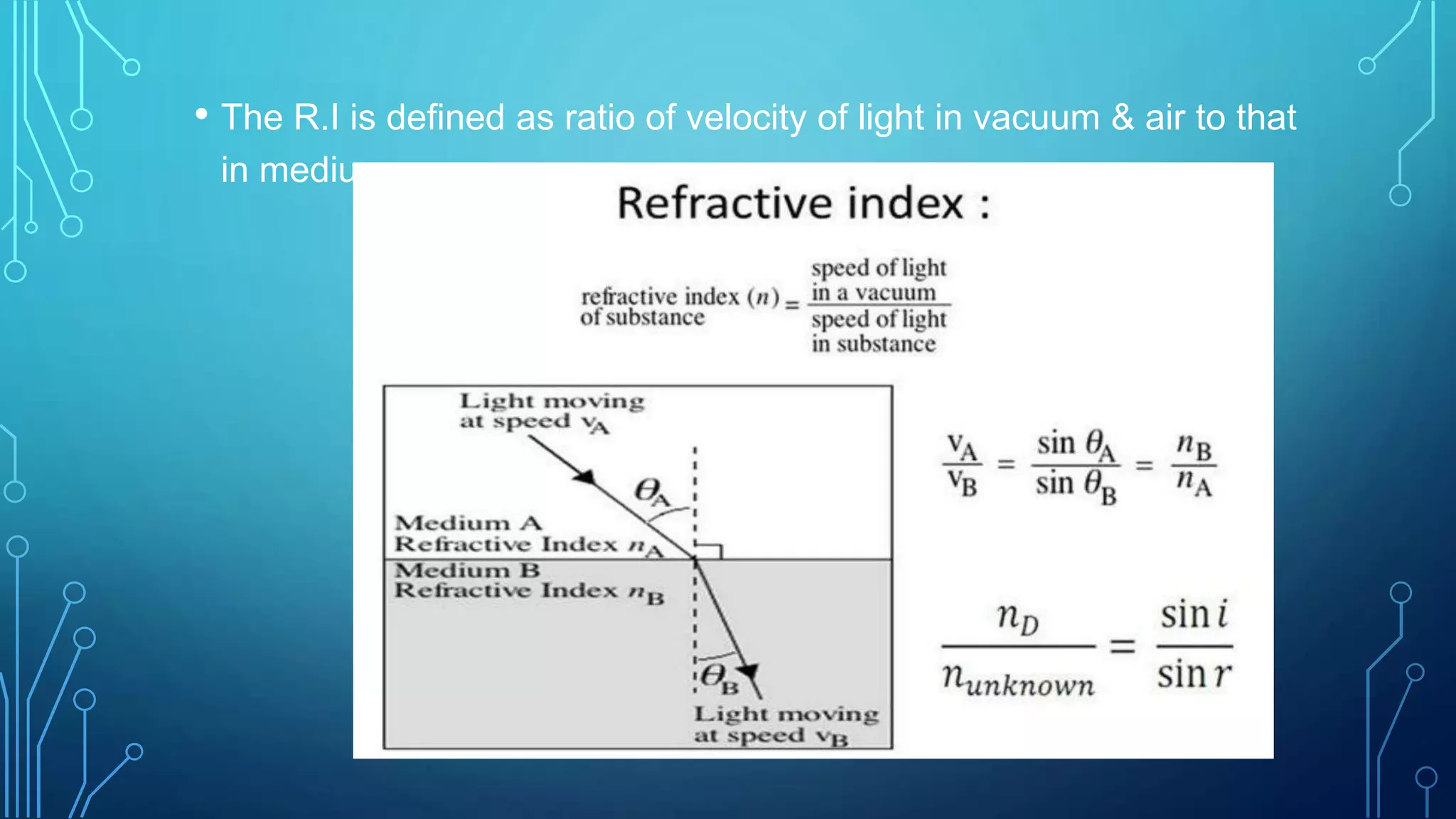
- The principle of refractometry which involves measuring the angle of refraction when light passes from one medium to another of different densities.
- Applications of measuring refractive index including characterizing liquids and solids, measuring concentration of solutions, and checking purity.
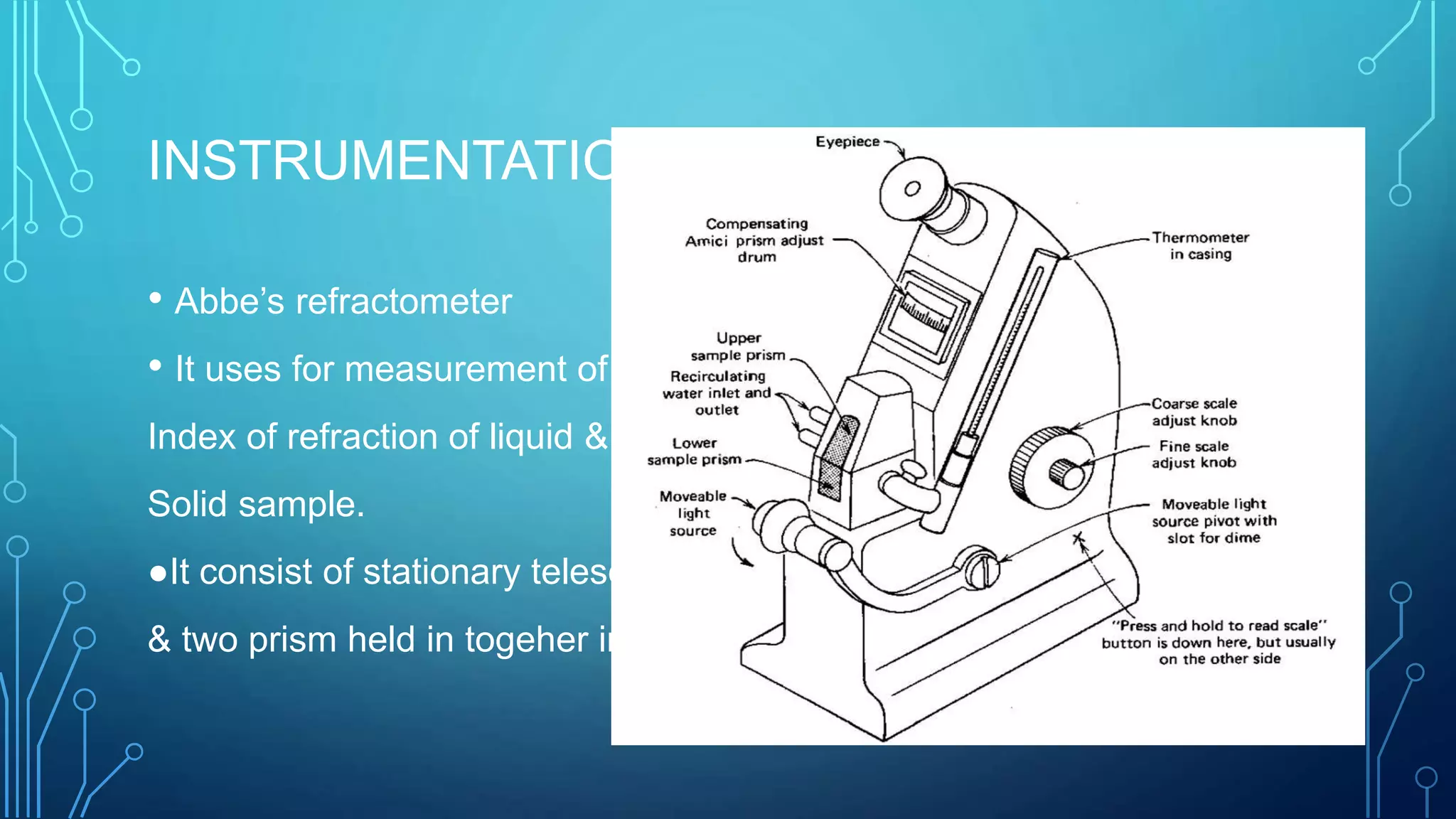
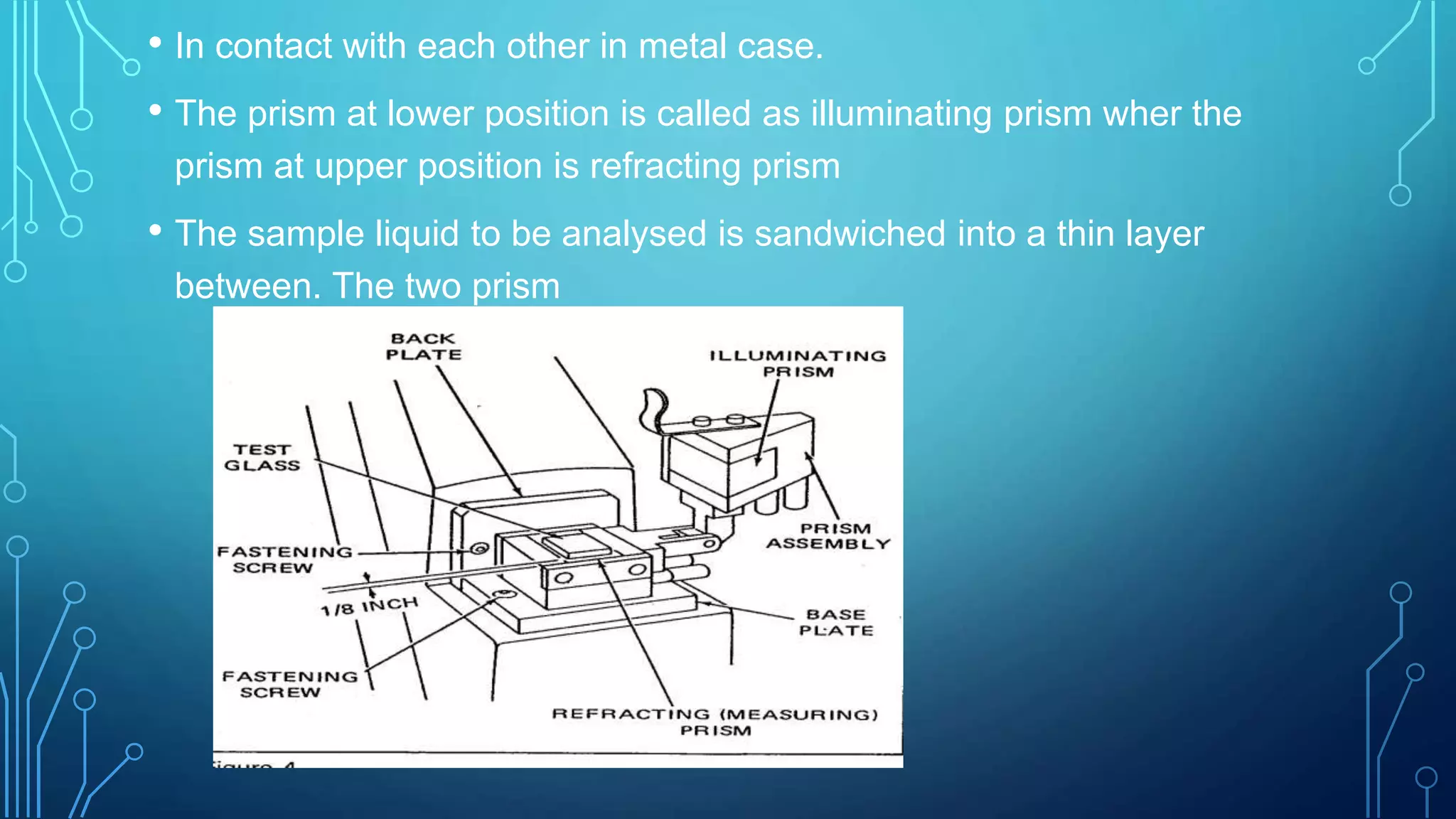
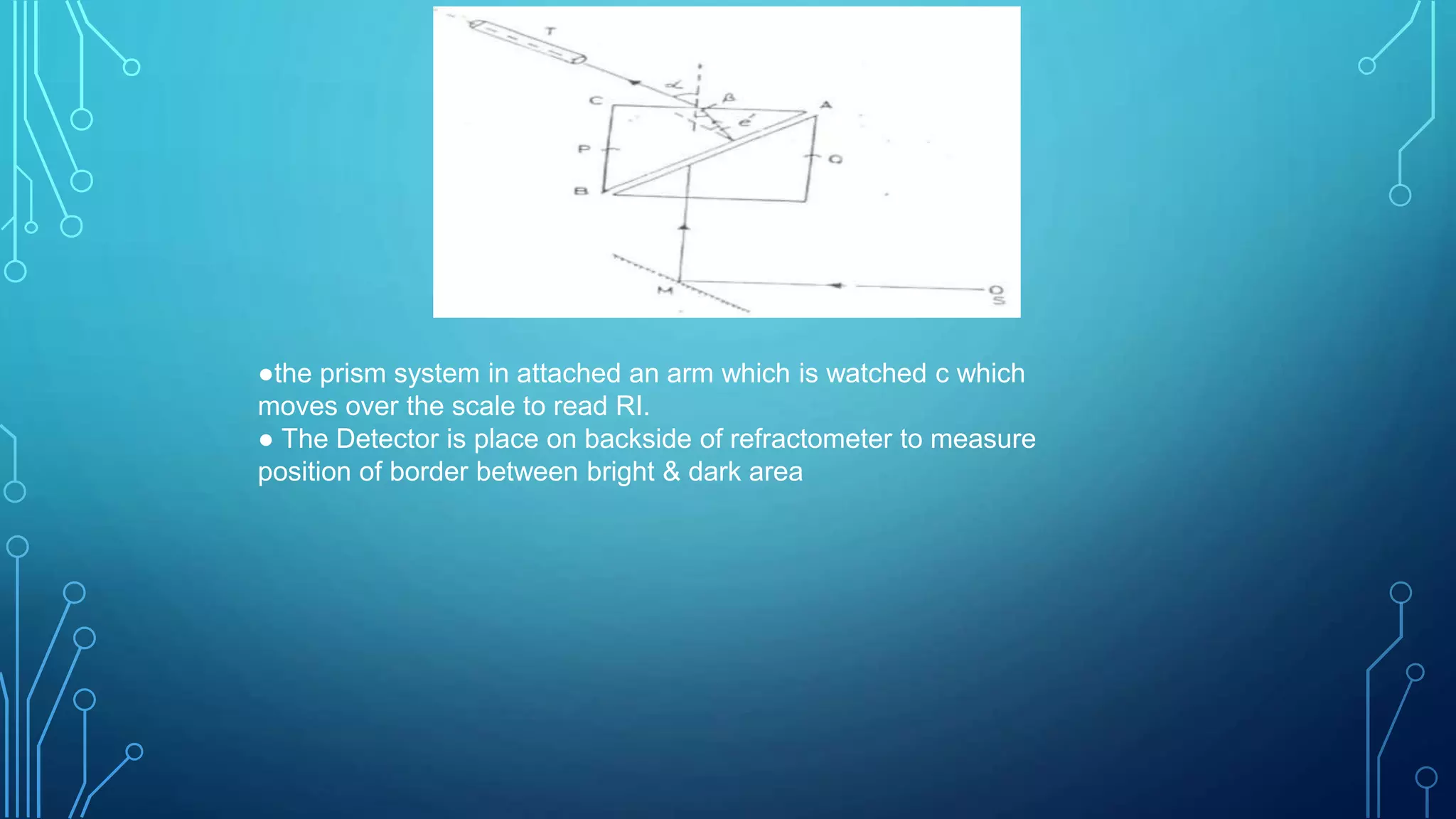
- The instrumentation of Abbe's refractometer which uses two prisms to create a thin film sample and measures the refractive index reading on an attached scale.
- Uses of refractometry such as determining sugar and alcohol content in solutions and qualitative/quantitative analysis of samples.