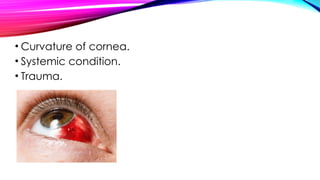
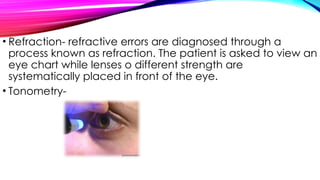
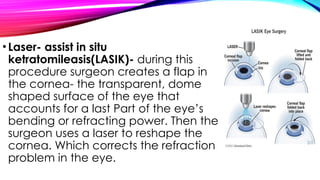
The document discusses refractive errors, common eye disorders that result in blurred vision due to improper focus of light on the retina. It highlights various types including myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and presbyopia, their causes, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, and management options, both medical and surgical. The prognosis for refractive errors is generally good, often manageable with corrective lenses or surgery, emphasizing the importance of regular eye examinations.