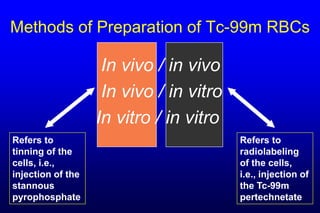
1. There are multiple methods for labeling red blood cells with Tc-99m, including in vivo, in vitro, and modified techniques.
2. GI bleeding studies are best done with Tc-99m RBCs prepared using the packed cell or UltraTag kit techniques to achieve high labeling efficiency.
3. White blood cells can be easily labeled with either Tc-99m or In-111 by isolating WBCs and incubating them with a lipophilic intermediate.
4. Red blood cell labeling with Cr-51 is very simple, not requiring isolation of RBCs, just incubation of blood with Cr-51.