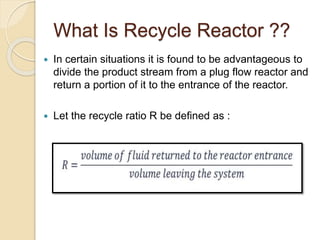
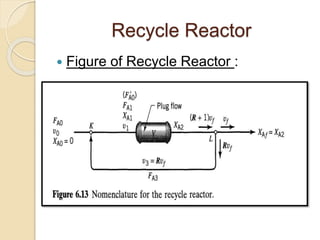
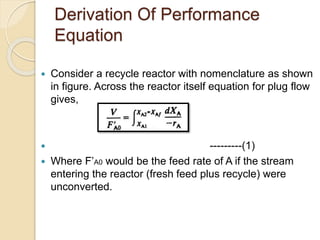
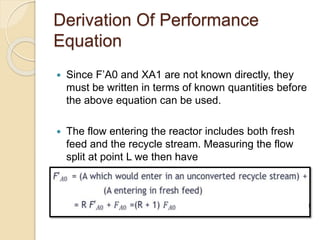
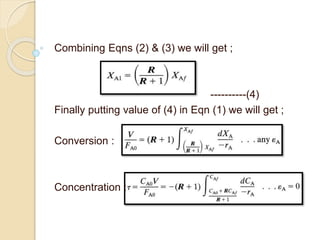
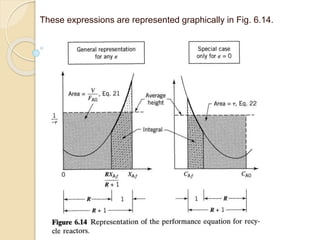
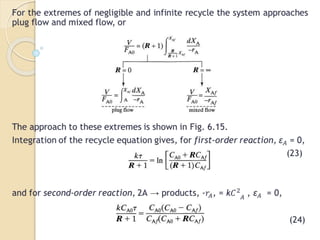
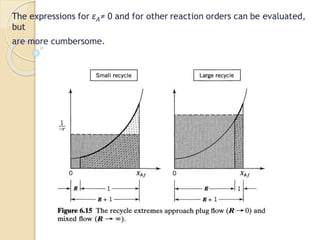
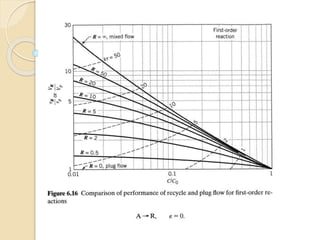
A recycle reactor allows a portion of the product stream from a plug flow reactor to be returned to its entrance, providing varying degrees of backmixing. Advantages include improved conversion rates compared to traditional plug flow reactors, but higher fixed and operating costs due to increased reactor volume. This type of reactor is particularly useful in the petroleum industry and for processes requiring the recycling of enzyme-rich streams.