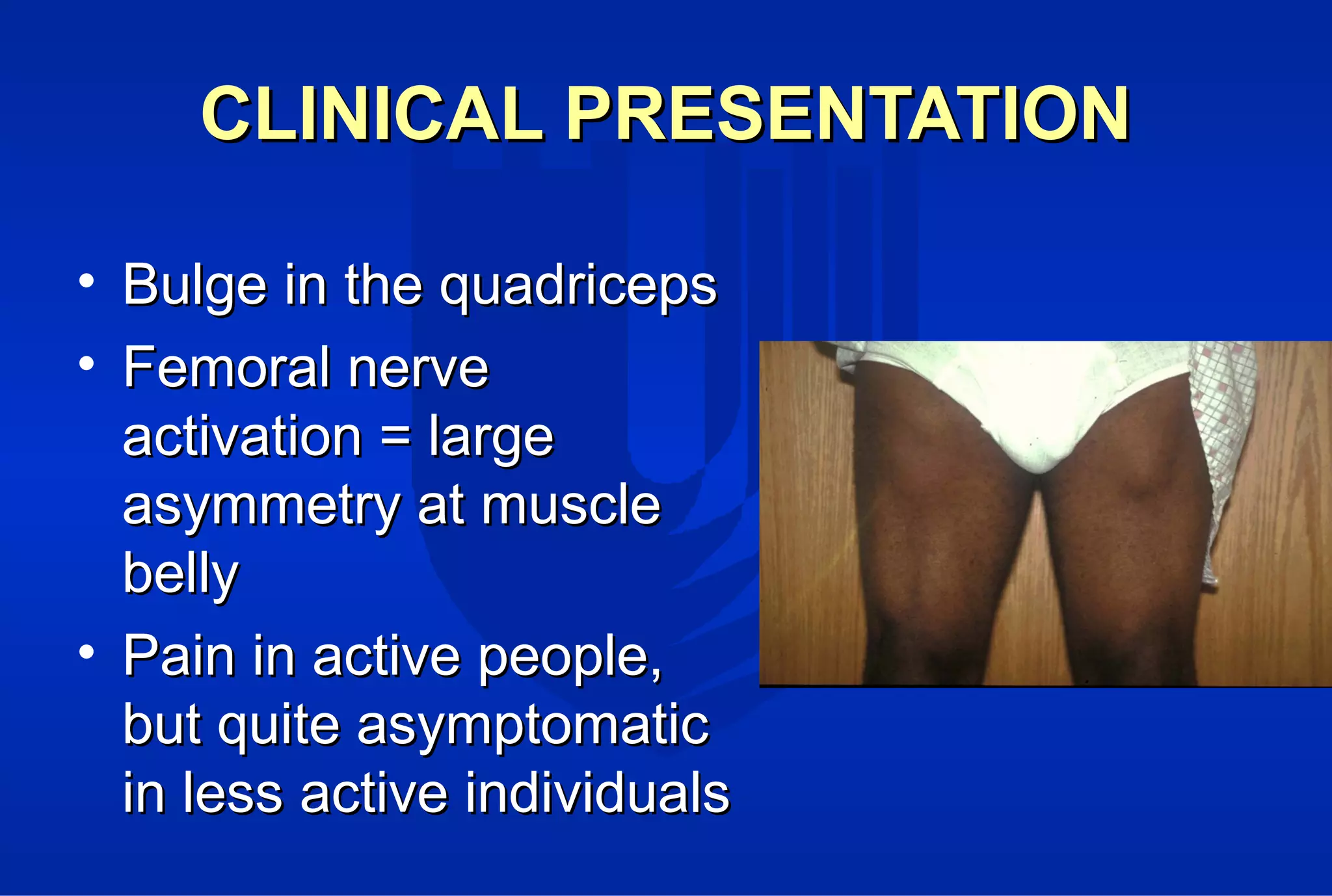
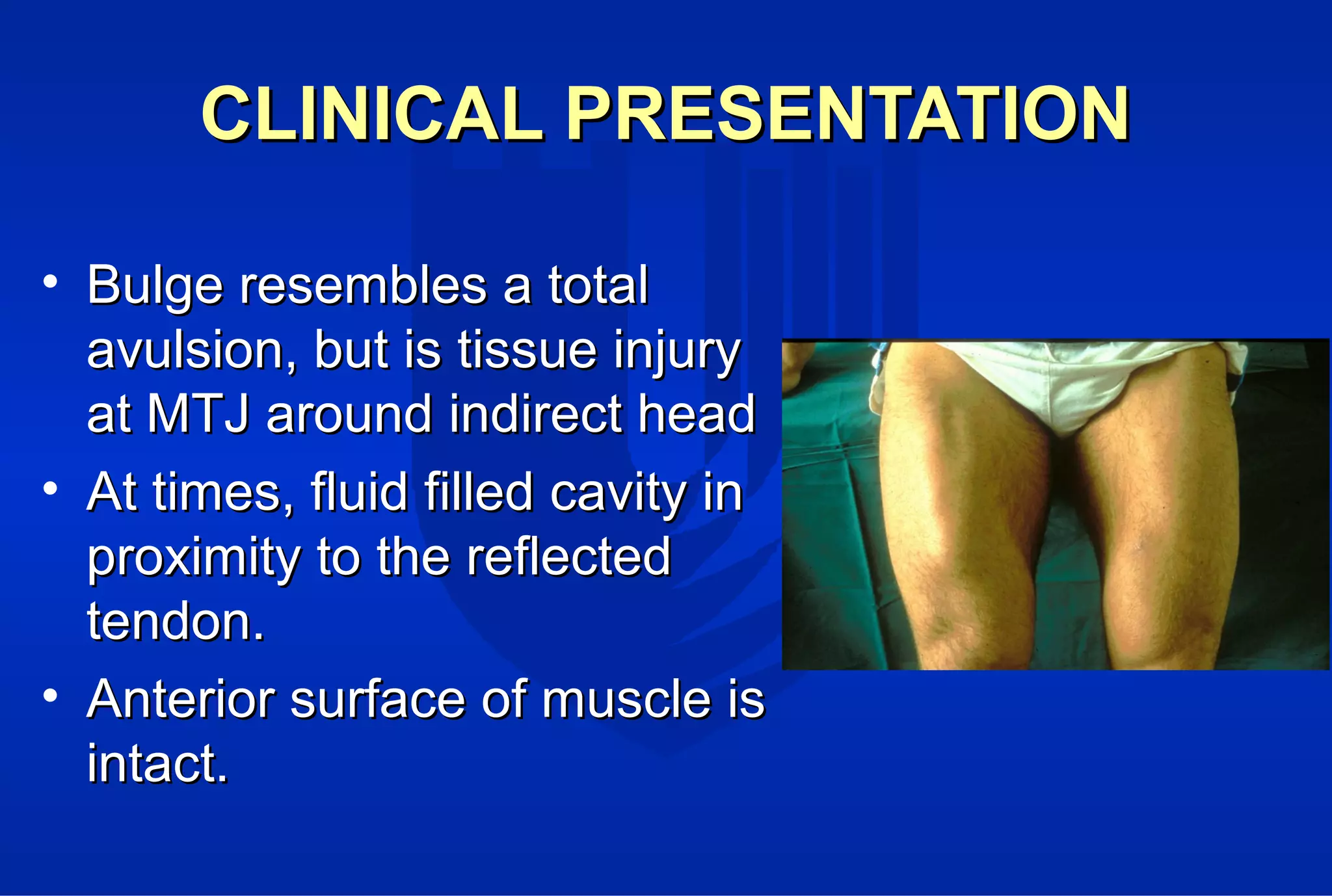
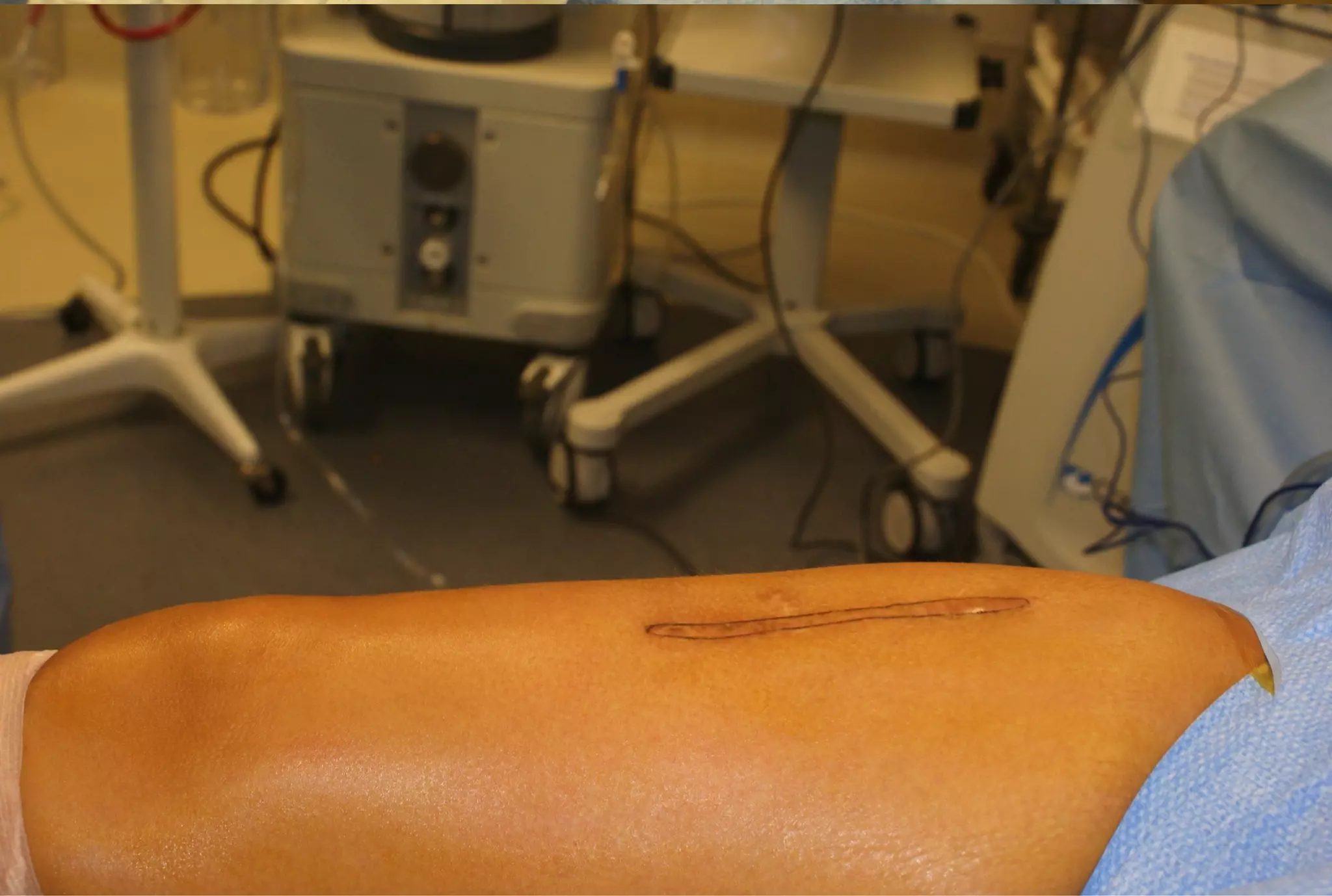
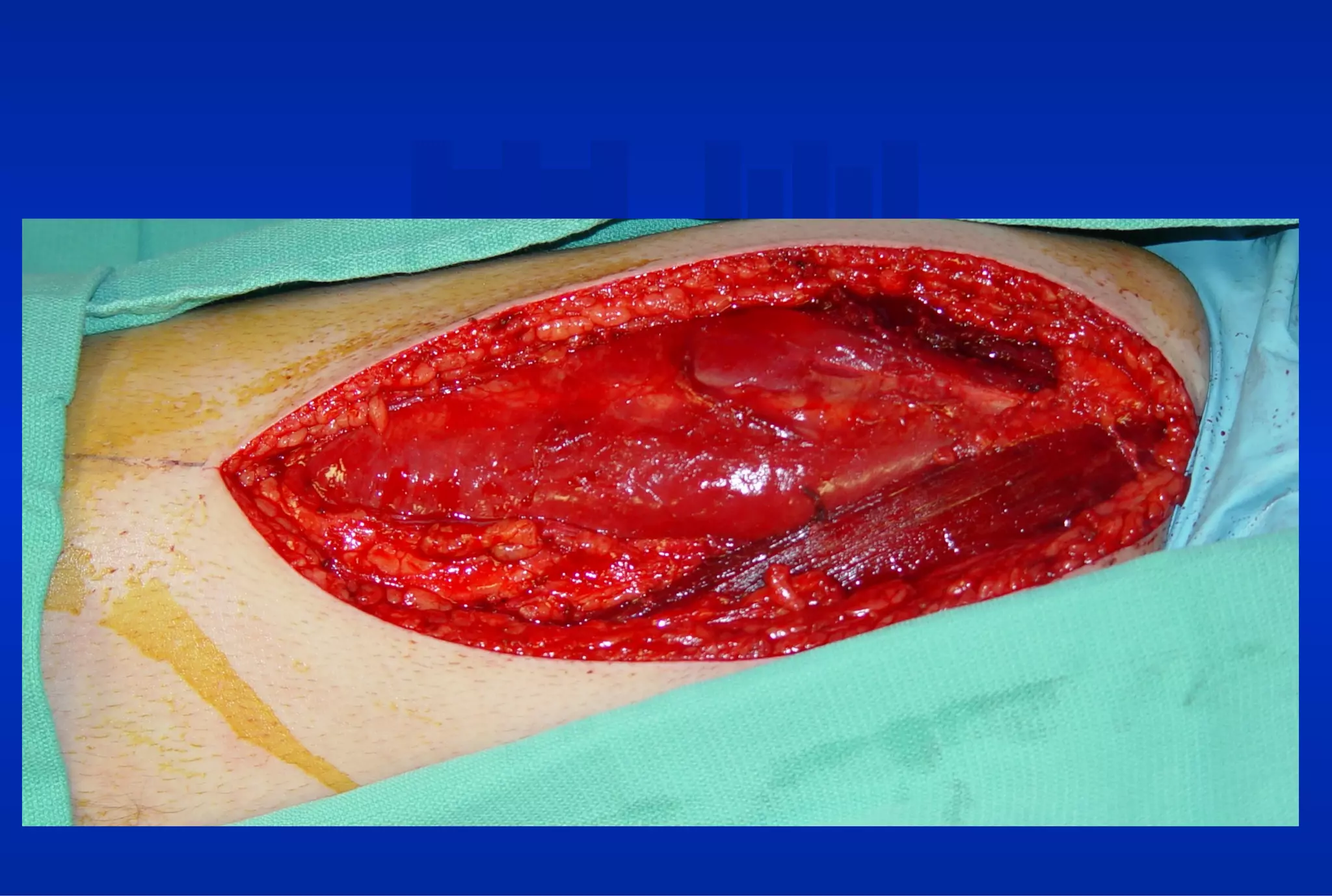
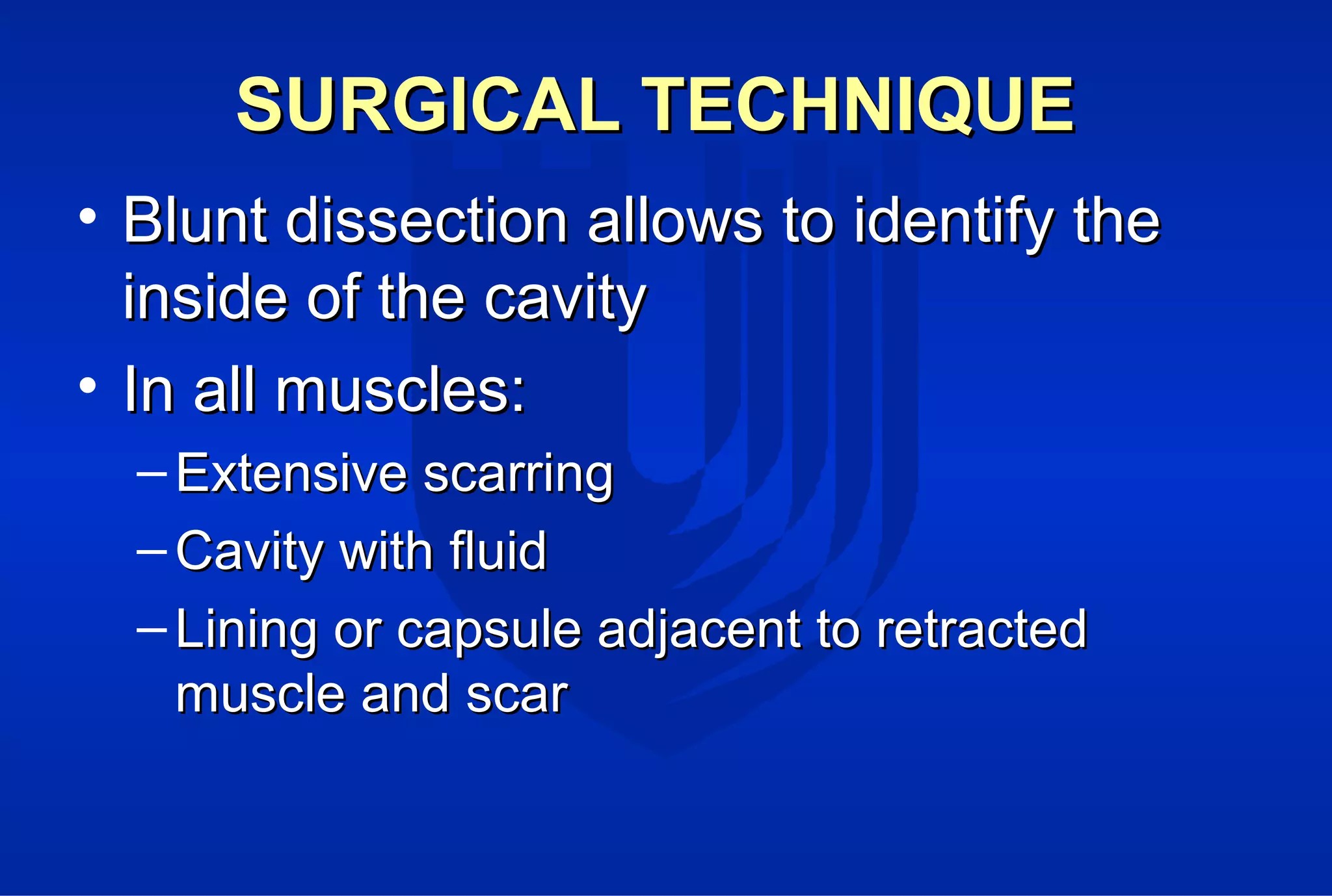
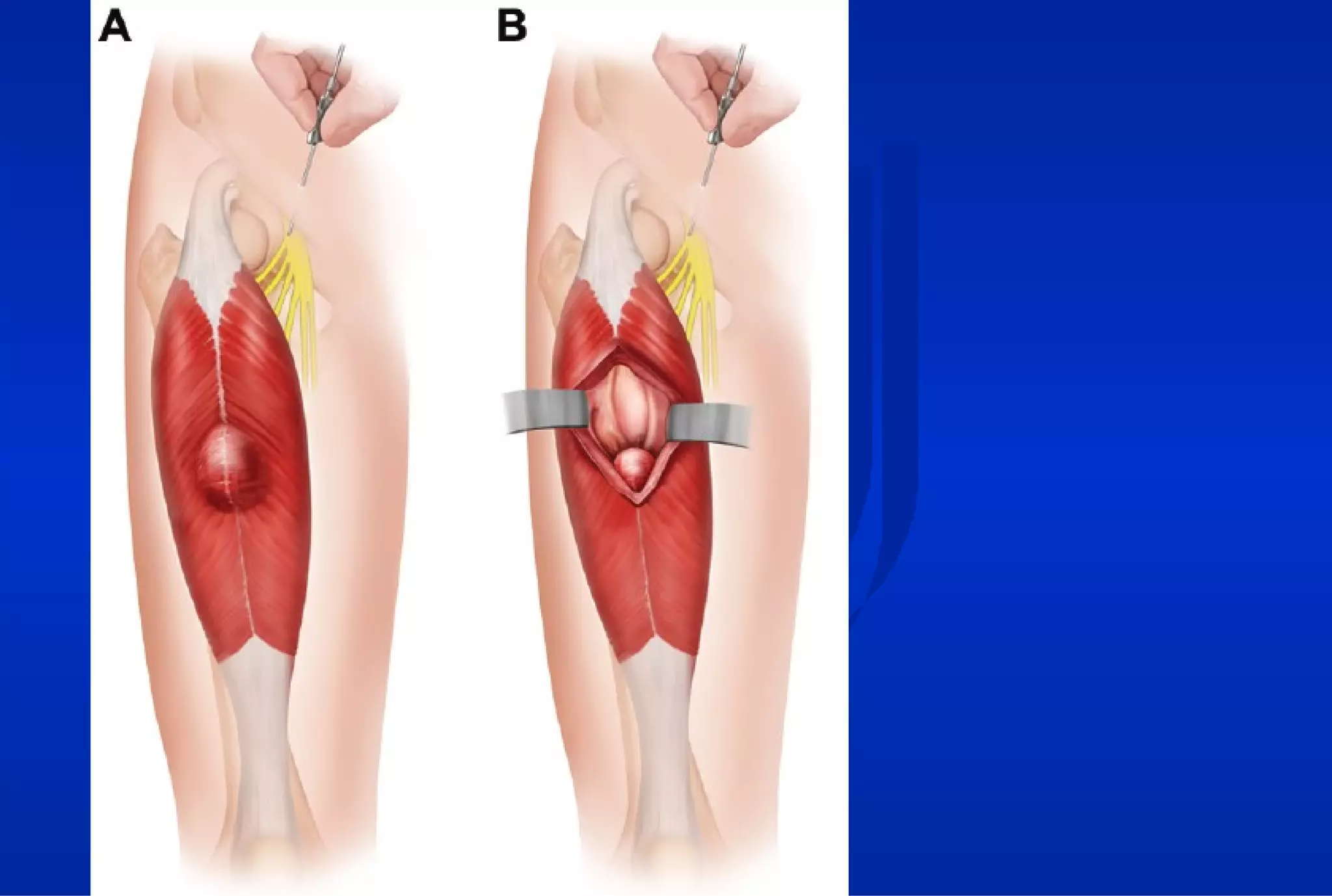
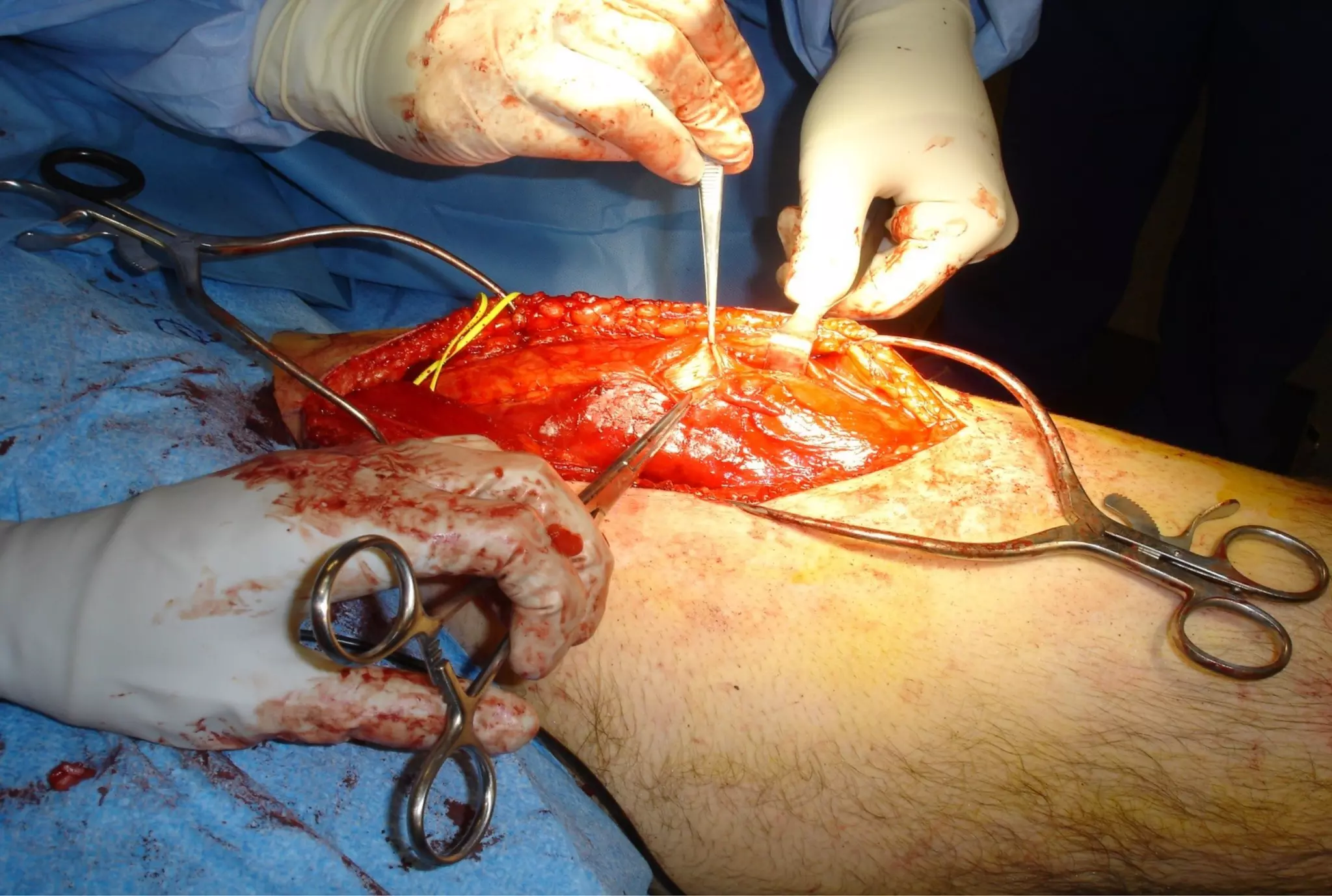
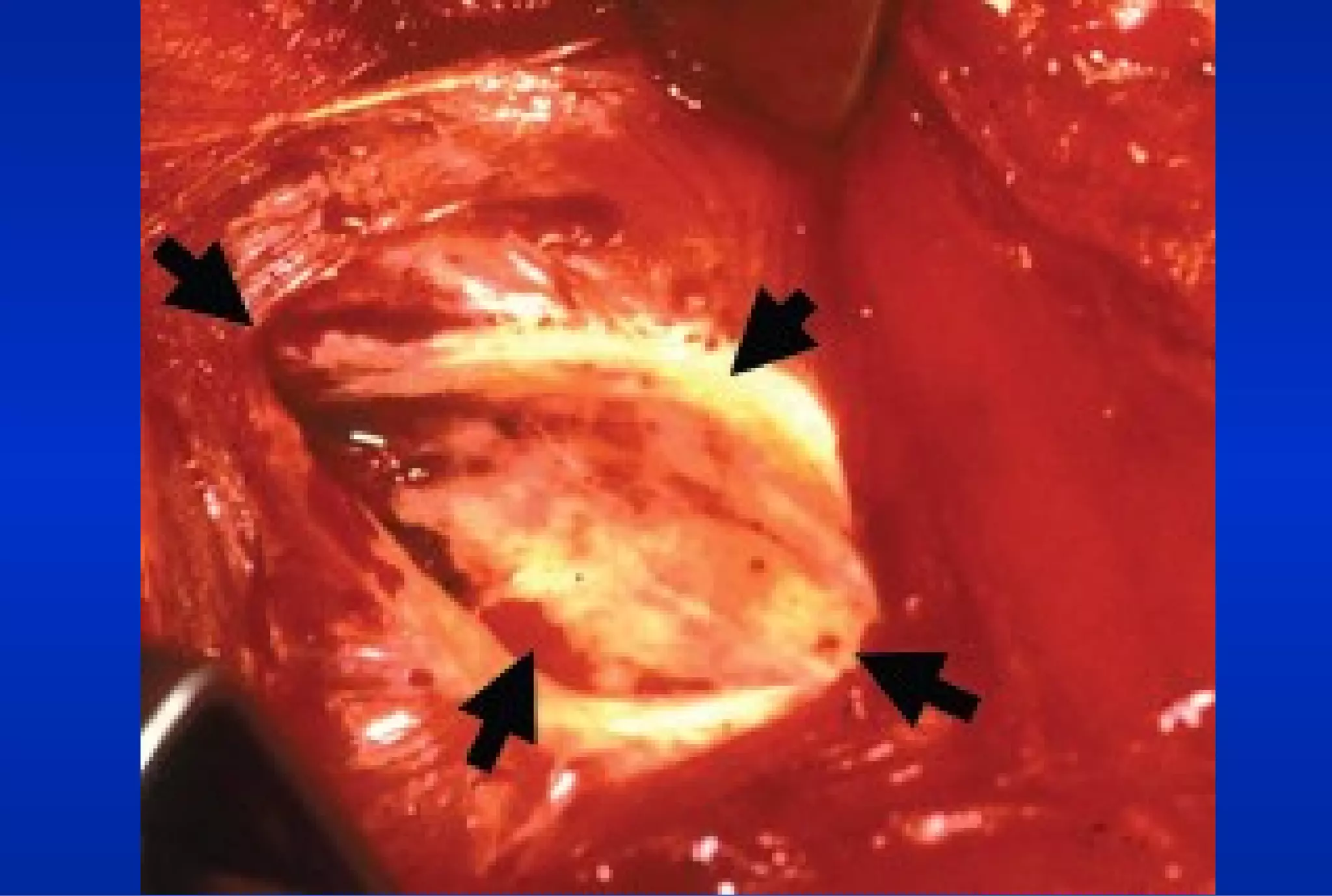
Surgical treatment of rectus femoris muscle injuries is typically only considered for indirect head injuries within the muscle belly that have not responded to conservative treatment involving physical therapy and injections. The surgical technique involves identifying the injured tissue within the muscle through nerve stimulation and blunt dissection, then removing the scarred muscle. While pain is often significantly reduced with surgery, athletes may experience some recurrence of symptoms upon return to sport within 7-12 months. However, surgery generally allows athletes to return to sports without limitations. Surgery should only be pursued if conservative treatments fail to allow an active patient to perform without pain limitations.