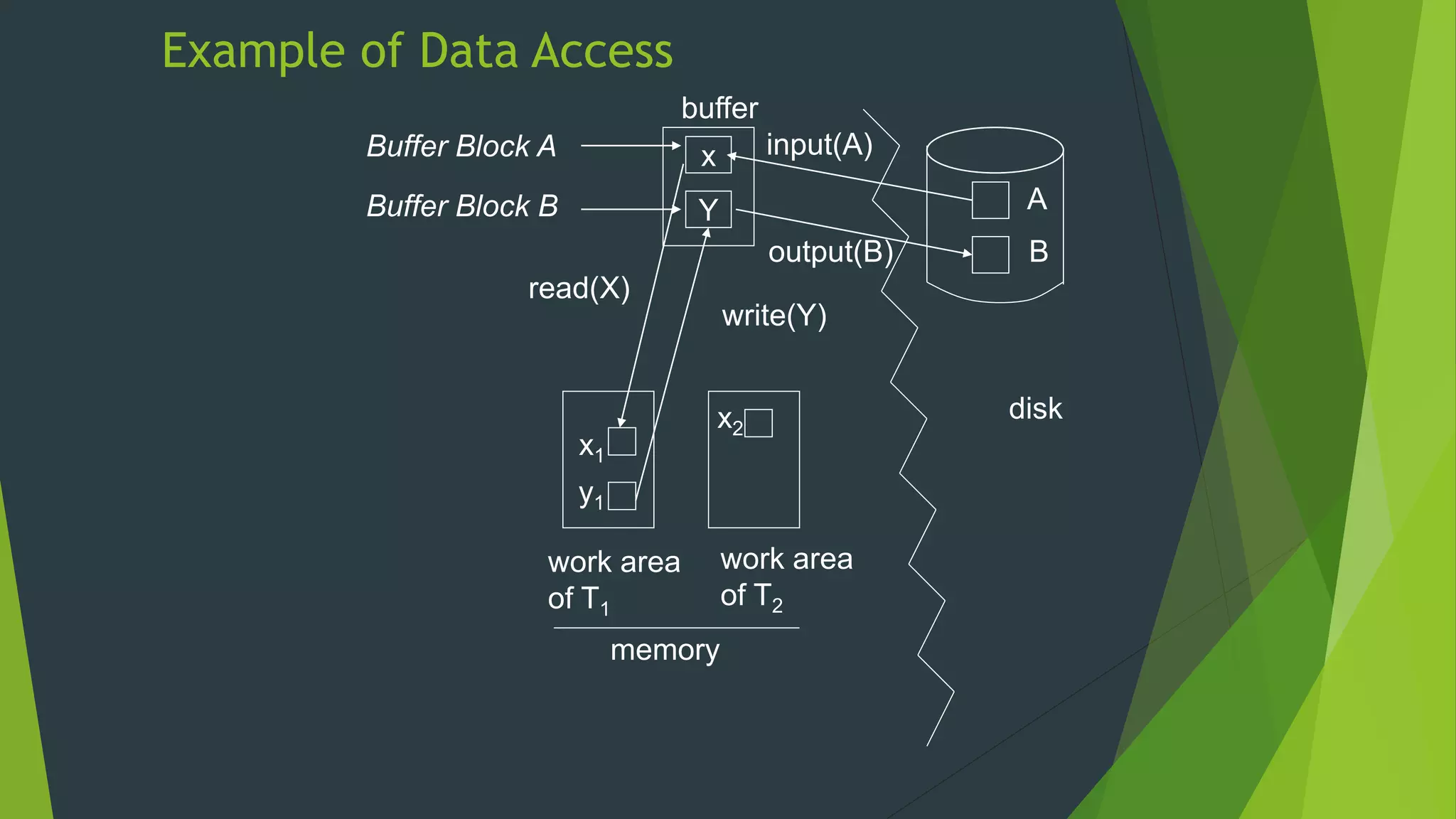
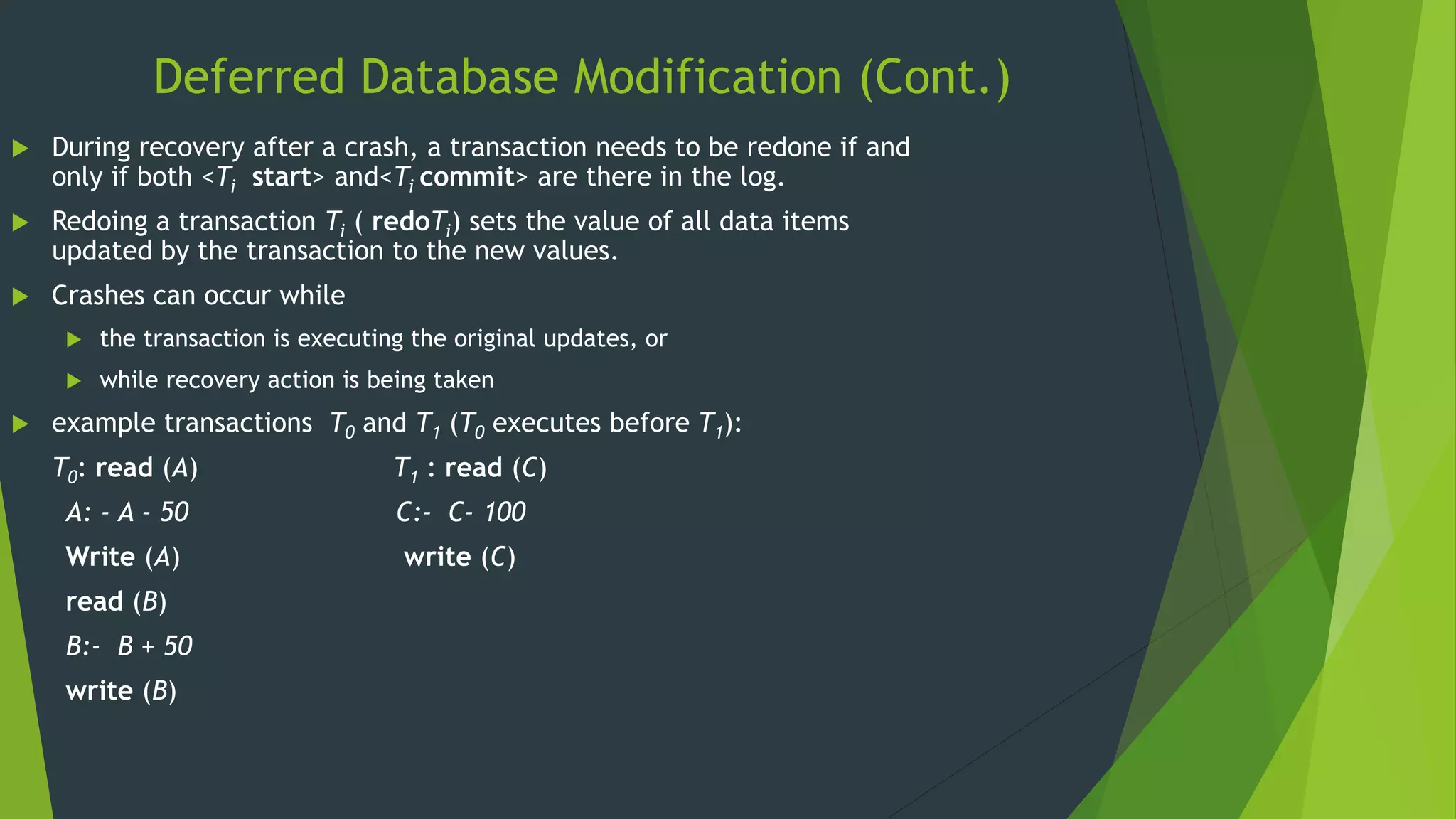
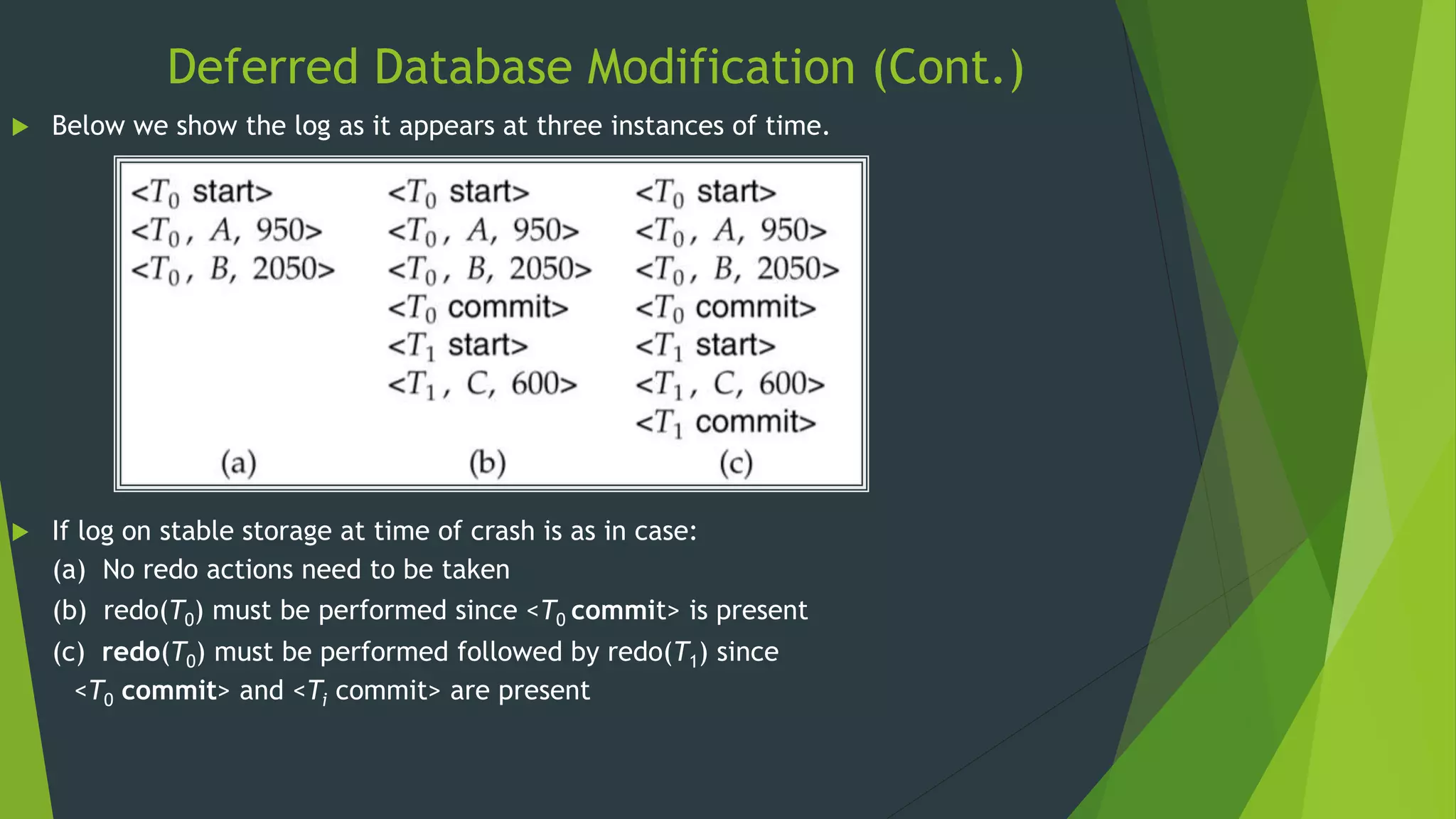
Recovery System
The document discusses database recovery systems. It defines recovery as recovering a system from a failure or crash. It covers failure classification, storage structures like volatile vs non-volatile storage, recovery algorithms like log-based recovery and shadow paging, logging techniques for concurrent transactions, and checkpointing to improve recovery performance.