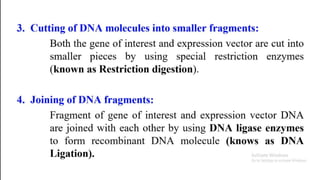
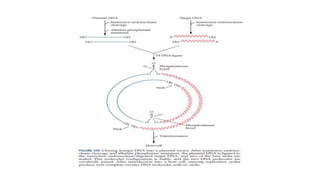
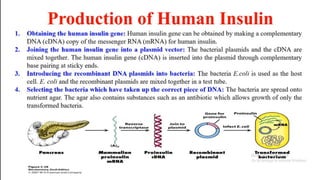
This document summarizes a presentation on advances in microbial biotechnology focusing on recombinant DNA technology and products produced by genetically engineered microorganisms. It introduces various enzymes used in recombinant DNA technology, including DNA ligase, reverse transcriptase, restriction endonucleases, terminal transferase, nuclease, DNA polymerase, and others. It then discusses some examples of products developed through recombinant DNA technology like golden rice, Flavr Savr tomato, and therapeutic proteins like human growth factors, enzymes for cystic fibrosis and Gaucher's disease.