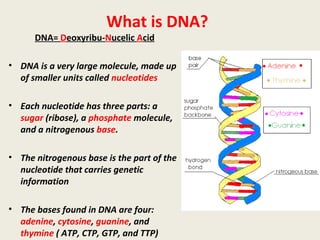
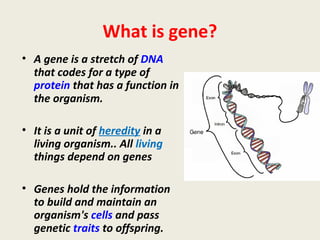
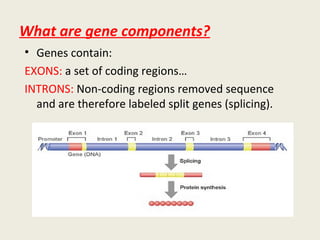
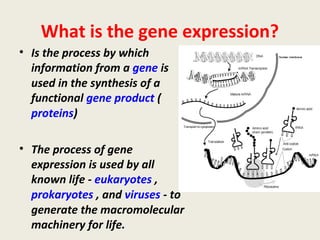
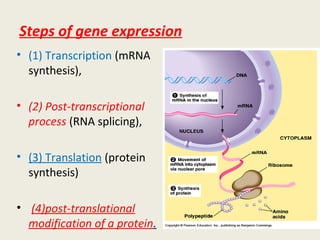
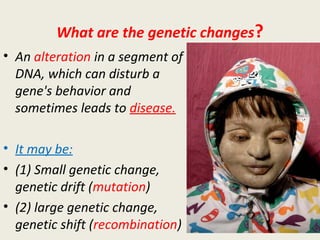
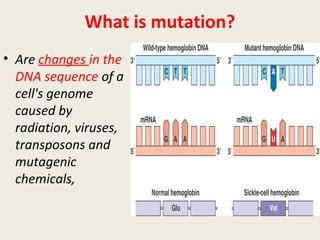
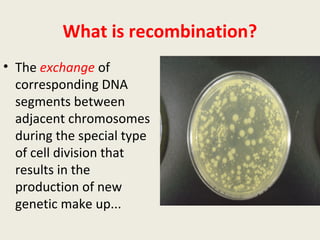
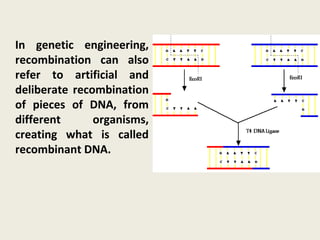
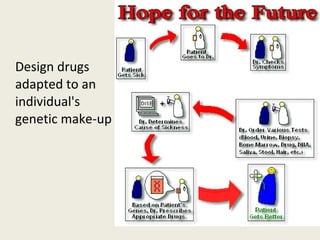
DNA contains genes that code for proteins and hold the genetic information passed down from parents to offspring. Recombinant DNA technology uses genetic engineering techniques to cut and join DNA molecules from different sources, creating recombinant DNA. This allows for important medical applications such as producing insulin and vaccines through recombinant DNA, treating genetic diseases with gene therapy, and developing pharmacogenomics to tailor drugs to a patient's genetic profile.