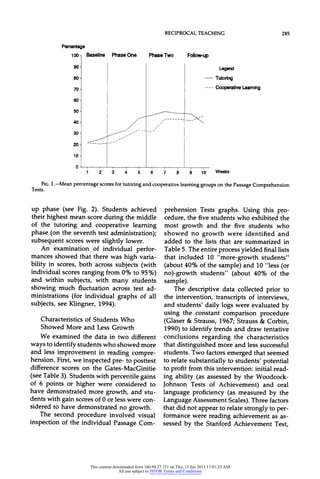
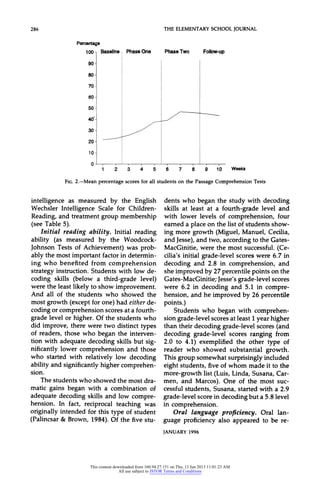
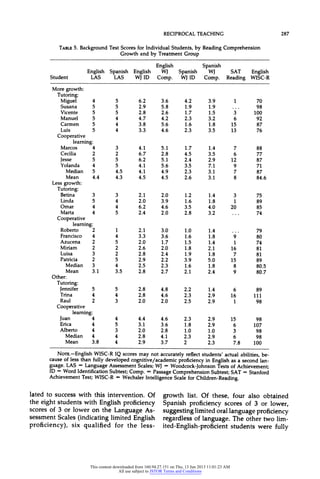
This study investigated the effects of two interventions on the reading comprehension of 26 7th and 8th grade students with learning disabilities who used English as a second language. All students first received 15 days of reciprocal teaching instruction in comprehension strategies. They were then randomly assigned to 12 days of either reciprocal teaching with cooperative grouping (n=13) or reciprocal teaching with cross-age tutoring (n=13). While no statistically significant differences were found between the groups, students in both groups made significant gains in reading comprehension. The study examined characteristics of more and less successful students to determine factors related to comprehension growth.