1) CP Optimizer is a modeling language that extends ILP and CP with interval variables and functions, allowing compact formulations for scheduling problems. It uses an automatic search algorithm that is complete, anytime, efficient, and scalable.
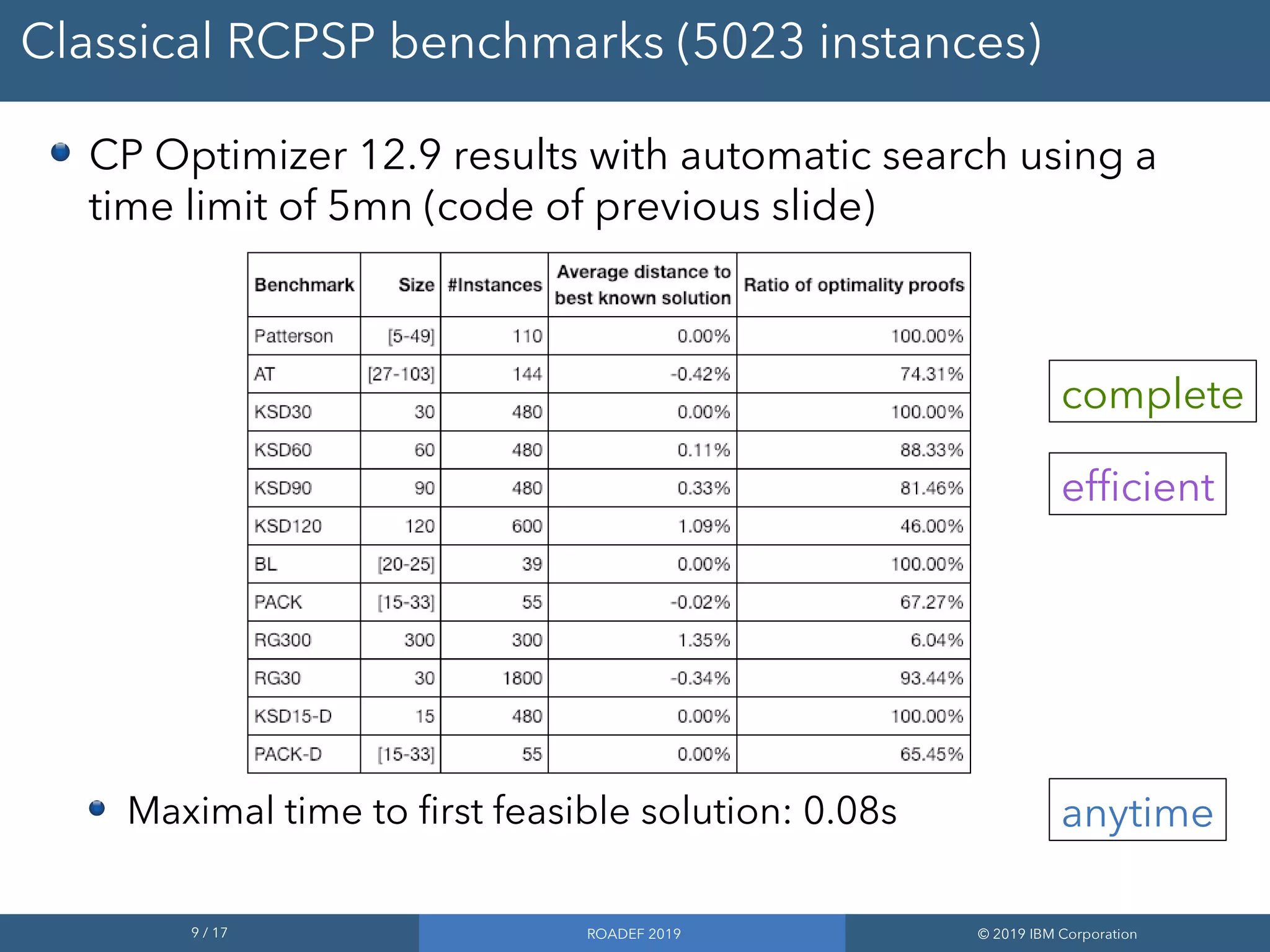
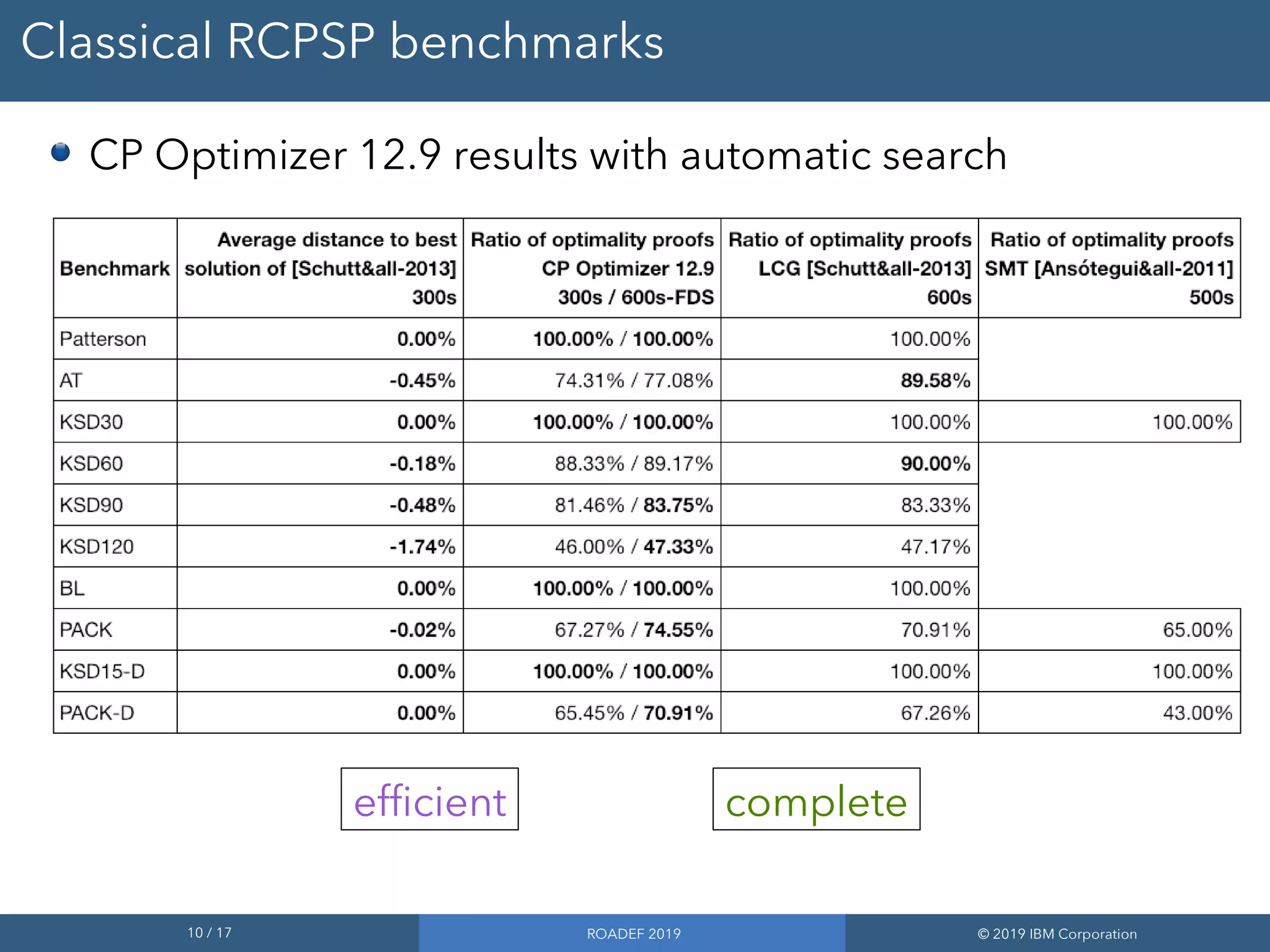
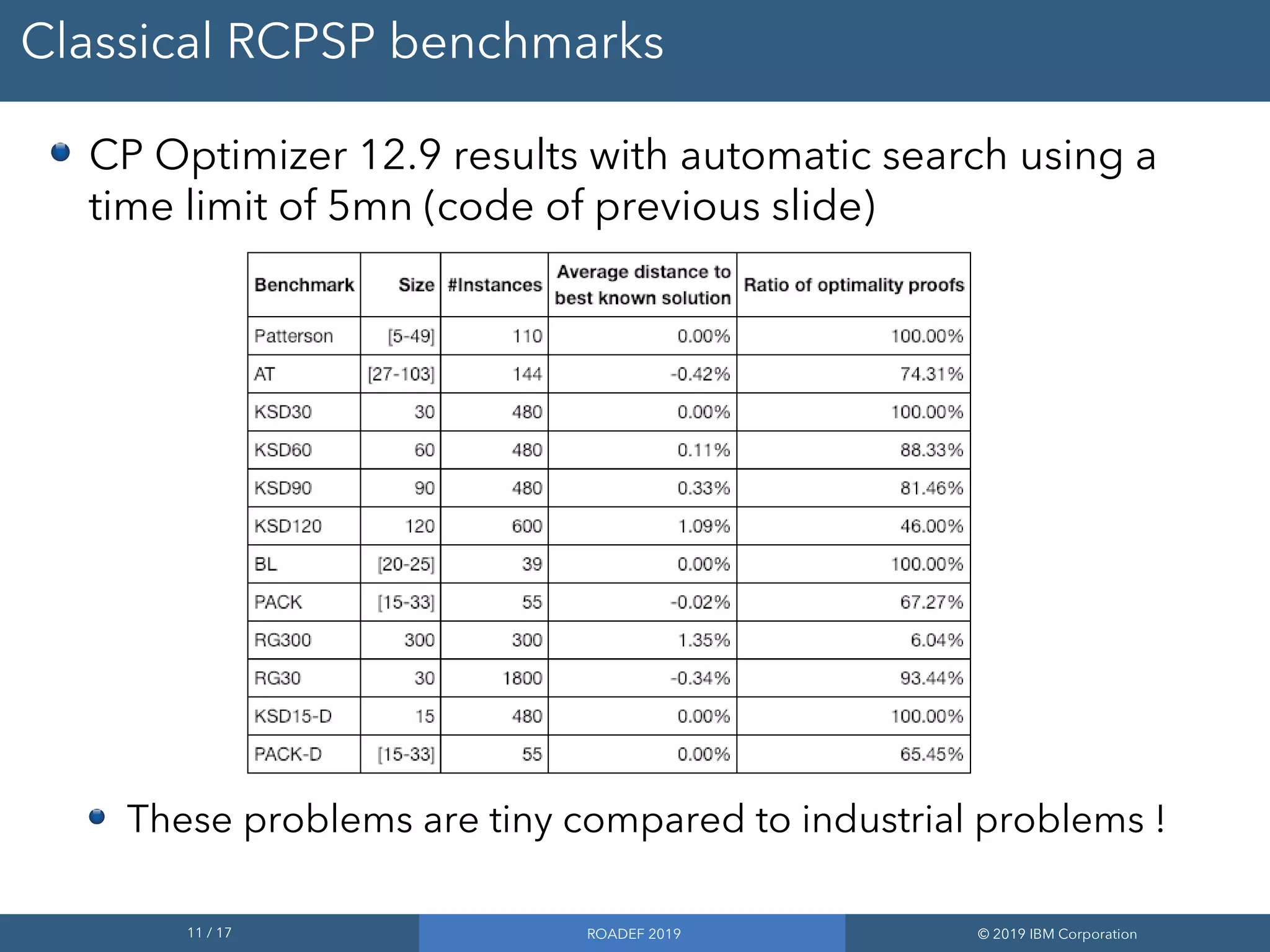
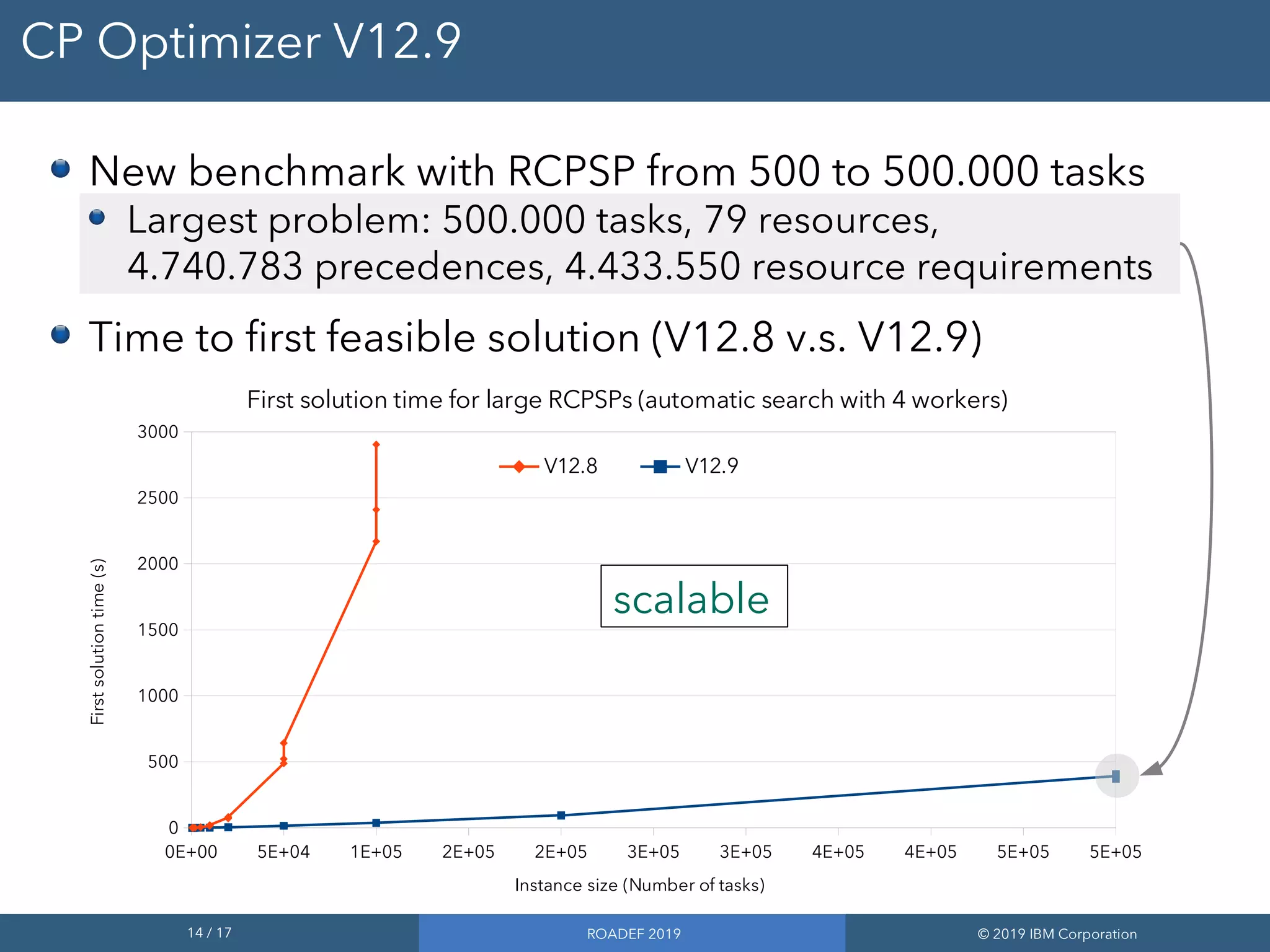
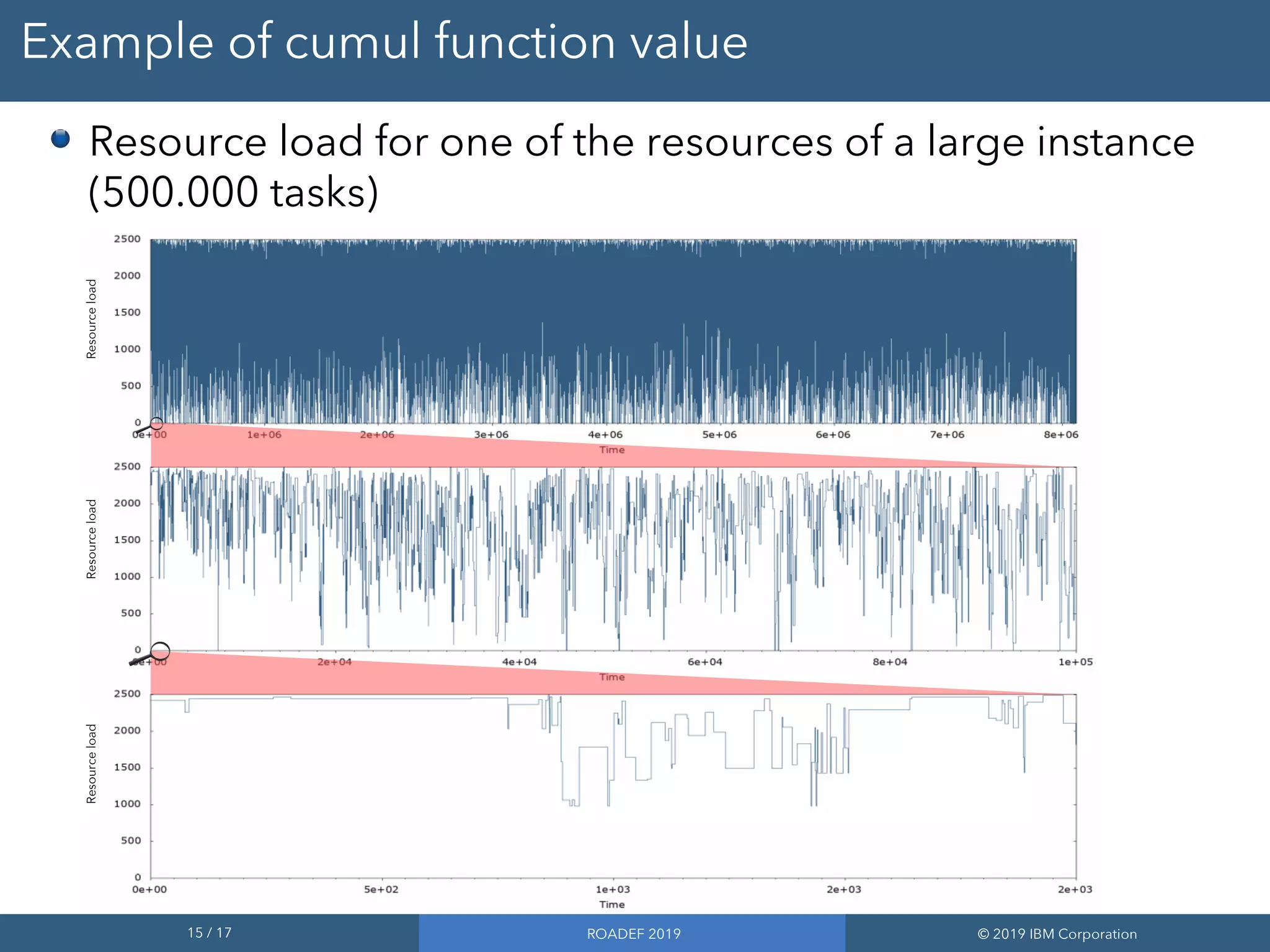
2) Performance improvements in the upcoming CP Optimizer 12.9 release allow it to solve classical RCPSP benchmarks quickly and address much larger instances with up to 500,000 tasks.
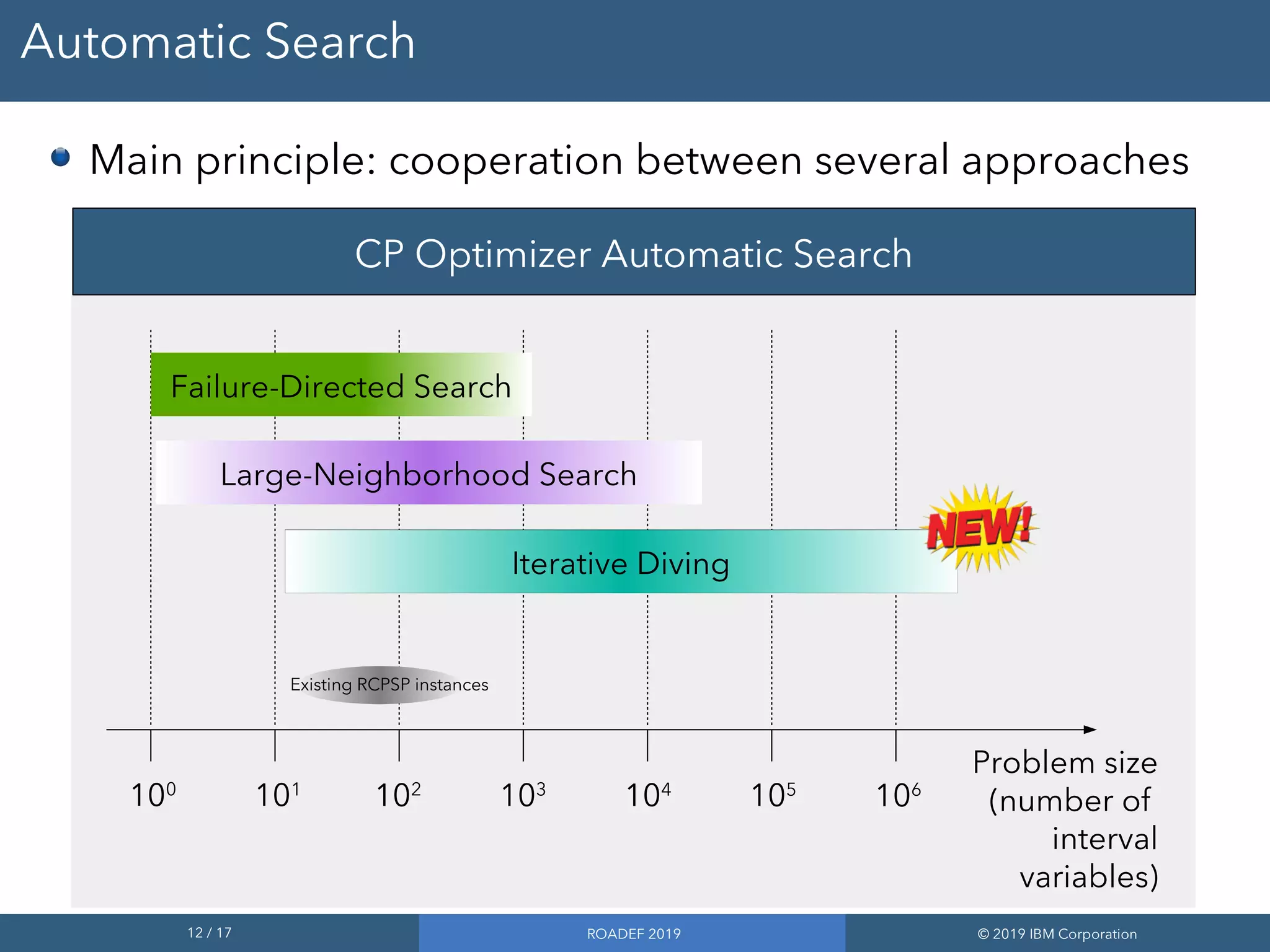
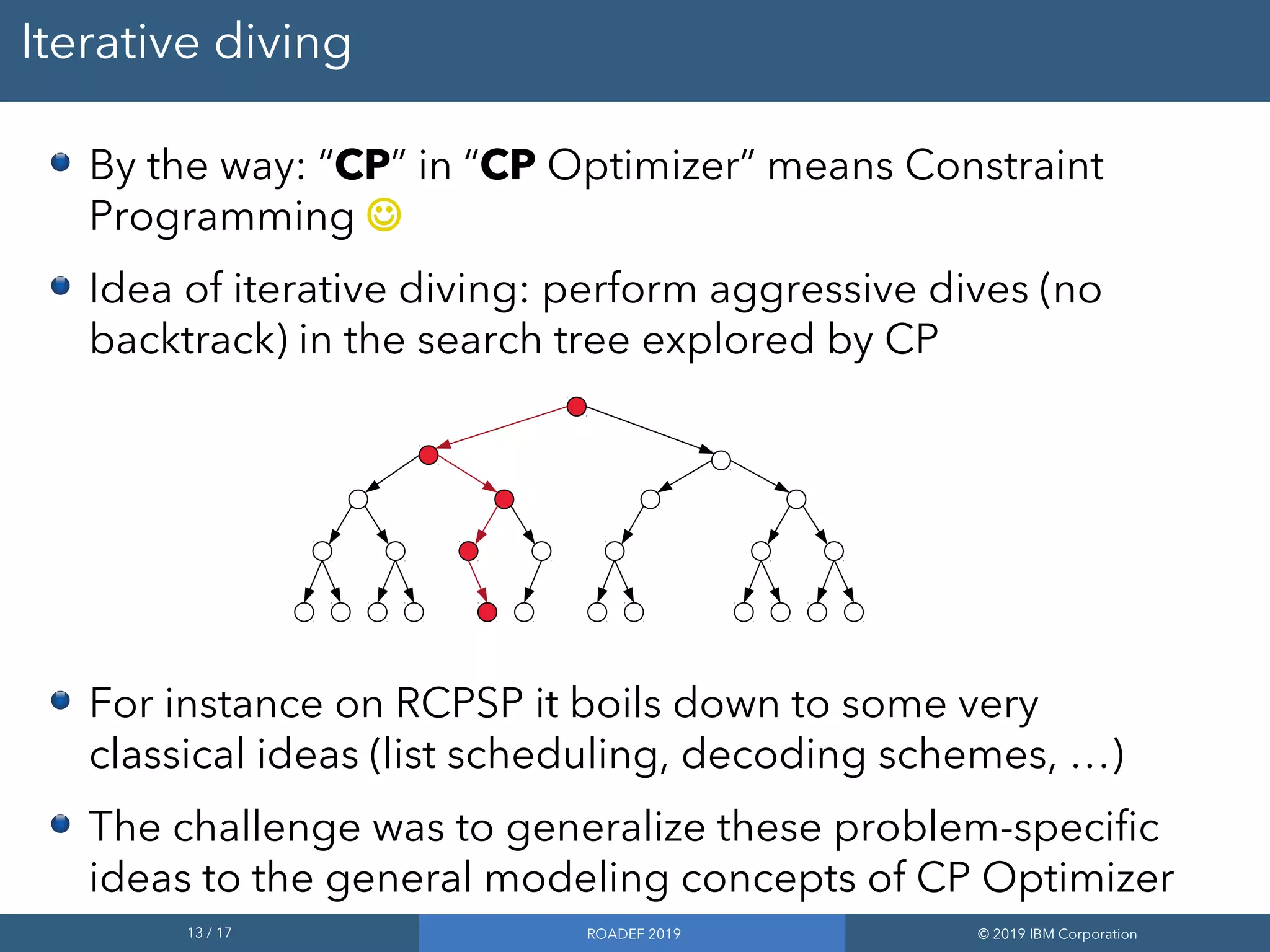
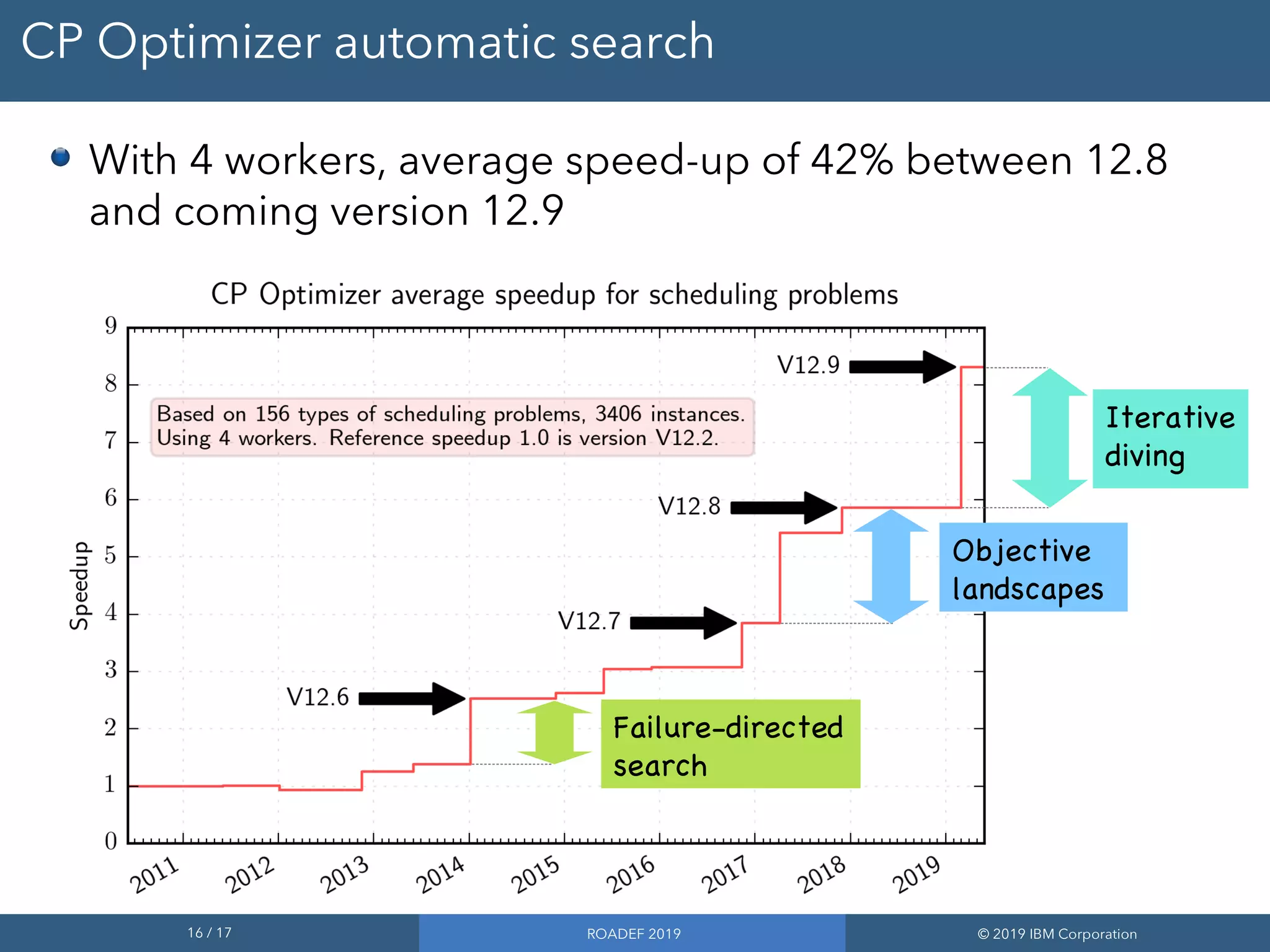
3) The automatic search employs techniques like failure-directed search, large neighborhood search, and iterative diving to cooperate and solve problems faster.


![8 / 17 ROADEF 2019 © 2019 IBM Corporation
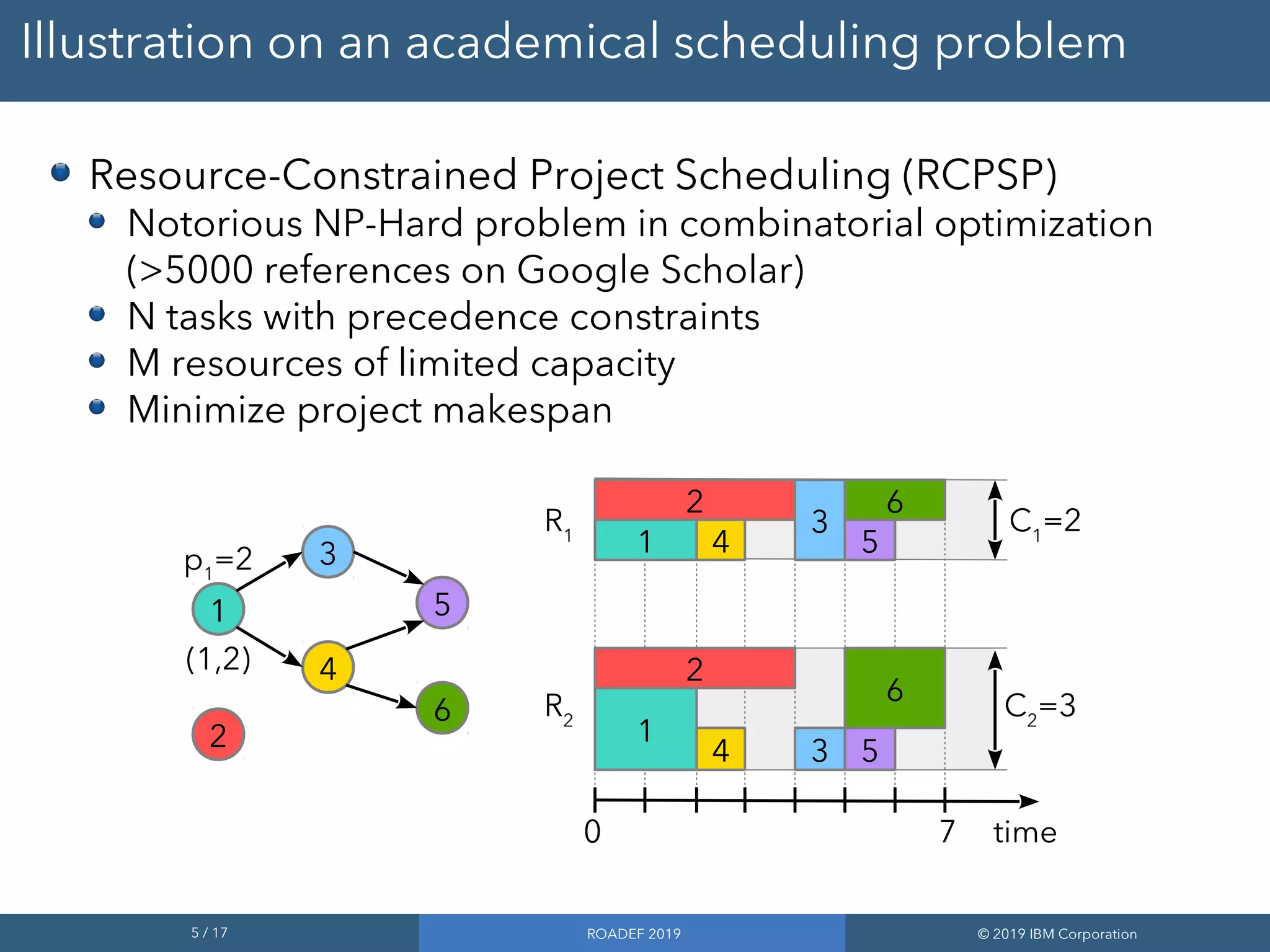
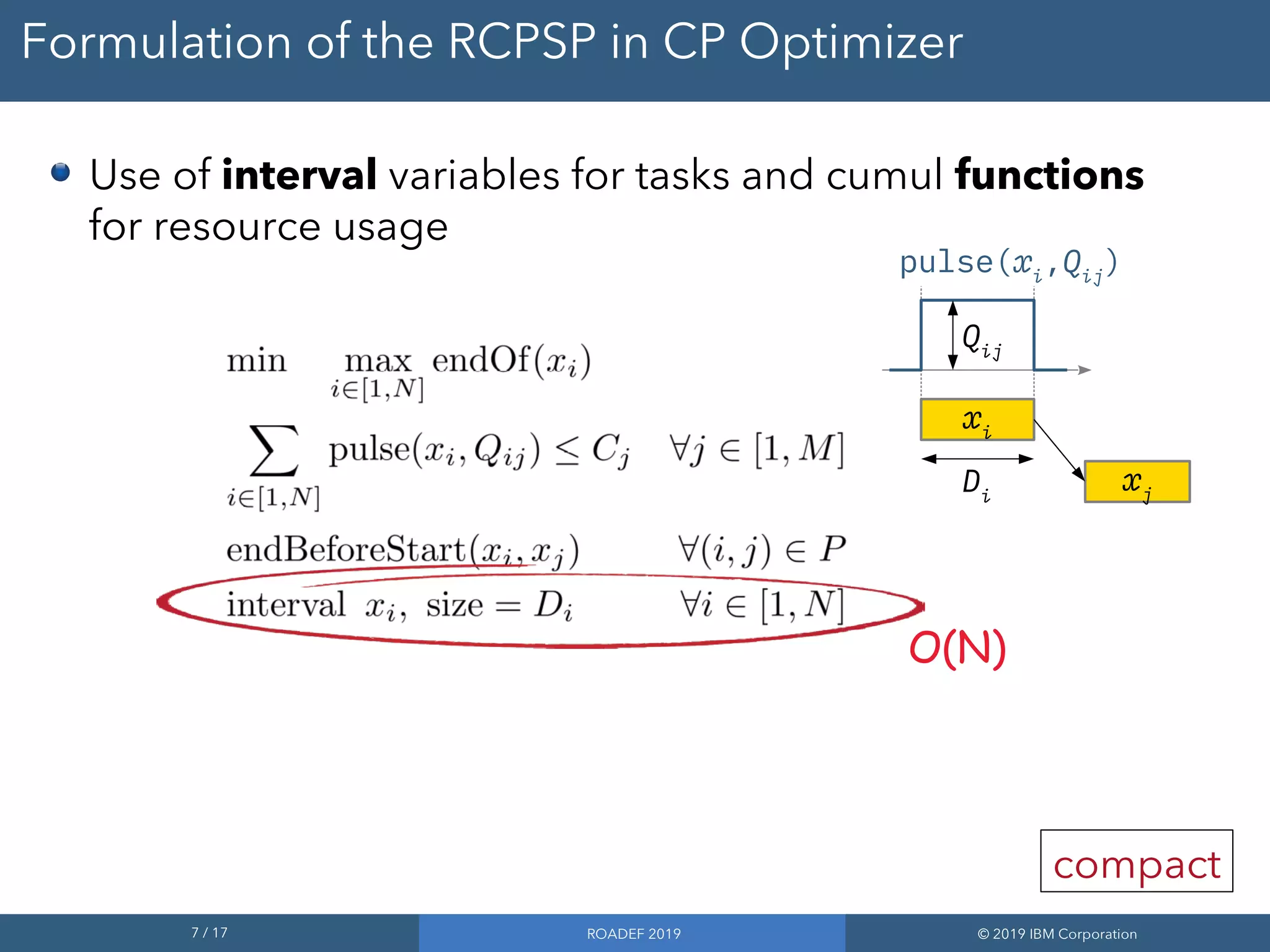
Formulation of the RCPSP in CP Optimizer
Use of interval variables for tasks and cumul functions
for resource usage
from docplex.cp.model import *
model = CpoModel()
# Decision variables: tasks x
x = [interval_var(size=D[i]) for i in N]
# Objective: minimize project makespan
model.add(minimize(max(end_of(x[i]) for i in N)))
# Constraints: resource capacities
for j in M: model.add(sum(pulse(x[i],q) for [i,q] in R[j]) <= C[j])
# Constraints: precedence between tasks
for [i,j] in P: model.add(end_before_start(x[i],x[j]))
# Solve the model
sol = model.solve(TimeLimit=300)
compact
xi
xj
Qij
Di
pulse(xi
,Qij
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpo-roadef-2019-190220122101/75/Recent-advances-on-large-scheduling-problems-in-CP-Optimizer-8-2048.jpg)