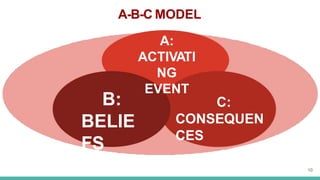
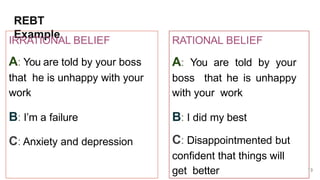
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) was developed by American psychologist Albert Ellis in 1955. The core idea of REBT is that dysfunctional emotions and behaviors result not from events themselves, but from a person's beliefs and interpretations of those events. REBT uses an A-B-C model where A is the activating event, B is the beliefs about that event, and C are the emotional and behavioral consequences. By identifying and disputing irrational and unhelpful beliefs, clients can reduce dysfunctional consequences and develop more constructive thinking patterns. The therapist helps clients examine their beliefs using logical analysis to minimize irrational ideas and replace them with more rational perspectives.