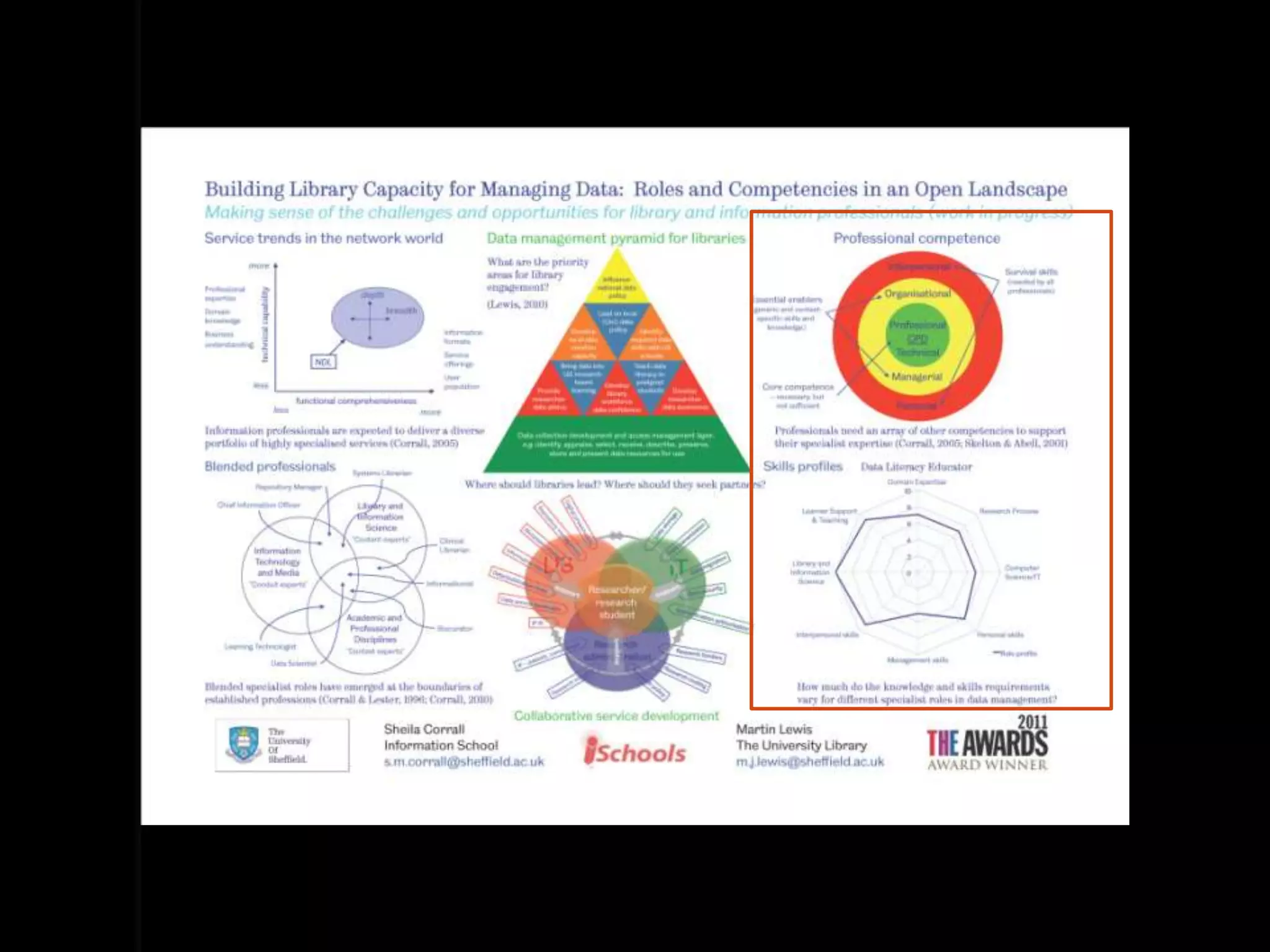
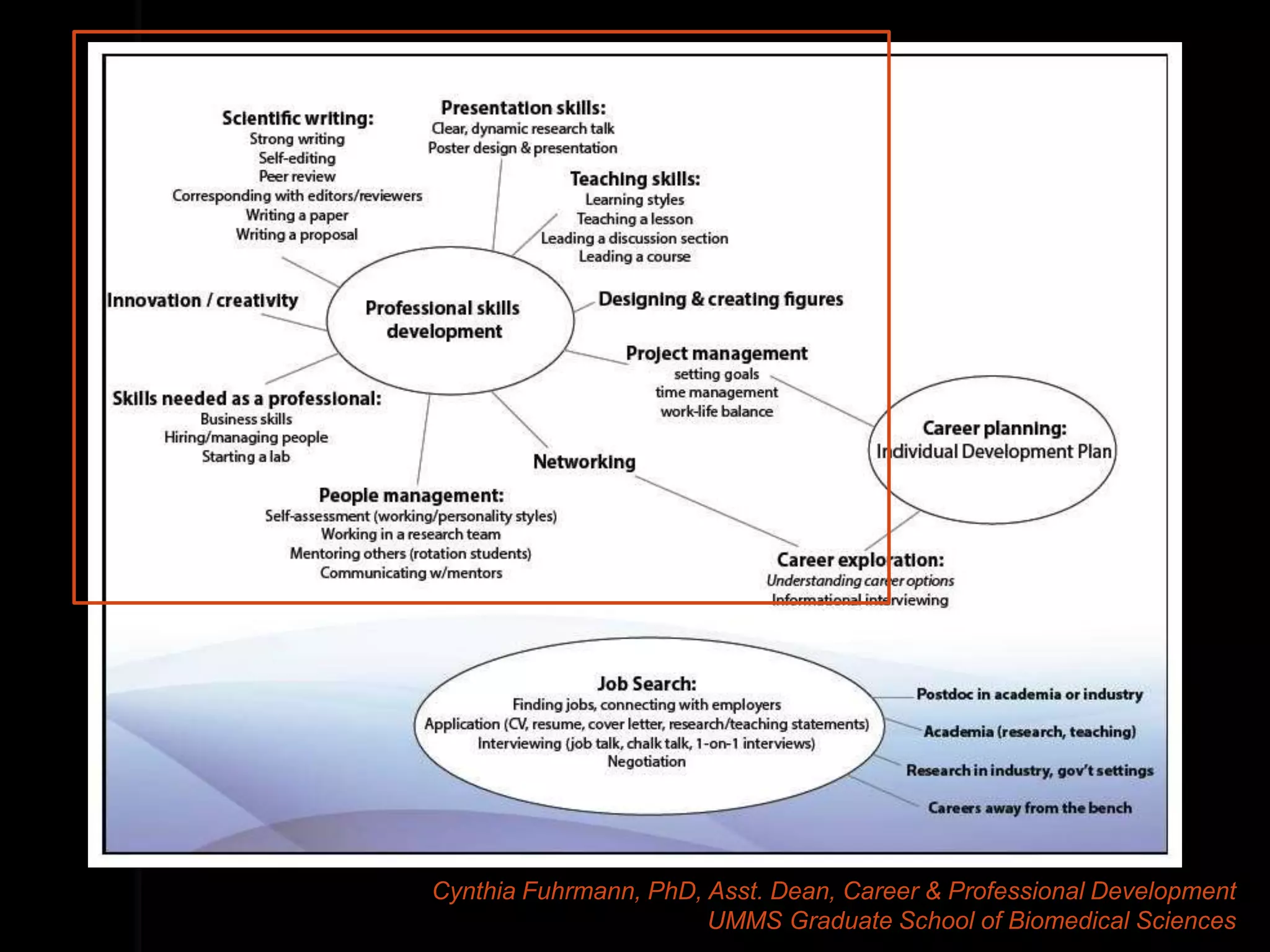
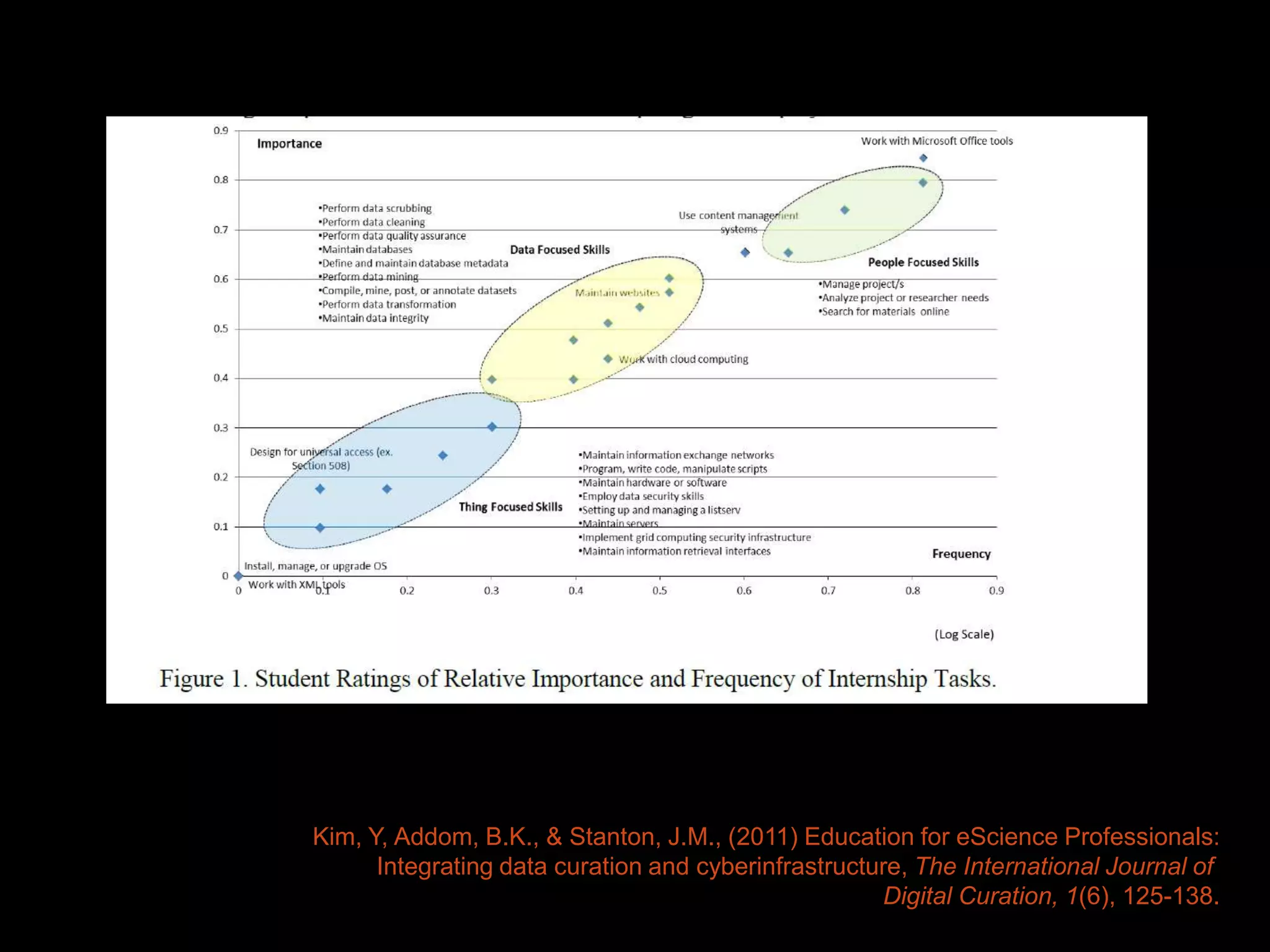
The document discusses the evolving roles of information professionals in research data management, highlighting the need for engagement with scientists and the development of data management plans. It emphasizes the skills and competencies required for various roles such as embedded librarians and data scientists, as well as the importance of collaboration and communication within research teams. The course aims to provide participants with the necessary tools and strategies to support research data practices in academic settings.