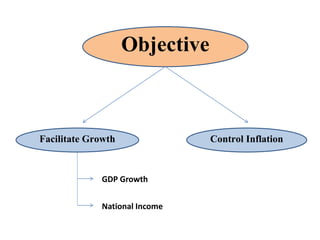
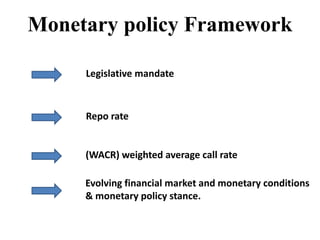
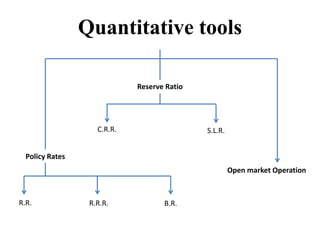
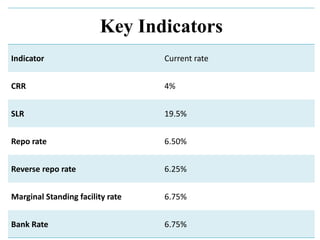
Monetary policy aims to control the supply of money and credit to achieve macroeconomic objectives like price stability and economic growth. In India, the Reserve Bank of India formulates monetary policy through its Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) which decides the policy repo rate. The MPC uses both qualitative tools like credit rationing and quantitative tools like open market operations and reserve ratios to influence money supply and achieve the inflation target set by the government. Key indicators of India's monetary policy include the repo rate, reverse repo rate, CRR, and SLR.