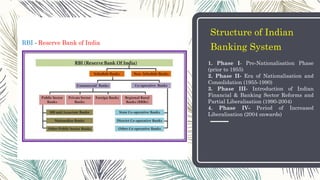
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), established in 1935, serves as the central bank responsible for managing the country's currency and credit system. It operates under various functions including monetary authority, regulator of banking systems, and maintaining financial stability while also facing limitations in its monetary policy, especially in rural areas. The document outlines the RBI's structure, policies, key historical phases, and the list of past governors.