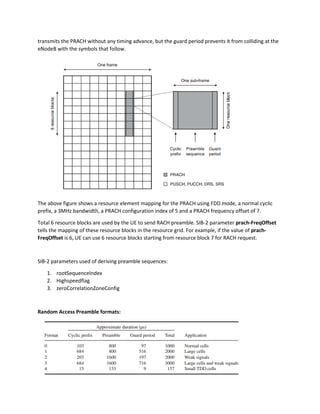
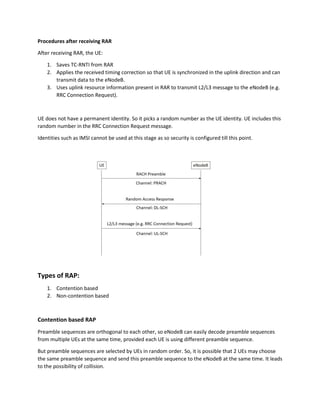
The random access procedure allows a UE to synchronize in the uplink and obtain radio resources to send L2/L3 messages to the eNodeB. The UE selects a random access preamble from one of two groups (A or B) based on the size of its message. It sends the preamble to the eNodeB, which responds with a Random Access Response including timing advance, resource allocation, and other information. The UE then sends its message using the allocated resources and obtains a temporary identifier. Contention-based random access can result in collisions if multiple UEs select the same preamble, while non-contention access reserves preambles to avoid collisions in certain situations like handover.