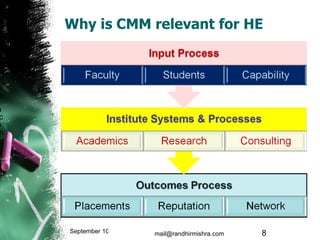
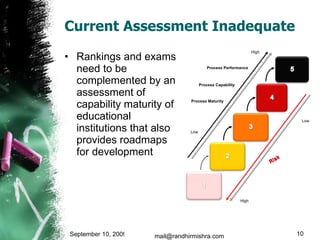
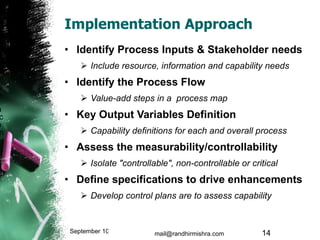
The document discusses challenges in the higher education sector, including inadequate courseware, industry disconnect, and the need for improved accreditation processes. It introduces the Capability Maturity Model (CMM) as a framework to evaluate and enhance the maturity of educational institutions, transitioning from CMM to the 5i framework which emphasizes intellect, infrastructure, industry ties, institutionalization, and internationalization. It concludes that adopting a collaborative approach and technology will drive significant improvements in education quality and effectiveness.














![[email_address] September 10, 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/randhiramaturitymodelforeducation-090910084009-phpapp01/85/Randhir-A-Maturity-Model-For-Education-18-320.jpg)